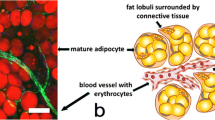
Abstract
An extensive, robust microvasculature is required to maintain the metabolic integrity of adipose tissue. This means that adipocytes and vascular endothelial cells maintain a constant communication that is mediated in part through paracrine signaling, a feature that requires cellular proximity. Adipocytes are atypical mesenchymal cells in that they form a basement membrane in the absence of direct contact with epithelial cells. Adipocyte development always occurs in context with a vascular plexus. Vascular endothelial cells interact with stromal support cells to produce a basement membrane complex. Thus, adipose tissue contains two basement membrane systems in close proximity. These two basement membrane systems also develop during the construction of a tissue engineered, pre-vascularized adipose tissue and form an integrated adipocyte/vascular complex. This complex contains the heparan sulfate proteoglycan perlecan. Perlecan is critical for angiogenesis since it sequesters, concentrates, and protects multiple pro-angiogenic bioactive factors. The basement membrane/vascular complex remains stable upon implantation into a live host. Thus, the basement membrane may be a target for control of adipose tissue since it is critical for vascular function.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aratani Y, Kitagawa Y. Enhanced synthesis and secretion of type IV collagen and entactin during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells and production of unorthodox laminin complex. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:16163–69.
Armani A, Mammi C, Marzolla V, Calanchini M, Antelmi A, Rosano GMC, Fabbri A, Caprio M. Cellular models for understanding adipogenesis, adipose dysfunction, and obesity. J Cell Biochem. 2010;110:564–72.
Au P, Tam J, Fukamura D, Jain RK. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells facilitate engineering of long-lasting function vasculature. Blood. 2008;111:4551–8.
Berthod F, Germain L, Tremblay N, Auger FA. Extracellular matrix deposition by fibroblasts is necessary to promote capillary-like tube formation in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 2006;207:491–8.
Bishop ET, Bell GT, Bloor S, Broom IJ, Hendry NFK, Wheatley DN. An in vitro model of angiogenesis: basic features. Angiogenesis. 1999;3:335–44.
Bix G, Iozzo RV. Novel interactions of perlecan: unraveling perlecan’s role in angiogenesis. Microsc Res Tech. 2008;71:339–48.
Borges J, Mueller MC, Padron T, Tegtmeier F, Lang EM, Stark GB. Engineered adipose tissue supplied by functional microvessels. Tissue Eng. 2003;9:1263–70.
Cao Y. Adipose tissue angiogenesis as a therapeutic target for obesity and metabolic diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9:107–15.
Chaubey A, Burg KJL. Extracellular matrix components as modulators of adult stem cell differentiation in an adipose system. J Bioact Compat Polym. 2008;23:20–37.
Choi JH, Gimble JM, Lee K, Marra KG, Rubin JP, Yoo JJ, Vunjak-Novakovic G, Kaplan DL. Adipose tissue engineering for soft tissue regeneration. Tissue Eng Part B. 2010;16:414–26.
Christiaens V, Lijnen HR. Angiogenesis and development of adipose tissue. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010;318:2–9.
Corselli M, Chen CW, Crisan M, Lazzari L, Peault B. Perivascular ancestors of adult multipotent stem cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010;30:1104–9.
Crisan M, Yap S, Casteilla L, Chen C-W, Corselli M, Park TS, Andriolo G, Sun B, Zheng B, Zhang L, Norotte C, Teng P-N, Traas J, Schugar R, Deasy BM, Badylak S, Buhring H-J, Giacobino J-P, Lazzari L, Huard J, Peault B. A perivascular origin for mesenchymal stem cells in multiple human organs. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3:301–13.
Flynn LE. The use of decellularized adipose tissue to provide an inductive microenvironment for the adipogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells. Biomaterials. 2010;31:4715–24.
Friedl A. Proteoglycans: master modulators of paracrine fibroblast-carcinoma cell interactions. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010;21:66–71.
Fukumura D, Ushiyama A, Duda DG, Xu L, Tam J, Chatterjee KK, Garkavtsev I, Jain RK. Paracrine regulation of angiogenesis and adipocyte differentiation during in vivo adipogenesis. Circ Res. 2003;93:e88–97.
Gerhardt H, Betsholtz C. Endothelial-pericyte interactions in angiogenesis. Cell Tissue Res. 2003;314:15–23.
Gomes RR, Farach-Carson MC, Carson DD. Perlecan functions in chondrogenesis: insights from in vitro and in vivo models. Cells Tissues Organs. 2004;176:79–86.
Gomillion CT, Burg KJL. Stem cells and adipose tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2006;27:6052–63.
Grotendorst GR. Connective tissue growth factor: a mediator of TGF-β action on fibroblasts. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1997;8:171–9.
Hata R-I, Senoo H. L-ascorbic adid 2-phosphate stimulates collagen accumulation, cell proliferation, and formation of a three-dimensional tissue-like substance by skin fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1989;138:8–16.
Hausman GJ, Richardson RL. Adipose tissue angiogenesis. J Anim Sci. 2004;82:925–34.
Hausman GJ, Wright JT, Thomas GB. Vascular and cellular development in fetal adipose tissue: lectin binding studies and immunocytochemistry for laminin and type IV collagen. Microvasc Res. 1991;41:111–25.
Hirschi KK, Rohovsky SA, D’Amore PA. PDGF, TGF-β, and heterotypic cell-cell interactions mediate endothelial cell-induced recruitment of 10T1/2 cells and their differentiation to a smooth muscle fate. J Cell Biol. 1998;141:805–14.
Iozzo RV. Basement membrane proteoglycans: from cellar to ceiling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:646–56.
Iozzo RV, San Antonio JD. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans: heavy hitters in the angiogenesis arena. J Clin Invest. 2001;108:349–55.
Johnson CL, Holbrook KA. Development of human embryonic and fetal dermal vasculature. J Invest Dermatol. 1989;93:10S–17S.
Junker JPE, Sommar P, Skog M, Johnson H. Adipogenic, chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation of clonally derived human dermal fibroblasts. Cells Tissues Organs. 2010;191:105–18.
Kimura Y, Ozeki M, Inamoto T, Tabata Y. Time course of de novo adipogenesis in Matrigel by gelatin microspheres incorporating basic fibroblast growth factor. Tissue Eng. 2002;8:603–13.
Kruegel J, Miosge N. Basement membrane components are key players in specialized extracellular matrices. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010;67:2879–95.
Mauney J, Volloch V. Human bone marrow-derived stromal cells show highly efficient stress-resistant adipogenesis on denatured collagen IV matrix but not on its native counterpart: implications for obesity. Matrix Biol. 2010;29:9–14.
McKenzie EA. Heparanase: a target for drug discovery in cancer and inflammation. Br J Pharmacol. 2007;151:1–14.
Melrose J, Hayes AJ, Whitelock JM, Little CB. Perlecan, the “jack of all trades” proteoglycan of cartilaginous weight-bearing connective tissues. Bioessays. 2008;30:457–69.
Merfeld-Clauss S, Collahalli N, March KL, Traktuev DO. Adipose tissue progenitor cells directly interact with endothelial cells to induce vascular network formation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16:2953–66.
Nakajima I, Yamaguchi T, Ozutsumi K, Aso H. Adipose tissue extracellular matrix: newly organized by adipocytes during differentiation. Differentiation. 1998;63:193–200.
Nakajima I, Muroya S, Tanabe R-I, Chikuni K. Extracellular matrix development during differentiation into adipocytes with a unique increase in type V and VI collagen. Biol Cell. 2002;94:197–203.
Napolitano L. The differentiation of white adipose cells. An electron microscope study. J Cell Biol. 1963;18:663–79.
Niemelä S, Miettinen S, Sarkanen JR, Ashammakhi N. Adipose tissue and adipocyte differentiation: molecular and cellular aspects and tissue engineering applications. In: Ashammakhi N, Reis R, Chiellini F, editors. Topics in tissue engineering, vol. 4. Oulu, Finland: University of Oulu; 2008. p. 1–26.
Nikolova G, Strilic B, Lammert E. The vascular niche and its basement membrane. Trends Cell Biol. 2008;17:19–25.
Norrby K. Low-molecular-weight heparins and angiogenesis. APMIS. 2006;114:79–102.
Patrick CW. Adipose tissue engineering: the future of breast and soft tissue reconstruction following tumor resection. Semin Surg Oncol. 2000;19:302–11.
Patrick CW, Wu X. Integrin-mediated preadipocyte adhesion and migration on laminin-1. Ann Biomed Eng. 2003;31:505–14.
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S, Marshak DR. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284:143–7.
Sanz L, Santos-Valle P, Alonso-Camino V, Salas C, Serrano A, Vicario JL, Cuesta AM, Compte M, Sanchez-Martin D, Alvarez-Vallina L. Long-term in vivo imaging of human angiogenesis: critical role of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for the generation of durable blood vessels. Microvasc Res. 2008;75:308–14.
Sarkanen J-R, Kaila V, Mannerström B, Räty S, Kuokkanen H, Miettinen S, Ylikomi T. Human adipose tissue extract induces angiogenesis and adipogenesis in vitro. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18:17–25.
Sbarbati A, Accorsi D, Benati D, Marchetti L, Orsini G, Rigotti G, Panettiere P. Subcutaneous adipose tissue classification. Eur J Histochem. 2010;54:e48.
Sharma NS, Nagrath D, Yarmush ML. Adipocyte-derived basement membrane extract with biological activity: applications in hepatocyte functional augmentation in vitro. FASEB J. 2010;24:2364–74.
Sillat T, Saat R, Pollanen R, Hukkanen M, Takagi M, Konttinen YT. Basement membrane collagen type IV expression by human mesenchymal stem cells during adipogenic differentiation. J Cell Mol Med. 2012;16:1485–95.
Smith LT, Holbrook KA. Embryogenesis of the dermis in human skin. Pediatr Dermatol. 1986;3:271–80.
Sorrell JM, Baber MA, Caplan AI. Human dermal fibroblast subpopulations: differential interactions with vascular endothelial cells in coculture: non-soluble factors in the extracellular matrix influence interactions. Wound Repair Regen. 2008;16:300–9.
Sorrell JM, Baber MA, Caplan AI. Influence of adult mesenchymal stem cells on in vitro vascular formation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15:1751–61.
Sorrell JM, Baber MA, Traktuev DO, March KL, Caplan AI. The creation of an in vitro adipose tissue that contains a vascular-adipocyte complex. Biomaterials. 2011;32:9667–76.
Tavassoli M. Ultrastructural development of bone marrow adipose cells. Acta Anat. 1976;94:65–77.
Uriel S, Huang J-J, Moya ML, Francis ME, Wang R, Chang S-Y, Cheng M-H, Brey EM. The role of adipose protein derived hydrogels in adipogenesis. Biomaterials. 2008;29:3712–19.
Vashi AV, Abberton KM, Thomas GP, Morrison WA, O’Connor AJ, Cooper-White JJ, Thompson EW. Adipose tissue engineering based on the controlled release of fibroblast growth factor-2 in a collagen matrix. Tissue Eng. 2006;12:3035–43.
Vermette M, Trottier V, Ménard V, Saint-Pierre L, Roy A, Fradette J. Production of a new tissue-engineered adipose substitute from human adipose-derived stromal cells. Biomaterials. 2007;28:2850–60.
Verseijden F, Posthumus-van Sluijs SJ, Pavijasevic P, Hofer SOP, van Osch GJVM, Farrell E. Adult human bone marrow- and adipose tissue-derived stromal cells support the formation of prevascular-like structures from endothelial cells in vitro. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16:101–14.
Zimmerlin L, Donnenberg VS, Pfeifer ME, Meyer EM, Peault B, Rubin JP, Donnenberg AD. Stromal vascular progenitors in adult human adipose tissue. Cytometry A. 2010;77A:22–30.
Zimmermann D, Ruoslahti E. Multiple domains of the large fibroblast proteoglycan, versican. EMBO J. 1989;8:2975–81.
Zizola CF, Julianelli V, Bertolesi G, Yanagishita M, Calvo JC. Role of versican and hyaluronan in the differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells into preadipocytes and mature adipocytes. Matrix Biol. 2007;26:419–30.
Zoeller JJ, Whitelock JM, Iozzo RV. Perlecan regulates developmental angiogenesis by modulating the VEGF-VEGFR2 axis. Matrix Biol. 2009;28:284–91.
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, Huang J, Futrell JW, Katz AJ, Benhaim P, Lorenz HP, Hedrick MH. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7:211–28.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by a grant from the Ohio Third Frontier for the Clinical Tissue Engineering Center and it was also supported in part by a grant from the David and Virginia Baldwin Research Fund. The ASCs used for this study were provided by Drs. Keith March (University of Indiana, Indianapolis IN) and Farshid Guliak (Duke University, Durham, NC).
I would also like to thank Marilyn Baber, Dimitry Traktuev, Keith March, and Arnold Caplan who were co-authors of a previous study Biomaterials 32:9667, 2011 from which this chapter was adapted. Selected figures and Table 4.2 were adapted with permission of the publisher (Elsevier, B.V.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Sorrell, J.M. (2013). Vascular Adipose Complex. In: Cao, Y. (eds) Angiogenesis in Adipose Tissue. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-8069-3_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-8069-3_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4614-8068-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-4614-8069-3
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)