Abstract
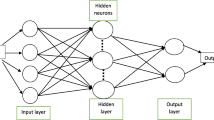
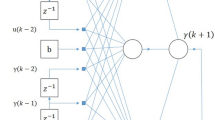
The early warning of saltwater intrusion is an important work for ensuring the drinking water supplies. To forecast and predict the daily maximum salinity for the water withdrawn for the waterworks located along the Qiantang River, the nonlinear autoregressive networks with exogenous inputs (NARX) model was applied. Since the multivariate time series of flow, the tide range, the salinities and the water levels observed at 8 gauging stations have great impact on the salt concentration in the river, this will bring in a large number of inputs when these variables directly fed into the NARX model and add unnecessary model complexity and poor performance. Therefore, the dynamic principal component analysis (DPCA) was used to reduce the data redundancy. Simulation predicted results show that the NARX model using DPCA can predict salinity in the river accurately, moreover, this method not only reduces the input dimension and over-fit the equation, but also enhances the model performance and the generalization ability considerably.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Savenije, H.H.G.: Predictive model for salt intrusion in estuaries. J. Hydrol. 148(1–4), 203–218 (1993)
Aerts, J.C.J.H., et al.: Using GIS tools and rapid assessment techniques for determining salt intrusion: STREAM, a river basin management instrument. Phys. Chem. Earth 25(3), 265–273 (2000)
Huang, W., Foo, S.: Neural network modeling of salinity variation in Apalachicola River. Water Res. 36, 356–362 (2002)
Han, Z., et al.: Effect of large-scale reservoir and river regulation/reclamation on saltwater intrusion in Qiantang Estuary. Sci. China Ser. B. 44 (suppl): 221–229 (2001)
Lu, X.: Model experiment on saltwater intrusion of the Qiantang river estuary. J. Hydro-Sci. Eng. 3(4), 403–410 (1991) (In Chinese)
Diaconescu, E.: The use of NARX neural network to predict chaotic time series. WSEAS Trans. Comput. Res. 3, 182–191 (2008)
Ku, W., et al.: Disturbance detection and isolation by dynamic principal component analysis. Chemometr. Intell. Lab 30, 179–196 (1995)
Nguyen, D., Widrow, B.: Improving the learning speed of 2-layer neural networks by choosing initial values of the adaptive weights. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, vol. 2, pp. 21–26 (1990)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this paper
Cite this paper
Yang, X., Zhang, H., Zhou, H. (2013). Salinity Time Series Prediction and Forecasting Using Dynamic Neural Networks in the Qiantang River Estuary. In: Wong, W.E., Ma, T. (eds) Emerging Technologies for Information Systems, Computing, and Management. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 236. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-7010-6_79
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-7010-6_79
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4614-7009-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-4614-7010-6
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)