Abstract
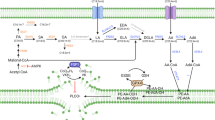
Ferroptosis is a regulated form of cell death characterized by the accumulation of oxidized phospholipids, particularly oxidized phosphatidylethanolamines (PE), which serve as important biomarkers in the progression of various diseases. To facilitate the comprehensive investigation of ferroptosis in biological systems, we present a robust and versatile untargeted redox phospholipidomics method employing normal-phase liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). This high-throughput technique enables the identification and quantification of dozens of oxidized phospholipid species in a single run, providing valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying ferroptosis. It has been successfully applied to diverse biological samples, including human patients, animals, and cell cultures, and offers a powerful tool for investigating the roles of oxidized phospholipids in the development and progression of various diseases.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doll S, Proneth B, Tyurina YY et al (2017) ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat Chem Biol 13:91–98
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR et al (2012) Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 149:1060–1072
Kagan VE, Mao GW, Qu F et al (2017) Oxidized arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol 13:81–90
Kuhn H, Banthiya S, van Leyen K (2015) Mammalian lipoxygenases and their biological relevance. Biochim Biophys Acta 1851:308–330
Yamanaka K, Saito Y, Sakiyama J et al (2012) A novel fluorescent probe with high sensitivity and selective detection of lipid hydroperoxides in cells. RSC Adv 2:7894
Kagan VE, Tyurina YY, Sun WY et al (2020) Redox phospholipidomics of enzymatically generated oxygenated phospholipids as specific signals of programmed cell death. Free Radic Biol Med 147:231–241
Sun WY, Tyurin VA, Mikulska-Ruminska K et al (2021) Phospholipase iPLA(2)beta averts ferroptosis by eliminating a redox lipid death signal. Nat Chem Biol 17:465–476
Luo X, Gong HB, Gao HY et al (2021) Oxygenated phosphatidylethanolamine navigates phagocytosis of ferroptotic cells by interacting with TLR2. Cell Death Differ 28:1971–1989
Li W, Luo LX, Zhou QQ et al (2022) Phospholipid peroxidation inhibits autophagy via stimulating the delipidation of oxidized LC3-PE. Redox Biol 55:102421
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Tsugawa H, Ikeda K, Takahashi M et al (2020) A lipidome atlas in MS-DIAL 4. Nat Biotechnol 38:1159–1163
Fahy E, Sud M, Cotter D et al (2007) LIPID MAPS online tools for lipid research. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W606–W612
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Sun, WY., Wang, R., He, RR. (2023). LC-MS-Based Redox Phosphoipidomics Analysis in Ferroptosis. In: Kroemer, G., Tang, D. (eds) Ferroptosis. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2712. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3433-2_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3433-2_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-3432-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-3433-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols