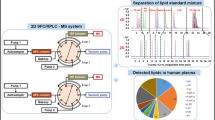
Abstract
Liposomes are spherical, closed vesicles consisting of at least one lipid bilayer with a water chamber and are widely used to encapsulate bioactive molecules. Lipid membranes, composed of different types of lipids or lipophilic components, determine whether liposomes can achieve the desired purpose and determine the overall quality of liposomes. Thus, the quantification of lipid components and encapsulated molecules is essential to characterize and control the quality of liposomes. Moreover, multicomponent simultaneous determination is the preferred method for lipid component analysis in liposomes. Therefore, the present work describes an analytical methodology for the simultaneous determination of commonly used lipids in liposome formulations, using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a tandem mass spectrometry (MS) detector (HPLC-MS/MS). HPLC-MS/MS consists of a rapid and highly efficient chromatographic separation of the liposomal components with a C18 column and the subsequent detection of the ingredients through an MS detector, along with an accurate mass fragmentation pattern. The analytical process mainly includes lipid extraction, solution preparation, the optimization of chromatographic conditions, and method validation. We hope this analytical methodology is valuable and efficient and can be applied to the analysis of multiple types of lipids in liposomes, such as raw material quality analysis, formulation study, overall quality control, etc.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mehdi Hasan MH, Mondal JC, Al Hasan M, Talukder S, Rashid HA (2017) Liposomes: an advance tools for novel drug delivery system. Pharma Innov J 6:304–311
Petros RA, DeSimone JM (2010) Strategies in the design of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9:615–627
Akbarzadeh A, Rezaei-Sadabady R, Davaran S, Joo SW, Zarghami N, Hanifehpour Y et al (2013) Liposome: classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res Lett 8(1):102
Soema PC, Willems GJ, Jiskoot W, Amorij JP, Kersten GF (2015) Predicting the influence of liposomal lipid composition on liposome size, zeta potential and liposome-induced dendritic cell maturation using a design of experiments approach. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 94:427–435
Anderson M, Omri A (2004) The effect of different lipid components on the in vitro stability and release kinetics of liposome formulations. Drug Deliv 11:33–39
He H, Lu Y, Qi J, Zhu Q, Chen Z, Wu W (2019) Adapting liposomes for oral drug delivery. Acta Pharm Sin B 9:36–48
Yandrapati RK (2012) Effect of lipid composition on the physical properties of liposomes: a light scattering study. Masters Theses 6864
Poelma DL, Ju MR, Bakker SC, Zimmermann LJ, Lachmann BF, van Iwaarden JF (2004) A common pathway for the uptake of surfactant lipids by alveolar cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 30:751–758
Ciani L, Casini A, Gabbiani C, Ristori S, Messori L, Martini G (2007) DOTAP/DOPE and DC-Chol/DOPE lipoplexes for gene delivery studied by circular dichroism and other biophysical techniques. Biophys Chem 127:213–220
Briuglia ML, Rotella C, McFarlane A, Lamprou DA (2015) Influence of cholesterol on liposome stability and on in vitro drug release. Drug Deliv Transl Res 5:231–242
Kaddah S, Khreich N, Kaddah F, Charcosset C, Greige-Gerges H (2018) Cholesterol modulates the liposome membrane fluidity and permeability for a hydrophilic molecule. Food Chem Toxicol 113:40–48
Haeri A, Alinaghian B, Daeihamed M, Dadashzadeh S (2014) Preparation and characterization of stable nanoliposomal formulation of fluoxetine as a potential adjuvant therapy for drug-resistant tumors. Iran J Pharm Res 13:3–14
Caracciolo G, Pozzi D, Capriotti AL, Cavaliere C, Piovesana S, Amenitsch H et al (2015) Lipid composition: a “key factor” for the rational manipulation of the liposome–protein corona by liposome design. RSC Adv 5:5967–5975
Liposome drug products – chemistry, manufacturing, and controls; Human pharmacokinetics and bioavailability; and labeling documentation – guidance for industry. 2015
Sophia Hatziantoniou CD (2010) Method of simultaneous analysis of liposome components using HPTLC/FID. Methods Mol Biol 606:363–368
Sophia Hatziantoniou CD (2017) Method of simultaneous analysis of liposome components using HPTLC/FID. Methods Mol Biol 1522:49–54
Hatziantoniou S, Demetzos C (2006) Qualitative and quantitative one-step analysis of lipids and encapsulated bioactive molecules in liposome preparations by HPTLC/FID (IATROSCAN). J Liposome Res 16:321–330
Suchocka Z, Gronostajska D, Suchocki P, Pachecka J (2003) New HPLC method for separation of blood plasma phospholipids. J Pharm Biomed Anal 32:859–865
Singh R, Ajagbe M, Bhamidipati S, Ahmad Z, Ahmad I (2005) A rapid isocratic high-performance liquid chromatography method for determination of cholesterol and 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine in liposome-based drug formulations. J Chromatogr A 1073:347–353
Hvattum E, Uran S, Sandbaek AG, Karlsson AA, Skotland T (2006) Quantification of phosphatidylserine, phosphatidic acid and free fatty acids in an ultrasound contrast agent by normal-phase high-performance liquid chromatography with evaporative light scattering detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal 42:506–512
Alsaadi MM, Christine Carter K, Mullen AB (2013) High performance liquid chromatography with evaporative light scattering detection for the characterisation of a vesicular delivery system during stability studies. J Chromatogr A 1320:80–85
Kothalawala N, Mudalige TK, Sisco P, Linder SW (2018) Novel analytical methods to assess the chemical and physical properties of liposomes. J Chromatogr B 1091:14–20
Lesnefsky EJ, Stoll MS, Minkler PE, Hoppel CL (2000) Separation and quantitation of phospholipids and lysophospholipids by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem 285:246–254
Siriwardane DA, Wang C, Jiang W, Mudalige T (2020) Quantification of phospholipid degradation products in liposomal pharmaceutical formulations by ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS). Int J Pharm 578:119077
Wang C, Siriwardane DA, Jiang W, Mudalige T (2019) Quantitative analysis of cholesterol oxidation products and desmosterol in parenteral liposomal pharmaceutical formulations. Int J Pharm 569:118576
Jeschek D, Lhota G, Wallner J, Vorauer-Uhl K (2016) A versatile, quantitative analytical method for pharmaceutical relevant lipids in drug delivery systems. J Pharm Biomed Anal 119:37–44
Meyer O, Roch O, Elmlinger D, Kolbe HVJ (2000) Direct lipid quantitation of cationic liposomes by reversed-phase HPLC in lipoplex preparation process. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 50:353–356
Simonzadeh N (2009) An isocratic HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of cholesterol, Cardiolipin, and DOPC in lyophilized lipids and liposomal formulations. J Chromatogr Sci 47:304–308
Oswald M, Platscher M, Geissler S, Goepferich A (2016) HPLC analysis as a tool for assessing targeted liposome composition. Int J Pharm 497:293–300
Zhou Q, Liu L, Zhang D, Fan X (2012) Analysis of gemcitabine liposome injection by HPLC with evaporative light scattering detection. J Liposome Res 22:263–269
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Shi, Y., Li, X. (2023). High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Identification and Quantification of Lipids in Liposomes. In: D'Souza, G.G., Zhang, H. (eds) Liposomes. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2622. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2954-3_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2954-3_20
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-2953-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-2954-3
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols