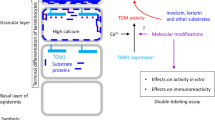
Abstract
Unlike other caspase family members, caspase-14 shows restricted expression, being found mostly in epidermis and its appendages. It has been suggested that caspase-14 is not involved in apoptosis or inflammation, but participates in keratinocyte terminal differentiation. Its activation occurs at the corneocyte formation. In previous work, we have purified active caspase-14 from human corneocyte extracts. In addition, we have clarified activation mechanism of caspase-14, where kallikrein-related peptidase 7 (KLK7) generates an intermediate form from procaspase-14 and this form finally converts procaspase-14 to active, mature caspase-14. Here we describe techniques for measurement of caspase-14 activity using synthetic substrate, purification of caspase-14 from corneocyte extract, preparation of constitutively active caspase-14 and specific antibody, quantification of total and active caspase-14 in corneocyte extracts using ELISA, as well as methods for caspase-14 activation and its visualization by immunohistochemistry.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eckhart L, Ban J, Fischer H, Tschachler E (2000) Caspase-14: analysis of gene structure and mRNA expression during keratinocyte differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 277:655–659
Van de Craen M, Van Loo G, Pype S, Van Criekinge W, Van den brande I, Molemans F, Fiers W, Declercq W, Vandenabeele P (1998) Identification of a new caspase homologue: caspase-14. Cell Death Differ 5:838–846
Eckhart L, Declercq W, Ban J, Rendl M, Lengauer B, Mayer C, Lippens S, Vandenabeele P, Tschachler E (2000) Terminal differentiation of human keratinocytes and stratum corneum formation is associated with caspase-14 activation. J Invest Dermatol 115:1148–1151
Watt FM (1983) Involucrin and other markers of keratinocyte terminal differentiation. J Invest Dermatol 81:100s–103s
Wertz PW (1997) Integral lipids of hair and stratum corneum. EXS 78:227–237
Hitomi K (2005) Transglutaminases in skin epidermis. Eur J Dermatol 15:313–319
Yoneda K, Demitsu T, Manabe M, Igarashi J, Kosaka H, Inagaki N, Takahashi H, Kon A, Kakurai M, Kubota Y (2010) Expression of wild-type, but not mutant, loricrin causes programmed cell death in HaCaT keratinocytes. J Dermatol 37:956–964
Hibino T, Fujita E, Tsuji Y, Nakanishi J, Iwaki H, Katagiri C, Momoi T (2010) Purification and characterization of active caspase-14 from human epidermis and development of the cleavage site-directed antibody. J Cell Biochem 109:487–497
Yamamoto M, Kamata Y, Iida T, Fukushima H, Nomura J, Saito M, Tajima M, Okubo Y, Momoi T, Tsuboi R, Hibino T (2011) Quantification of activated and total caspase-14 with newly developed ELISA systems in normal and atopic skin. J Dermatol Sci 61:110–117
Yamamoto M, Miyai M, Matsumoto Y, Tsuboi R, Hibino T (2012) Kallikrein-related peptidase-7 regulates caspase-14 maturation during keratinocyte terminal differentiation by generating an intermediate form. J Biol Chem 287:32825–32834
Lamkanfi M, Festjens N, Declercq W, Vanden Berghe T, Vandenabeele P (2007) Caspases in cell survival, proliferation and differentiation. Cell Death Differ 14:44–55
Xu G, Shi Y (2007) Apoptosis signaling pathways and lymphocyte homeostasis. Cell Res 17:759–771
Sato Y, Mukai K, Furuya S, Kameya T, Hirohashi S (1992) The AMeX method: a multipurpose tissue-processing and paraffin-embedding method. Extraction of protein and application to immunoblotting. Am J Pathol 140:775–779
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Yamamoto-Tanaka, M., Hibino, T. (2014). Caspase-14 Protocols. In: V. Bozhkov, P., Salvesen, G. (eds) Caspases,Paracaspases, and Metacaspases. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1133. Humana Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0357-3_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-0357-3_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4939-0356-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-4939-0357-3
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols