Abstract
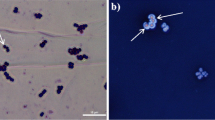
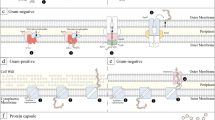
Microorganisms produce a diverse range of carbohydrates, including cytoplasmic storage polymers (glycogens) and structural polymers (glycans) that make up a portion of the microbial envelope. Glycan polymers include capsular polysaccharides (if polymer tightly bound to the cell surface) or exopolysaccharides (if loosely attached to the extracellular surface). Many Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria have been found to have capsular polysaccharides as virulence features. Therefore, the bacterial isolates which produce capsules cannot be considered probiotics. The capsules can be detected by various microscopy methods. Moreover, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) based method can detect specific capsule gene harbored by the bacterial strain.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cress BF, Englaender JA, He W, Kasper D, Linhardt RJ, Koffas MA (2014) Masquerading microbial pathogens: capsular polysaccharides mimic host-tissue molecules. FEMS Microbiol Rev 38:660–697
Lebeer S, Verhoeven TL, Francius G, Schoofs G, Lambrichts I, Dufrêne Y, Vanderleyden J, De Keersmaecker SCJ (2009) Identification of a gene cluster for the biosynthesis of a long, galactose-rich exopolysaccharide in Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and functional analysis of the priming glycosyltransferase. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:3554–3563
Yasuda E, Serata M, Sako T (2008) Suppressive effect on activation of macrophages by Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota genes determining the synthesis of cell wall-associated polysaccharides. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:4746–4755
Anthony E Jr (1931) A note on capsule staining. Science 73:319–320
Hiss PH Jr (1905) A contribution to the physiological differentiation of pneumococcus and streptococcus, and to methods of staining capsules. J Exp Med 6:317–345
Maneval W (1941) Staining bacteria and yeasts with acid dyes. Stain Technol 16:13–19
Owen MP, Kiernan JA (2004) The M’Fadyean reaction: a stain for anthrax bacilli. Biotech Histochem 79:107–108
Duguid J (1951) The demonstration of bacterial capsules and slime. J Pathol Bacteriol 63:673–685
Butt EM, Bonynge CW, Joyce RL (1936) The demonstration of capsules about hemolytic streptococci with India ink or azo blue. J Infect Dis 58:5–9
Oleksy M, Klewicka E (2017) Capsular polysaccharides of Lactobacillus spp.: theoretical and practical aspects of simple visualization methods. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 9:425–434
Remus DM, van Kranenburg R, van Swam II, Taverne N, Bongers RS, Wels M, Bron PA, Kleerebezem M (2012) Impact of 4 Lactobacillus plantarum capsular polysaccharide clusters on surface glycan composition and host cell signaling. Microb Cell Fact 11:1–10
Pan YJ, Fang HC, Yang HC, Lin TL, Hsieh PF, Tsai FC, Keynan Y, Wang JT (2008) Capsular polysaccharide synthesis regions in Klebsiella pneumoniae serotype K57 and a new capsular serotype. J Clin Microbiol 46:2231–2240
Chen Y, Dai J, Morris JG, Johnson JA (2010) Genetic analysis of the capsule polysaccharide (K antigen) and exopolysaccharide genes in pandemic Vibrio parahaemolyticus O3: K6. BMC Microbiol 10:1–10
Waite RD, Penfold DW, Struthers JK, Dowson CG (2003) Spontaneous sequence duplications within capsule genes cap8E and tts control phase variation in Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes 8 and 37. Microbiology 149:497–504
Townsend KM, Boyce JD, Chung JY, Frost AJ, Adler B (2001) Genetic organization of Pasteurella multocida cap loci and development of a multiplex capsular PCR typing system. J Clin Microbiol 39:924–929
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Shah, R., Amaresan, N., Dwivedi, M.K. (2022). Assessment of Capsule Formation. In: Dwivedi, M.K., Amaresan, N., Sankaranarayanan, A., Begum, R. (eds) Biosafety Assessment of Probiotic Potential. Methods and Protocols in Food Science . Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2509-5_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2509-5_17
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-2508-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-2509-5
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols