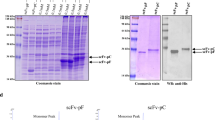
Abstract
Recombinant antibody fragments such as Fab, scFvs, and diabodies against α-syn have become a viable alternative to the conventional full-length antibodies in immunotherapeutic approaches due to their benefits which include smaller size, higher stability, specificity, and affinity. However, the majority of recombinant antibody fragments typically express as inclusion bodies (IBs) in E. coli, which makes their purification incredibly difficult. Here, we describe a method involving a mild solubilizing protocol followed by slow on-column refolding to purify active single-chain variable fragment (scFv-pF) antibody that can recognize the pathogenic α-syn fibrils.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ardah MT, Paleologou KE, Lv G et al (2015) Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits fibrillation and toxicity of alpha-synuclein and disaggregates preformed fibrils. Neurobiol Dis 74:89–101
Chia KY, Ng KY, Koh RY et al (2018) Single-chain Fv antibodies for targeting neurodegenerative diseases. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 17:671–679
El-Agnaf O, Overk C, Rockenstein E et al (2017) Differential effects of immunotherapy with antibodies targeting alpha-synuclein oligomers and fibrils in a transgenic model of synucleinopathy. Neurobiol Dis 104:85–96
Freskgard PO, Urich E (2017) Antibody therapies in CNS diseases. Neuropharmacology 120:38–55
Huang L, Su X, Federoff HJ (2013) Single-chain fragment variable passive immunotherapies for neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci 14:19109–19127
Jellinger KA (2003) Neuropathological spectrum of synucleinopathies. Mov Disord 18(Suppl 6):S2–S12
Jevsevar S, Gaberc-Porekar V, Fonda I et al (2005) Production of nonclassical inclusion bodies from which correctly folded protein can be extracted. Biotechnol Prog 21:632–639
Manoutcharian K, Perez-Garmendia R, Gevorkian G (2017) Recombinant antibody fragments for neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Neuropharmacol 15:779–788
Qi X, Sun Y, Xiong S (2015) A single freeze-thawing cycle for highly efficient solubilization of inclusion body proteins and its refolding into bioactive form. Microbial Cell Fact 14:24
Singh A, Upadhyay V, Panda AK (2015) Solubilization and refolding of inclusion body proteins. Methods Mol Biol 1258:283–291
Singh SM, Panda AK (2005) Solubilization and refolding of bacterial inclusion body proteins. J Biosci Bioeng 99:303–310
Singh SM, Sharma A, Upadhyay AK et al (2012) Solubilization of inclusion body proteins using n-propanol and its refolding into bioactive form. Protein Expr Purif 81:75–82
Skrlj N, Drevensek G, Hudoklin S et al (2013) Recombinant single-chain antibody with the Trojan peptide penetratin positioned in the linker region enables cargo transfer across the blood-brain barrier. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169:159–169
Spillantini MG, Goedert M (2000) The alpha-synucleinopathies: Parkinson’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and multiple system atrophy. Ann N Y Acad Sci 920:16–27
Vaikath NN, Majbour NK, Paleologou KE et al (2015) Generation and characterization of novel conformation-specific monoclonal antibodies for alpha-synuclein pathology. Neurobiol Dis 79:81–99
Ventura S, Villaverde A (2006) Protein quality in bacterial inclusion bodies. Trends Biotechnol 24:179–185
Zella SMA, Metzdorf J, Ciftci E et al (2019) Emerging immunotherapies for Parkinson disease. Neurol Ther 8:29–44
Acknowledgments
Dr. El-Agnaf’s laboratory is funded by Qatar Biomedical Research Institute under the Start-up Fund SF 2017-007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Gupta, V., Hmila, I., Vaikath, N.N., Sudhakaran, I.P., El-Agnaf, O.M.A. (2023). Production of α-Synuclein Fibrillar-Specific scFv from Inclusion Bodies. In: Kopp, J., Spadiut, O. (eds) Inclusion Bodies. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2617. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2930-7_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2930-7_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-2929-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-2930-7
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols