Abstract
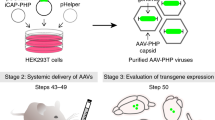
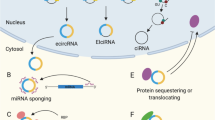
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have recently emerged as a promising modality for gene and RNA-based therapies. They are more stable than their linear counterpart and can be designed for efficient expression in different cell and tissue types. In this chapter, we developed different backsplicing circRNA cassettes that can enable efficient gene expression in various cell and tissue types. Furthermore, we packaged cassettes encoding circRNAs into adeno-associated viral (AAV) vectors that can be delivered via intracerebroventricular (ICV) injections to achieve expression in murine brain tissue. We provide detailed methods for the design of backsplicing circRNAs, circRNA detection, and generation of AAV-circRNA vectors for CNS dosing and expression in mice.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holdt LM, Kohlmaier A, Teupser D (2018) Circular RNAs as therapeutic agents and targets. Front Physiol 9:1262. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01262
Stoll L, Sobel J, Rodriguez-Trejo A, Guay C, Lee K, Venø MT et al (2018) Circular RNAs as novel regulators of β-cell functions in normal and disease conditions. Mol Metab 9:69–83
Bai Y, Zhang Y, Han B, Yang L, Chen X, Huang R et al (2018) Circular RNA DLGAP4 ameliorates ischemic stroke outcomes by targeting miR-143 to regulate endothelial-mesenchymal transition associated with blood–brain barrier integrity. J Neurosci 38(1):32–50
Li Z, Huang C, Bao C, Chen L, Lin M, Wang X, Zhong G, Yu B, Hu W, Dai L, Zhu P, Chang Z, Wu Q, Zhao Y, Jia Y, Xu P, Liu H, Shan G (2015) Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat Struct Mol Biol 22(3):256–264
Liu B, Ye B, Zhu X, Yang L, Li H, Liu N, Zhu P, Lu T, He L, Tian Y, Fan Z (2020) An inducible circular RNA circKcnt2 inhibits ILC3 activation to facilitate colitis resolution. Nat Commun 11(1):4076
Ashwal-Fluss R, Meyer M, Pamudurti NR, Ivanov A, Bartok O, Hanan M, Evantal N, Memczak S, Rajewsky N, Kadener S (2014) circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell 56(1):55–66
Gong X, Tian M, Cao N, Yang P, Xu Z, Zheng S et al (2021) Circular RNA circEsyt2 regulates vascular smooth muscle cell remodeling via splicing regulation. J Clin Investig 131(24):e147031
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, Kjems J (2013) Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 495(7441):384–388
Man W, Cui Y, Li J, Li Y, Jin J, Jin Y, Wu X, Zhong R, Li X, Yao H, Lin Y, Jiang L, Wang Y (2022) circTAB2 inhibits lung cancer proliferation, migration and invasion by sponging miR-3142 to upregulate GLIS2. Apoptosis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-022-01805-1
Chen CY, Sarnow P (1995) Initiation of protein synthesis by the eukaryotic translational apparatus on circular RNAs. Science (New York, NY) 268(5209):415–417
Zhang Y, Zhang X, Shen Z, Qiu Q, Tong X, Pan J, Zhu M, Hu X, Gong C (2022) BmNPV circular RNA-encoded peptide VSP39 promotes viral replication. Int J Biol Macromol 228:299–310
Enuka Y, Lauriola M, Feldman ME, Sas-Chen A, Ulitsky I, Yarden Y (2016) Circular RNAs are long-lived and display only minimal early alterations in response to a growth factor. Nucleic Acids Res 44(3):1370–1383
Wilusz JE (2018) A 360° view of circular RNAs: from biogenesis to functions. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 9(4):e1478. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrna.1478
Monat C, Cousineau B (2016) Circularization pathway of a bacterial group II intron. Nucleic Acids Res 44(4):1845–1853
Lu Z, Filonov GS, Noto JJ, Schmidt CA, Hatkevich TL, Wen Y et al (2015) Metazoan tRNA introns generate stable circular RNAs in vivo. RNA 21(9):1554–1565
Wang Y, Wang Z (2015) Efficient backsplicing produces translatable circular mRNAs. RNA (New York, NY) 21(2):172–179
Chen R, Wang SK, Belk JA, Amaya L, Li Z, Cardenas A, Abe BT, Chen CK, Wender PA, Chang HY (2022) Engineering circular RNA for enhanced protein production. Nat Biotechnol 41:262. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-022-01393-0
Meganck RM, Liu J, Hale AE, Simon KE, Fanous MM, Vincent HA, Wilusz JE, Moorman NJ, Marzluff WF, Asokan A (2021) Engineering highly efficient backsplicing and translation of synthetic circRNAs. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 23:821–834
Zhao Y, Huang L (2014) Lipid nanoparticles for gene delivery. Adv Genet 88:13–36
Topal J, Panchal N, Barroeta A, Roppelt A, Mudde A, Gaspar HB, Thrasher AJ, Houghton BC, Booth C (2023) Lentiviral Gene Transfer Corrects Immune Abnormalities in XIAP Deficiency. J Clin Immunol 43(2):440–451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-022-01389-0gonz
Gonzalez TJ, Simon KE, Blondel LO, Fanous MM, Roger AL, Maysonet MS, Devlin GW, Smith TJ, Oh DK, Havlik LP, Castellanos Rivera RM, Piedrahita JA, ElMallah MK, Gersbach CA, Asokan A (2022) Cross-species evolution of a highly potent AAV variant for therapeutic gene transfer and genome editing. Nat Commun 13(1):5947
Stanton AC, Lagerborg KA, Tellez L, Krunnfusz A, King EM, Ye S, Solomon IH, Tabebordbar M, Sabeti PC (2023) Systemic administration of novel engineered AAV capsids facilitates enhanced transgene expression in the macaque CNS. Med (New York, NY) 4(1):31–50.e8
Meganck RM, Borchardt EK, Castellanos Rivera RM, Scalabrino ML, Wilusz JE, Marzluff WF, Asokan A (2018) Tissue-dependent expression and translation of circular RNAs with recombinant AAV vectors in vivo. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 13:89–98
Nieuwenhuis B, Laperrousaz E, Tribble JR, Verhaagen J, Fawcett JW, Martin KR, Williams PA, Osborne A (2023) Improving adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector-mediated transgene expression in retinal ganglion cells: comparison of five promoters. Gene Ther 30:503. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41434-022-00380-z
Qin JY, Zhang L, Clift KL, Hulur I, Xiang AP, Ren BZ, Lahn BT (2010) Systematic comparison of constitutive promoters and the doxycycline-inducible promoter. PLoS One 5(5):e10611
Kuhn B, Ozden I, Lampi Y, Hasan MT, Wang SS (2012) An amplified promoter system for targeted expression of calcium indicator proteins in the cerebellar cortex. Front Neural Circuits 6:49
Yao Z, Luo J, Hu K, Lin J, Huang H, Wang Q, Zhang P, Xiong Z, He C, Huang Z, Liu B, Yang Y (2017) ZKSCAN1 gene and its related circular RNA (circZKSCAN1) both inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth, migration, and invasion but through different signaling pathways. Mol Oncol 11(4):422–437
Liang D, Wilusz JE (2014) Short intronic repeat sequences facilitate circular RNA production. Genes Dev 28(20):2233–2247
Noren NK, Pasquale EB (2007) Paradoxes of the EphB4 receptor in cancer. Cancer Res 67(9):3994–3997
Xu T, Wu J, Han P, Zhao Z, Song X (2017) Circular RNA expression profiles and features in human tissues: a study using RNA-seq data. BMC Genomics 18(Suppl 6):680
Meganck RM, Borchardt EK, Castellanos Rivera RM, Scalabrino ML, Wilusz JE, Marzluff WF, Asokan A (2018) Tissue-dependent expression and translation of circular RNAs with recombinant AAV vectors in vivo. Mol Therapy Nucleic acids 13:89–98
Wang D, Tai PWL, Gao G (2019) Adeno-associated virus vector as a platform for gene therapy delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 18(5):358–378
Pupo A, Fernández A, Low SH, François A, Suárez-Amarán L, Samulski RJ (2022) AAV vectors: the Rubik’s cube of human gene therapy. Mol Ther 30(12):3515–3541
Elmore ZC, Patrick Havlik L, Oh DK, Anderson L, Daaboul G, Devlin GW, Vincent HA, Asokan A (2021) The membrane associated accessory protein is an adeno-associated viral egress factor. Nat Commun 12(1):6239
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (R01NS099371 to A.A., W.F.M., and J.E.W. and R01HL089221, R01GM127708, and UG3AR075336 to A.A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Clements, K.N., Gonzalez, T.J., Asokan, A. (2024). Engineering Synthetic circRNAs for Efficient CNS Expression. In: Dieterich, C., Baudet, ML. (eds) Circular RNAs. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2765. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3678-7_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3678-7_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-3677-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-3678-7
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols