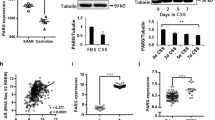
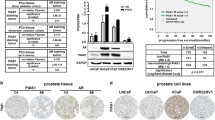
Abstract
Since the early 1940s, androgen ablation has been the cornerstone of treatment for prostate cancer (PC). Importantly, androgen receptor (AR) signaling is vital not only for the initiation of PC, which is initially androgen-dependent, but also for castration-resistant disease. Recent studies demonstrated clear promise of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1) inhibitors for targeting prostate cancer cells harboring mutations in DNA damage-repair genes. In addition, it has been established that PARP-1 inhibition suppresses growth of AR-positive prostate cancer cells in cell and animal models. Thus, prostate cancer represents a particularly promising disease site for targeting PARP-1, given that both DNA repair and AR-mediated transcription depend on PARP-1 function. Here, we describe the development and use of cell-based assay to evaluate the impact of PARP-1 inhibitors on the AR signaling in prostate cancer cells.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A (2022) Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin 72(1):7–33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21708
Aragon-Ching JB (2014) The evolution of prostate cancer therapy: targeting the androgen receptor. Front Oncol 4:295. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2014.00295
Cai C, Chen S, Ng P, Bubley GJ, Nelson PS, Mostaghel EA, Marck B, Matsumoto AM, Simon NI, Wang H, Chen S, Balk SP (2011) Intratumoral de novo steroid synthesis activates androgen receptor in castration-resistant prostate cancer and is upregulated by treatment with CYP17A1 inhibitors. Cancer Res 71(20):6503–6513. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0532
Dehm SM, Tindall DJ (2007) Androgen receptor structural and functional elements: role and regulation in prostate cancer. Mol Endocrinol 21(12):2855–2863. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2007-0223
Lonergan PE, Tindall DJ (2011) Androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer development and progression. J Carcinog 10:20. https://doi.org/10.4103/1477-3163.83937
Pisano C, Tucci M, Di Stefano RF, Turco F, Scagliotti GV, Di Maio M, Buttigliero C (2021) Interactions between androgen receptor signaling and other molecular pathways in prostate cancer progression: current and future clinical implications. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 157:103185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2020.103185
Mori K, Miura N, Mostafaei H, Quhal F, Sari Motlagh R, Pradere B, Kimura S, Kimura T, Egawa S, Briganti A, Karakiewicz PI, Shariat SF (2020) Sequential therapy of abiraterone and enzalutamide in castration-resistant prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41391-020-0222-6
Scher HI, Fizazi K, Saad F, Taplin ME, Sternberg CN, Miller K, de Wit R, Mulders P, Chi KN, Shore ND, Armstrong AJ, Flaig TW, Flechon A, Mainwaring P, Fleming M, Hainsworth JD, Hirmand M, Selby B, Seely L, de Bono JS, Investigators A (2012) Increased survival with enzalutamide in prostate cancer after chemotherapy. New Engl J Med 367(13):1187–1197. https://doi.org/10.1056/Nejmoa1207506
Attard G, Reid AH, A'Hern R, Parker C, Oommen NB, Folkerd E, Messiou C, Molife LR, Maier G, Thompson E, Olmos D, Sinha R, Lee G, Dowsett M, Kaye SB, Dearnaley D, Kheoh T, Molina A, de Bono JS (2009) Selective inhibition of CYP17 with abiraterone acetate is highly active in the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol 27(23):3742–3748. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2008.20.0642
de Bono JS, Logothetis CJ, Molina A, Fizazi K, North S, Chu L, Chi KN, Jones RJ, Goodman OB Jr, Saad F, Staffurth JN, Mainwaring P, Harland S, Flaig TW, Hutson TE, Cheng T, Patterson H, Hainsworth JD, Ryan CJ, Sternberg CN, Ellard SL, Flechon A, Saleh M, Scholz M, Efstathiou E, Zivi A, Bianchini D, Loriot Y, Chieffo N, Kheoh T, Haqq CM, Scher HI (2011) Abiraterone and increased survival in metastatic prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 364(21):1995–2005. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1014618
Buttigliero C, Tucci M, Bertaglia V, Vignani F, Bironzo P, Di Maio M, Scagliotti GV (2015) Understanding and overcoming the mechanisms of primary and acquired resistance to abiraterone and enzalutamide in castration resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 41(10):884–892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2015.08.002
Li Y, Chan SC, Brand LJ, Hwang TH, Silverstein KA, Dehm SM (2013) Androgen receptor splice variants mediate enzalutamide resistance in castration-resistant prostate cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 73(2):483–489. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3630
Vellky JE, Ricke WA (2020) Development and prevalence of castration-resistant prostate cancer subtypes. Neoplasia 22(11):566–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2020.09.002
Galletti G, Leach BI, Lam L, Tagawa ST (2017) Mechanisms of resistance to systemic therapy in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 57:16–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.04.008
Mitsiades N (2013) A road map to comprehensive androgen receptor axis targeting for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res 73(15):4599–4605. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4414
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2016) Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 66(1):7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21332
Deshmukh D, Qiu Y (2015) Role of PARP-1 in prostate cancer. Am J Clin Exp Urol 3(1):1–12
Mateo J, Carreira S, Sandhu S, Miranda S, Mossop H, Perez-Lopez R, Nava Rodrigues D, Robinson D, Omlin A, Tunariu N, Boysen G, Porta N, Flohr P, Gillman A, Figueiredo I, Paulding C, Seed G, Jain S, Ralph C, Protheroe A, Hussain S, Jones R, Elliott T, McGovern U, Bianchini D, Goodall J, Zafeiriou Z, Williamson CT, Ferraldeschi R, Riisnaes R, Ebbs B, Fowler G, Roda D, Yuan W, Wu YM, Cao X, Brough R, Pemberton H, A'Hern R, Swain A, Kunju LP, Eeles R, Attard G, Lord CJ, Ashworth A, Rubin MA, Knudsen KE, Feng FY, Chinnaiyan AM, Hall E, de Bono JS (2015) DNA-repair defects and olaparib in metastatic prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 373(18):1697–1708. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1506859
Schiewer MJ, Goodwin JF, Han S, Brenner JC, Augello MA, Dean JL, Liu F, Planck JL, Ravindranathan P, Chinnaiyan AM, McCue P, Gomella LG, Raj GV, Dicker AP, Brody JR, Pascal JM, Centenera MM, Butler LM, Tilley WD, Feng FY, Knudsen KE (2012) Dual roles of PARP-1 promote cancer growth and progression. Cancer Discov 2(12):1134–1149. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0120
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health Grants R03 CA216173, CA246011 (to P.M.); R03 CA235060 (to V.M.K.); the Department of Defense Idea Development Awards KC170127 and PC210308 (to V.M.K.); MPI FCCC pilot application (to V.M.K. and N.W.S.) and the NCI Core Grant NCI P30 CA006927 (to Fox Chase Cancer Center).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Makhov, P., Fazliyeva, R., Tufano, A., Uzzo, R.G., Kolenko, V.M. (2023). Examining the Effect of PARP-1 Inhibitors on Transcriptional Activity of Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer Cells. In: Tulin, A.V. (eds) Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2609. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2891-1_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2891-1_19
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-2890-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-2891-1
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols