Abstract
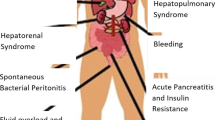
The liver is a metabolically active organ where there is continuous synthesis and detoxification of several biologically active substances such as albumin, clotting factors, neurotransmitters and vasoactive amines. In end-stage chronic liver disease (CLD), there is an imbalance between the production and degradation of these biologically active substances. This leads to a disturbance of end-organ homeostasis particularly in the brain, kidney and lungs. The severity of end-organ dysfunction might not be proportional to the degree of liver synthetic functional impairment, and progressive complexity of dysfunction should be expected. It is important that these complications are anticipated and treatment is initiated in a timely manner. This chapter focuses on cerebral, renal, pulmonary, skeletal and cardiac complications associated with chronic liver disease. Complications related to portal hypertension, ascites, SBP and hepatorenal syndrome are discussed in the preceding chapter.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iwasa M, et al. Decrease of regional cerebral blood flow in liver cirrhosis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000;12(9):1001–6.
Cash WJ, et al. Current concepts in the assessment and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. QJM. 2010;103(1):9–16.
Ferenci P, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy – definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantification: final report of the working party at the 11th World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998. Hepatology. 2002;35(3):716–21.
Jones EA, Weissenborn K. Neurology and the liver. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1997;63(3):279–93.
Frederick RT. Current concepts in the pathophysiology and management of hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2011;7(4):222–33.
Vince AJ, Burridge SM. Ammonia production by intestinal bacteria: the effects of lactose, lactulose and glucose. J Med Microbiol. 1980;13(2):177–91.
Romero-Gomez M, et al. Gut ammonia production and its modulation. Metab Brain Dis. 2009;24(1):147–57.
Merli M, et al. Muscle depletion increases the risk of overt and minimal hepatic encephalopathy: results of a prospective study. Metab Brain Dis. 2013;28(2):281–4.
Dejong CH, et al. Aromatic amino acid metabolism during liver failure. J Nutr. 2007;137(6 Suppl 1):1579S–85; discussion 1597S–8S.
Fischer JE, et al. The effect of normalization of plasma amino acids on hepatic encephalopathy in man. Surgery. 1976;80(1):77–91.
Skowronska M, Albrecht J. Alterations of blood brain barrier function in hyperammonemia: an overview. Neurotox Res. 2012;21(2):236–44.
Al Mardini H, et al. Effect of methionine loading and endogenous hypermethioninaemia on blood mercaptans in man. Clin Chim Acta. 1988;176(1):83–9.
Mortensen PB, et al. The degradation of amino acids, proteins, and blood to short-chain fatty acids in colon is prevented by lactulose. Gastroenterology. 1990;98(2):353–60.
Macfarlane S, Macfarlane GT. Regulation of short-chain fatty acid production. Proc Nutr Soc. 2003;62(1):67–72.
Riggio O, et al. Peripheral and splanchnic indole and oxindole levels in cirrhotic patients: a study on the pathophysiology of hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105(6):1374–81.
Baraldi M, et al. Natural endogenous ligands for benzodiazepine receptors in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis. 2009;24(1):81–93.
Ahboucha S, et al. Increased brain concentrations of a neuroinhibitory steroid in human hepatic encephalopathy. Ann Neurol. 2005;58(1):169–70.
Guevara M, et al. Hyponatremia is a risk factor of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: a prospective study with time-dependent analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104(6):1382–9.
Odeh M. Pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy: the tumour necrosis factor-alpha theory. Eur J Clin Invest. 2007;37(4):291–304.
Odeh M, et al. Relationship between tumor necrosis factor-alpha and ammonia in patients with hepatic encephalopathy due to chronic liver failure. Ann Med. 2005;37(8):603–12.
Odeh M, et al. Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha correlate with severity of hepatic encephalopathy due to chronic liver failure. Liver Int. 2004;24(2):110–6.
Goral V, Atayan Y, Kaplan A. The relation between pathogenesis of liver cirrhosis, hepatic encephalopathy and serum cytokine levels: what is the role of tumor necrosis factor alpha? Hepatogastroenterology. 2011;58(107–108):943–8.
Quero Guillen JC, Herrerias Gutierrez JM. Diagnostic methods in hepatic encephalopathy. Clin Chim Acta. 2006;365(1–2):1–8.
Dhiman RK, et al. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy: consensus statement of a working party of the Indian National Association for Study of the Liver. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25(6):1029–41.
Govindarajan S, et al. Immunohistochemical distribution of renal prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase and prostacyclin synthase: diminished endoperoxide synthase in the hepatorenal syndrome. Hepatology. 1987;7(4):654–9.
Yadav SK, et al. Encephalopathy assessment in children with extra-hepatic portal vein obstruction with MR, psychometry and critical flicker frequency. J Hepatol. 2010;52(3):348–54.
Kircheis G, et al. Critical flicker frequency for quantification of low-grade hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology. 2002;35(2):357–66.
Kullmann F, et al. Brain electrical activity mapping of EEG for the diagnosis of (sub)clinical hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001;13(5):513–22.
Terao Y, Ugawa Y. Basic mechanisms of TMS. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2002;19(4):322–43.
Weber M, Eisen AA. Magnetic stimulation of the central and peripheral nervous systems. Muscle Nerve. 2002;25(2):160–75.
Arya R, Gulati S, Deopujari S. Management of hepatic encephalopathy in children. Postgrad Med J. 2010;86(1011):34–41; quiz 40.
Ito Y, et al. Effect of lactulose on short-chain fatty acids and lactate production and on the growth of faecal flora, with special reference to Clostridium difficile. J Med Microbiol. 1997;46(1):80–4.
Holecek M. Three targets of branched-chain amino acid supplementation in the treatment of liver disease. Nutrition. 2010;26(5):482–90.
Agrawal A, et al. Secondary prophylaxis of hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhosis: an open-label, randomized controlled trial of lactulose, probiotics, and no therapy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107(7):1043–50.
Bajaj JS, et al. A longitudinal systems biology analysis of lactulose withdrawal in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis. 2012;27(2):205–15.
Patil DH, et al. Comparative modes of action of lactitol and lactulose in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. Gut. 1987;28(3):255–9.
Festi D, et al. Management of hepatic encephalopathy: focus on antibiotic therapy. Digestion. 2006;73 Suppl 1:94–101.
Rivkin A, Gim S. Rifaximin: new therapeutic indication and future directions. Clin Ther. 2011;33(7):812–27.
Gluud LL, et al. Lactulose, rifaximin or branched chain amino acids for hepatic encephalopathy: what is the evidence? Metab Brain Dis. 2013 (in press).
Malaguarnera M, et al. Bifidobacterium longum with fructo-oligosaccharide (FOS) treatment in minimal hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Dig Dis Sci. 2007;52(11):3259–65.
Sharma P, et al. An open-label randomized controlled trial of lactulose and probiotics in the treatment of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;20(6):506–11.
Holte K, Krag A, Gluud LL. Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials on probiotics for hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatol Res. 2012;42(10):1008–15.
McGee RG, et al. Probiotics for patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(11):CD008716.
Olde Damink SW, et al. Interorgan ammonia and amino acid metabolism in metabolically stable patients with cirrhosis and a TIPSS. Hepatology. 2002;36(5):1163–71.
Rose C, et al. L-ornithine-L-aspartate lowers plasma and cerebrospinal fluid ammonia and prevents brain edema in rats with acute liver failure. Hepatology. 1999;30(3):636–40.
Al Sibae MR, McGuire BM. Current trends in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2009;5(3):617–26.
Shores NJ, Keeffe EB. Is oral L-acyl-carnitine an effective therapy for hepatic encephalopathy? Review of the literature. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53(9):2330–3.
Malaguarnera M, et al. Acetyl-L-carnitine improves cognitive functions in severe hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized and controlled clinical trial. Metab Brain Dis. 2011;26(4):281–9.
Malaguarnera M, et al. Oral acetyl-L-carnitine therapy reduces fatigue in overt hepatic encephalopathy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;93(4):799–808.
Loomba V, et al. Serum zinc levels in hepatic encephalopathy. Indian J Gastroenterol. 1995;14(2):51–3.
Takuma Y, et al. Clinical trial: oral zinc in hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;32(9):1080–90.
Reding P, Duchateau J, Bataille C. Oral zinc supplementation improves hepatic encephalopathy. Results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 1984;2(8401):493–5.
Burkhard PR, et al. Chronic Parkinsonism associated with cirrhosis: a distinct subset of acquired hepatocerebral degeneration. Arch Neurol. 2003;60(4):521–8.
Corenblum B, Shaffer EA. Hyperprolactinemia in hepatic encephalopathy may result from impaired central dopaminergic neurotransmission. Horm Metab Res. 1989;21(12):675–7.
Als-Nielsen B, Gluud LL, Gluud C. Dopaminergic agonists for hepatic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(4):CD003047.
Als-Nielsen B, Gluud LL, Gluud C. Benzodiazepine receptor antagonists for hepatic encephalopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(2):CD002798.
Spahr L, et al. Increased blood manganese in cirrhotic patients: relationship to pallidal magnetic resonance signal hyperintensity and neurological symptoms. Hepatology. 1996;24(5):1116–20.
Schaefer B, Schmitt CP. The role of molecular adsorbent recirculating system dialysis for extracorporeal liver support in children. Pediatr Nephrol. 2013;28(9):1763–9.
Abrams GA, et al. Use of macroaggregated albumin lung perfusion scan to diagnose hepatopulmonary syndrome: a new approach. Gastroenterology. 1998;114(2):305–10.
Wang YW, Lin HC. Recent advances in hepatopulmonary syndrome. J Chin Med Assoc. 2005;68(11):500–5.
Whyte MK, et al. Analysis of intrapulmonary right to left shunt in the hepatopulmonary syndrome. J Hepatol. 1998;29(1):85–93.
Varghese J, et al. Hepatopulmonary syndrome – past to present. Ann Hepatol. 2007;6(3):135–42.
Sasaki T, et al. Development of intrapulmonary arteriovenous shunting in postoperative biliary atresia: evaluation by contrast-enhanced echocardiography. J Pediatr Surg. 2000;35(11):1647–50.
Noli K, et al. Prevalence of hepatopulmonary syndrome in children. Pediatrics. 2008;121(3):e522–7.
Fallon MB, et al. Common bile duct ligation in the rat: a model of intrapulmonary vasodilatation and hepatopulmonary syndrome. Am J Physiol. 1997;272(4 Pt 1):G779–84.
Barbe T, et al. Pulmonary arteriovenous shunting in children with liver disease. J Pediatr. 1995;126(4):571–9.
Gupta D, et al. Prevalence of hepatopulmonary syndrome in cirrhosis and extrahepatic portal venous obstruction. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001;96(12):3395–9.
Rolla G, et al. Exhaled nitric oxide and impaired oxygenation in cirrhotic patients before and after liver transplantation. Ann Intern Med. 1998;129(5):375–8.
Fallon MB, et al. The role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the pathogenesis of a rat model of hepatopulmonary syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1997;113(2):606–14.
Gomez FP, et al. Effects of nebulized N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester in patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome. Hepatology. 2006;43(5):1084–91.
Zhang HY, et al. Experimental study on the role of endotoxin in the development of hepatopulmonary syndrome. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11(4):567–72.
Sztrymf B, et al. Prevention of hepatopulmonary syndrome and hyperdynamic state by pentoxifylline in cirrhotic rats. Eur Respir J. 2004;23(5):752–8.
Sztrymf B, et al. Cirrhotic rats with bacterial translocation have higher incidence and severity of hepatopulmonary syndrome. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005;20(10):1538–44.
Gomez FP, et al. Gas exchange mechanism of orthodeoxia in hepatopulmonary syndrome. Hepatology. 2004;40(3):660–6.
Dickinson CJ. The aetiology of clubbing and hypertrophic osteoarthropathy. Eur J Clin Invest. 1993;23(6):330–8.
Alves L, et al. Preoperative pulmonary assessment of children for liver transplantation. Pediatr Transplant. 2008;12(5):536–40.
El-Shabrawi MH, et al. (99m)Technetium-macroaggregated albumin perfusion lung scan versus contrast enhanced echocardiography in the diagnosis of the hepatopulmonary syndrome in children with chronic liver disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;22(8):1006–12.
Lee KN, et al. Hypoxemia and liver cirrhosis (hepatopulmonary syndrome) in eight patients: comparison of the central and peripheral pulmonary vasculature. Radiology. 1999;211(2):549–53.
Kuntz E, Kuntz HD. Hepatopulmonary syndrome, in hepatology. In: Kuntz E, Kuntz HD, editors. Textbook and atlas. Heidelberg: Springer; 2008. p. 340–5.
Schenk P, et al. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: prevalence and predictive value of various cut offs for arterial oxygenation and their clinical consequences. Gut. 2002;51(6):853–9.
Herve P, et al. Pulmonary vascular disorders in portal hypertension. Eur Respir J. 1998;11(5):1153–66.
Martinez-Palli G, et al. Effect of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt on pulmonary gas exchange in patients with portal hypertension and hepatopulmonary syndrome. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11(43):6858–62.
Battaglia SE, et al. Resolution of gas exchange abnormalities and intrapulmonary shunting following liver transplantation. Hepatology. 1997;25(5):1228–32.
Abrams GA, et al. Hepatopulmonary syndrome and venous emboli causing intracerebral hemorrhages after liver transplantation: a case report. Transplantation. 1999;68(11):1809–11.
Arguedas MR, et al. Prospective evaluation of outcomes and predictors of mortality in patients with hepatopulmonary syndrome undergoing liver transplantation. Hepatology. 2003;37(1):192–7.
Simonneau G, et al. Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54(1 Suppl):S43–54.
Hoeper MM, Krowka MJ, Strassburg CP. Portopulmonary hypertension and hepatopulmonary syndrome. Lancet. 2004;363(9419):1461–8.
Castro M, et al. Frequency and clinical implications of increased pulmonary artery pressures in liver transplant patients. Mayo Clin Proc. 1996;71(6):543–51.
Krowka MJ. Hepatopulmonary syndromes. Gut. 2000;46(1):1–4.
Budhiraja R, Hassoun PM. Portopulmonary hypertension: a tale of two circulations. Chest. 2003;123(2):562–76.
Edwards BS, et al. Coexistent pulmonary and portal hypertension: morphologic and clinical features. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1987;10(6):1233–8.
Robalino BD, Moodie DS. Association between primary pulmonary hypertension and portal hypertension: analysis of its pathophysiology and clinical, laboratory and hemodynamic manifestations. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1991;17(2):492–8.
McDonnell PJ, Toye PA, Hutchins GM. Primary pulmonary hypertension and cirrhosis: are they related? Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983;127(4):437–41.
Lammers AE, Hislop AA, Haworth SG. Prognostic value of B-type natriuretic peptide in children with pulmonary hypertension. Int J Cardiol. 2009;135(1):21–6.
Ivy DD, et al. Non-congenital heart disease associated pediatric pulmonary arterial hypertension. Prog Pediatr Cardiol. 2009;27(1–2):13–23.
Talwalkar JA, et al. Prevalence of spontaneous portosystemic shunts in patients with portopulmonary hypertension and effect on treatment. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(5):1673–9.
Barst RJ, et al. Pharmacokinetics, safety, and efficacy of bosentan in pediatric patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2003;73(4):372–82.
Austin MJ, et al. Safety and efficacy of combined use of sildenafil, bosentan, and iloprost before and after liver transplantation in severe portopulmonary hypertension. Liver Transpl. 2008;14(3):287–91.
Ashfaq M, et al. The impact of treatment of portopulmonary hypertension on survival following liver transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2007;7(5):1258–64.
Goel V, Kar P. Hepatic osteodystrophy. Trop Gastroenterol. 2010;31(2):82–6.
Klein GL, et al. Hepatic osteodystrophy in chronic cholestasis: evidence for a multifactorial etiology. Pediatr Transplant. 2002;6(2):136–40.
Hogler W, Baumann U, Kelly D. Growth and bone health in chronic liver disease and following liver transplantation in children. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2010;7(3):266–74.
Hogler W, Baumann U, Kelly D. Endocrine and bone metabolic complications in chronic liver disease and after liver transplantation in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012;54(3):313–21.
Baik SK, Fouad TR, Lee SS. Cirrhotic cardiomyopathy. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:15.
Liu H, Song D, Lee SS. Cirrhotic cardiomyopathy. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2002;26(10):842–7.
Desai MS, et al. Cardiac structural and functional alterations in infants and children with biliary atresia, listed for liver transplantation. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(4):1264–72, 1272.e1–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Shanmugam, N.P., Karthikeyan, P., Dhawan, A. (2014). Chronic Liver Disease, Cirrhosis and Complications: Part 2: Hepatic Encephalopathy and Other Systemic Effects. In: Murray, K., Horslen, S. (eds) Diseases of the Liver in Children. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-9005-0_26
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-9005-0_26
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4614-9004-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-4614-9005-0
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)