Abstract
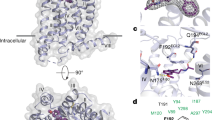
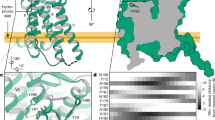
Melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine) is a neurohormone which possesses a wide range of biological effects. The effects mediated by melatonin are in part attributed to the antioxidant properties of the molecule, which may act as scavenger of free radicals, and also to the binding of melatonin to its protein targets. For a long time, melatonin had been described as a ligand of a putative “receptor” present in the mammalian brain. Several studies were thus carried out with the goal of clarifying the nature of this melatonin “receptor,” which led to the discovery of MT3 as the third melatonin binding site. This binding site was confirmed independently by several groups, and it was eventually demonstrated that MT3 was the enzyme quinone reductase 2 (NQO2). Among the different approaches used to validate that MT3 was indeed NQO2, the co-crystallization of NQO2 with melatonin was key in demonstrating the exact binding site and mode of melatonin to the enzyme and led to a clear understanding of the residues important for protein binding and inhibition. In this chapter, we described the details for the cloning, expression, and purification of the human enzyme NQO2. We also describe a detailed protocol for the crystallization of melatonin with this protein.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liao S, Dulaney JT, Williams-Ashman HG (1962) Purification and properties of a flavoprotein catalyzing the oxidation of reduced ribosyl nicotinamide. J Biol Chem 237:2981–2987
Liao S, Williams-Ashman HG (1961) Enzymatic oxidation of some non-phosphorylated derivatives of dihydronicotinamide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 4:208–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291X(61)90272-8
Zhao Q, Yang XL, Holtzclaw WD et al (1997) Unexpected genetic and structural relationships of a long-forgotten flavoenzyme to NAD(P)H:quinone reductase (DT-diaphorase). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:1669–1674. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.5.1669
Vella F, Ferry G, Delagrange P et al (2005) NRH:quinone reductase 2: an enzyme of surprises and mysteries. Biochem Pharmacol 71:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2005.09.019
Janda E, Nepveu F, Calamini B et al (2020) Molecular pharmacology of NRH:quinone oxidoreductase 2: a detoxifying enzyme acting as an undercover toxifying enzyme. Mol Pharmacol 98:620–633. https://doi.org/10.1124/molpharm.120.000105
Nosjean O, Ferro M, Coge F et al (2000) Identification of the melatonin-binding site MT3 as the quinone reductase 2. J Biol Chem 275:31311–31317. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M005141200
Ladbury JE, Chowdhry BZ (1996) Sensing the heat: the application of isothermal titration calorimetry to thermodynamic studies of biomolecular interactions. Chem Biol 3:791–801. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1074-5521(96)90063-0
Maveyraud L, Mourey L (2020) Protein X-ray crystallography and drug discovery. Molecules 25:1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25051030
Zuercher WJ, Elkins JM, Knapp S (2016) The intersection of structural and chemical biology – an essential synergy. Cell Chem Biol 23:173–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2015.12.005
Beck A, Terral G, Debaene F et al (2016) Cutting-edge mass spectrometry methods for the multi-level structural characterization of antibody-drug conjugates. Expert Rev Proteomics 13:157–183. https://doi.org/10.1586/14789450.2016.1132167
Foster CE, Bianchet MA, Talalay P et al (1999) Crystal structure of human quinone reductase type 2, a metalloflavoprotein. Biochemistry 38:9881–9886. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi990799v
Buryanovskyy L, Fu Y, Boyd M et al (2004) Crystal structure of quinone reductase 2 in complex with resveratrol. Biochemistry 43:11417–11426. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi049162o
Fu Y, Buryanovskyy L, Zhang Z (2005) Crystal structure of quinone reductase 2 in complex with cancer prodrug CB1954. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 336:332–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.08.081
Pegan SD, Sturdy M, Ferry G et al (2011) X-ray structural studies of quinone reductase 2 nanomolar range inhibitors. Protein Sci 20:1182–1195. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.647
Harlow E, Lane D (2006) Bradford assay. CSH Protoc 2006:pdb.prot4644. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot4644
Mayerhöfer TG, Pipa AV, Popp J (2019) Beer’s law-why integrated absorbance depends linearly on concentration. ChemPhysChem 20:2748–2753. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.201900787
Calamini B, Santarsiero BD, Boutin JA et al (2008) Kinetic, thermodynamic and X-ray structural insights into the interaction of melatonin and analogues with quinone reductase 2. Biochem J 413:81–91. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20071373
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Laurent Vuillard for preparing Fig. 2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Calamini, B., Ferry, G., Boutin, J.A. (2022). Cloning, Expression, Purification, Crystallization, and X-Ray Structural Determination of the Human NQO2 in Complex with Melatonin. In: Jockers, R., Cecon, E. (eds) Melatonin. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2550. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2593-4_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2593-4_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-2592-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-2593-4
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols