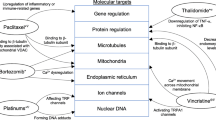
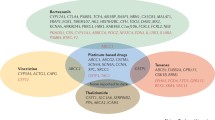
Abstract
Pharmacogenomics has been establishing itself as a powerful tool to predict individual response to treatment, in order to personalize therapy management; this field has been explored in particular in Oncology. Not only efficacy on the malignant disease has been investigated, but also the possibility to predict adverse effects due to drug administration. Chemotherapy-Induced Neurotoxicity (CIPN) is one of those. This potentially severe and long-lasting/permanent side effect of commonly administered anticancer drugs can severely impair Quality of Life (QoL) in a large cohort of long survival patients. So far, a pharmacogenomics-based approach in CIPN regard has been quite delusive, making a methodological improvement warranted in this field of interest: even the most refined genetic analysis cannot be effective if not applied correctly. Here, we try to devise why it is so, suggesting how THE “bench-side” (Pharmacogenomics) might benefit from and should cooperate with THE “bed-side” (Clinimetrics), in order to make genetic profiling effective if applied to CIPN.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Syvanen AC (2005) Toward genome-wide SNP genotyping. Nat Genet 37(Suppl):S5–S10
Argyriou AA, Bruna J, Marmiroli P, Cavaletti G (2012) Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity (CIPN): an update. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 82:51–77
Cavaletti G, Frigeni B, Lanzani F et al (2010) Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity assessment: a critical revision of the currently available tools. Eur J Cancer 46:479–494
Ekhart C, Rodenhuis S, Smits PH, Beijnen JH, Huitema AD (2009) An overview of the relations between polymorphisms in drug metabolising enzymes and drug transporters and survival after cancer drug treatment. Cancer Treat Rev 35:18–31
Strange RC, Spiteri MA, Ramachandran S, Fryer AA (2001) Glutathione-S-transferase family of enzymes. Mutat Res 482:21–26
Funke S, Timofeeva M, Risch A et al (2010) Genetic polymorphisms in GST genes and survival of colorectal cancer patients treated with chemotherapy. Pharmacogenomics 11:33–41
Stoehlmacher J, Park DJ, Zhang W et al (2002) Association between glutathione S-transferase P1, T1, and M1 genetic polymorphism and survival of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 94:936–942
Zarate R, Rodriguez J, Bandres E et al (2010) Oxaliplatin, irinotecan and capecitabine as first-line therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC): a dose-finding study and pharmacogenomic analysis. Br J Cancer 102:987–994
Martin LP, Hamilton TC, Schilder RJ (2008) Platinum resistance: the role of DNA repair pathways. Clin Cancer Res 14:1291–1295
Segurel L, Lafosse S, Heyer E, Vitalis R (2010) Frequency of the AGT Pro11Leu polymorphism in humans: does diet matter? Ann Hum Genet 74:57–64
Levi F, Perpoint B, Garufi C et al (1993) Oxaliplatin activity against metastatic colorectal cancer: a phase II study of 5-day continuous venous infusion at circadian rhythm modulated rate. Eur J Cancer 29A:1280–1284
Crowley E, Callaghan R (2010) Multidrug efflux pumps: drug binding – gates or cavity? FEBS J 277:530–539
Sharom FJ (2008) ABC multidrug transporters: structure, function and role in chemoresistance. Pharmacogenomics 9:105–127
Henningsson A, Marsh S, Loos WJ et al (2005) Association of CYP2C8, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and ABCB1 polymorphisms with the pharmacokinetics of paclitaxel. Clin Cancer Res 11: 8097–8104
Zhou SF, Liu JP, Chowbay B (2009) Polymorphism of human cytochrome P450 enzymes and its clinical impact. Drug Metab Rev 41:89–295
Mielke S, Sparreboom A, Steinberg SM et al (2005) Association of paclitaxel pharmacokinetics with the development of peripheral neuropathy in patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:4843–4850
Scuteri A, Galimberti A, Maggioni D et al (2009) Role of MAPKs in platinum-induced neuronal apoptosis. Neurotoxicology 30:312–319
Durand JP, Deplanque G, Montheil V et al (2009) Efficacy of venlafaxine for the prevention and relief of oxaliplatin-induced acute neurotoxicity: results of EFFOX, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Ann Oncol 20:736–740
Argyriou AA, Chroni E, Koutras A et al (2006) Preventing paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy: a phase II trial of vitamin E supplementation. J Pain Symptom Manage 32:237–244
Argyriou AA, Chroni E, Koutras A et al (2006) A randomized controlled trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of vitamin E supplementation for protection against cisplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy: final results. Support Care Cancer 14:1134–1140
Pace A, Giannarelli D, Galie E et al (2010) Vitamin E neuroprotection for cisplatin neuropathy: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Neurology 74:762–766
Lecomte T, Landi B, Beaune P, Laurent-Puig P, Loriot MA (2006) Glutathione S-transferase P1 polymorphism (Ile105Val) predicts cumulative neuropathy in patients receiving oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 12:3050–3056
Ruzzo A, Graziano F, Loupakis F et al (2007) Pharmacogenetic profiling in patients with advanced colorectal cancer treated with first-line FOLFOX-4 chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 25:1247–1254
Oldenburg J, Kraggerud SM, Brydoy M et al. (2007) Association between long-term neuro-toxicities in testicular cancer survivors and polymorphisms in glutathione-s-transferase-P1 and -M1, a retrospective cross sectional study. J Transl Med 5:70
Goekkurt E, Al-Batran SE, Hartmann JT et al (2009) Pharmacogenetic analyses of a phase III trial in metastatic gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma with fluorouracil and leucovorin plus either oxaliplatin or cisplatin: a study of the arbeitsgemeinschaft internistische onkologie. J Clin Oncol 27:2863–2873
Hong J, Han SW, Ham HS et al (2011) Phase II study of biweekly S-1 and oxaliplatin combination chemotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer and pharmacogenetic analysis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 67:1323–1331
Li QF, Yao RY, Liu KW et al (2010) Genetic polymorphism of GSTP1: prediction of clinical outcome to oxaliplatin/5-FU-based chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer. J Korean Med Sci 25:846–852
Inada M, Sato M, Morita S et al (2010) Associations between oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy and polymorphisms of the ERCC1 and GSTP1 genes. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 48:729–734
McLeod HL, Sargent DJ, Marsh S et al (2010) Pharmacogenetic predictors of adverse events and response to chemotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: results from North American Gastrointestinal Intergroup Trial N9741. J Clin Oncol 28:3227–3233
Khrunin AV, Moisseev A, Gorbunova V, Limborska S (2010) Genetic polymorphisms and the efficacy and toxicity of cisplatin-based chemotherapy in ovarian cancer patients. Pharmacogenomics J 10:54–61
Gamelin L, Capitain O, Morel A et al (2007) Predictive factors of oxaliplatin neurotoxicity: the involvement of the oxalate outcome pathway. Clin Cancer Res 13:6359–6368
Keam B, Im SA, Han SW et al (2008) Modified FOLFOX-6 chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer: results of phase II study and comprehensive analysis of polymorphisms as a predictive and prognostic marker. BMC Cancer 8:148
Paré L, Marcuello E, Altes A et al (2008) Pharmacogenetic prediction of clinical outcome in advanced colorectal cancer patients receiving oxaliplatin/5-fluorouracil as first-line chemotherapy. Br J Cancer 99:1050–1055
Seo BG, Kwon HC, Oh SY et al (2009) Comprehensive analysis of excision repair complementation group 1, glutathione S-transferase, thymidylate synthase and uridine diphosphate glucuronosyl transferase 1A1 polymorphisms predictive for treatment outcome in patients with advanced gastric cancer treated with FOLFOX or FOLFIRI. Oncol Rep 22:127–136
Boige V, Mendiboure J, Pignon JP et al (2010) Pharmacogenetic assessment of toxicity and outcome in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer treated with LV5FU2, FOLFOX, and FOLFIRI: FFCD 2000-05. J Clin Oncol 28:2556–2564
Kanai M, Yoshioka A, Tanaka S et al (2010) Associations between glutathione S-transferase π Ile105Val and glyoxylate aminotransferase Pro11Leu and Ile340Met polymorphisms and early-onset oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy. Cancer Epidemiol 34:189–193
Oguri T, Mitsuma A, Inada-Inoue M et al (2013) Genetic polymorphisms associated with oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neurotoxicity in Japanese patients with colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 51:475–481
Won HH, Lee J, Park JO et al (2012) Polymorphic markers associated with severe oxaliplatin-induced, chronic peripheral neuropathy in colon cancer patients. Cancer 118: 2828–2836
Mir O, Alexandre J, Tran A et al (2009) Relationship between GSTP1 Ile(105)Val polymorphism and docetaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy: clinical evidence of a role of oxidative stress in taxane toxicity. Ann Oncol 20:736–740
Booton R, Ward T, Heighway J et al (2006) Glutathione-S-transferase P1 isoenzyme polymorphisms, platinum-based chemotherapy, and non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 1:679–683
Kim HS, Kim MK, Chung HH et al (2009) Genetic polymorphisms affecting clinical outcomes in epithelial ovarian cancer patients treated with taxanes and platinum compounds: a Korean population-based study. Gynecol Oncol 113:264–269
Marsh S, Paul J, King CR et al (2007) Pharmacogenetic assessment of toxicity and outcome after platinum plus taxane chemotherapy in ovarian cancer: the Scottish randomised trial in ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol 25:4528–4535
Cho HJ, Eom HS, Kim HJ et al (2010) Glutathione-S-transferase genotypes influence the risk of chemotherapy-related toxicities and prognosis in Korean patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 198:40–46
Baldwin RM, Owzar K, Zembutsu H et al (2012) A genome-wide association study identifies novel loci for paclitaxel-induced sensory peripheral neuropathy in CALGB 40101. Clin Cancer Res 18:5099–5109
Delague V, Jacquier A, Hamadouche T et al (2007) Mutations in fgd4 encoding the rho gdp/gtp exchange factor frabin cause autosomal recessive charcot-marie-tooth type 4 h. Am J Hum Genet 81:1–16
Stendel C, Roos A, Deconinck T et al (2007) Peripheral nerve demyelination caused by a mutant rho gtpase guanine nucleotide exchange factor, frabin/fgd4. Am J Hum Genet 81:158–164
Fabrizi GM, Taioli F, Cavallaro T et al (2009) Further evidence that mutations in fgd4/frabin cause charcotmarie-tooth disease type 4 h. Neurology 72:1160–1164
Houlden H, Hammans S, Katifi H, Reilly MM (2009) A novel frabin (fgd4) nonsense mutation p.R275x associated with phenotypic variability in cmt4h. Neurology 72:617–620
Lee JJ, Swain SM (2006) Peripheral neuropathy induced by microtubule stabilizing agents. J Clin Oncol 24:1633–1642
Cavaletti G, Cornblath DR, Merkies IS, The CI-PeriNomS Group et al (2013) The chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy outcome measures standardization study: from consensus to the first validity and reliability findings. Ann Oncol 24:454–462
Trotti A, Colevas AD, Setser A et al (2003) CTCAE v3.0: development of a comprehensive grading system for the adverse effects of cancer treatment. Semin Radiat Oncol 13:176–181
Merkies IS, Schmitz PI, van der Meche FG, Inflammatory Neuropathy Cause and Treatment (INCAT) Group et al (2000) Psychometric evaluation of a new sensory scale in immune-mediated polyneuropathies. Neurology 54:943–949
Cavaletti G, Frigeni B, Lanzani F et al (2007) The total neuropathy score as an assessment tool for grading the course of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity: comparison with the National Cancer Institute-Common Toxicity Scale. J Peripher Nerv Syst 12:210–215
Argyriou AA, Cavaletti G, Antonacopoulou A et al (2013) Voltage-gated sodium channel polymorphisms play a pivotal role in the development of oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neurotoxicity – results from a prospective multicenter study. Cancer 119:3570–3577
Antonacopoulou AG, Argyriou AA, Scopa CD et al (2010) Integrin beta-3 L33P: a new insight into the pathogenesis of chronic oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy? Eur J Neurol 17:963–968
Basso M, Modoni A, Spada D et al (2011) Polymorphism of CAG motif of SK3 gene is associated with acute oxaliplatin neurotoxicity. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 67:1179–1187
Bergmann TK, Green H, Brasch-Andersen C et al (2011) Retrospective study of the impact of pharmacogenetic variants on paclitaxel toxicity and survival in patients with ovarian cancer. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 67:693–700
Broyl A, Corthals SL, Jongen JL et al (2010) Mechanisms of peripheral neuropathy associated with bortezomib and vincristine in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: a prospective analysis of data from the HOVON-65/GMMG-HD4 trial. Lancet Oncol 11:1057–1065
Caponigro F, Lacombe D, Twelves C et al (2009) An EORTC phase I study of bortezomib in combination with oxaliplatin, leucovorin and 5-fl uorouracil in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer 45:48–55
Chang H, Rha SY, Jeung HC et al (2009) Association of the ABCB1 gene polymorphisms 2677G > T/A and 3435C > T with clinical outcomes of paclitaxel monotherapy in metastatic breast cancer patients. Ann Oncol 20:272–277
Chen YC, Tzeng CH, Chen PM et al (2010) Influence of GSTP1 I105V polymorphism on cumulative neuropathy and outcome of FOLFOX-4 treatment in Asian patients with colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Sci 101: 530–535
Favis R, Sun Y, van de Velde H et al (2011) Genetic variation associated with bortezomib-induced peripheral neuropathy. Pharmacogenet Genomics 21:121–129
Green H, Soderkvist P, Rosenberg P et al (2009) Pharmacogenetic studies of paclitaxel in the treatment of ovarian cancer. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 104:130–137
Hertz DL, Motsinger-Reif AA, Drobish A et al (2012) CYP2C8*3 predicts benefit/risk profile in breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant paclitaxel. Breast Cancer Res Treat 134: 401–410
Isla D, Sarries C, Rosell R et al (2004) Single nucleotide polymorphisms and outcome in docetaxel-cisplatin-treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol 15: 1194–11203
Johnson DC, Corthals SL, Walker BA et al (2011) Genetic factors underlying the risk of thalidomide-related neuropathy in patients with multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol 29: 797–804
Leandro-Garcia LJ, Inglada-Pérez L, Pita G et al (2013) Genome-wide association study identifies ephrin type A receptors implicated in paclitaxel induced peripheral sensory neuropathy. J Med Genet 50:599–605
Leskela S, Jara C, Leandro-Garcia LJ et al (2011) Polymorphisms in cytochromes P450 2C8 and 3A5 are associated with paclitaxel neurotoxicity. Pharmacogenomics J 11: 121–129
Rizzo R, Spaggiari F, Indelli M et al (2010) Association of CYP1B1 with hypersensitivity induced by taxane therapy in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 124: 593–598
Sissung TM, Mross K, Steinberg SM et al (2006) Association of ABCB1 genotypes with paclitaxel-mediated peripheral neuropathy and neutropenia. Eur J Cancer 42:2893–2896
Sissung TM, Baum CE, Deeken J et al (2008) ABCB1 genetic variation influences the toxicity and clinical outcome of patients with androgen-independent prostate cancer treated with docetaxel. Clin Cancer Res 14:4543–4549
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Alberti, P., Cavaletti, G. (2014). Management of Side Effects in the Personalized Medicine Era: Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. In: Yan, Q. (eds) Pharmacogenomics in Drug Discovery and Development. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1175. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0956-8_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0956-8_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-0955-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-0956-8
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols