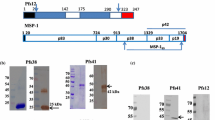
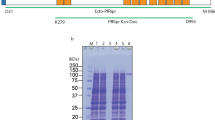
Abstract
Identification of P. falciparum infected erythrocyte surface ligands (such as PfEMP1) matched with the host receptors they interact with, as well as identification of PfEMP1 domains that are targets of protective immunity, are important for understanding of the pathophysiology of severe malaria (SM) and for design of novel vaccine candidates. In addition, identification of small-molecule drugs that can prevent or reverse receptor-ligand domain interactions could provide new tools for adjunctive therapy in SM. This protocol describes how to prepare functionally intact PfEMP1 proteins in mammalian cells (COS-7) and immobilize them on the surface of BioPlex beads. Furthermore, the protocol described how to identify PfEMP1 constructs that bind to specific host receptors or to immunoglobulins (IgG, IgM, etc.), and how to measure inhibition of the receptor binding to PfEMP1 constructs by small-molecule compounds or serum/plasma.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jensen AR, Adams Y, Hviid L (2020) Cerebral Plasmodium falciparum malaria: the role of PfEMP1 in its pathogenesis and immunity, and PfEMP1-based vaccines to prevent it. Immunol Rev 293(1):230–252. https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.12807
Wahlgren M, Goel S, Akhouri RR (2017) Variant surface antigens of Plasmodium falciparum and their roles in severe malaria. Nat Rev Microbiol 15(8):479–491. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2017.47
Khunrae P, Higgins MK (2010) Structural insights into chondroitin sulfate binding in pregnancy-associated malaria. Biochem Soc Trans 38(5):1337–1341
Chesnokov O, Merritt J, Tcherniuk SO, Milman N, Oleinikov AV (2018) Plasmodium falciparum infected erythrocytes can bind to host receptors integrins alphaVbeta3 and alphaVbeta6 through DBLdelta1_D4 domain of PFL2665c PfEMP1 protein. Sci Rep 8(1):17871. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-36071-2
Turner GD, Morrison H, Jones M, Davis TM, Looareesuwan S, Buley ID, Gatter KC, Newbold CI, Pukritayakamee S, Nagachinta B et al (1994) An immunohistochemical study of the pathology of fatal malaria. Evidence for widespread endothelial activation and a potential role for intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in cerebral sequestration. Am J Pathol 145(5):1057–1069
Lennartz F, Adams Y, Bengtsson A, Olsen RW, Turner L, Ndam NT, Ecklu-Mensah G, Moussiliou A, Ofori MF, Gamain B, Lusingu JP, Petersen JE, Wang CW, Nunes-Silva S, Jespersen JS, Lau CK, Theander TG, Lavstsen T, Hviid L, Higgins MK, Jensen AT (2017) Structure-guided identification of a family of dual receptor-binding PfEMP1 that is associated with cerebral malaria. Cell Host Microbe 21(3):403–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2017.02.009
Bull PC, Abdi AI (2016) The role of PfEMP1 as targets of naturally acquired immunity to childhood malaria: prospects for a vaccine. Parasitology 143(2):171–186. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182015001274
Fried M, Nosten F, Brockman A, Brabin BJ, Duffy PE (1998) Maternal antibodies block malaria. Nature 395(6705):851–852
Fried M, Duffy PE (2015) Designing a VAR2CSA-based vaccine to prevent placental malaria. Vaccine 33(52):7483–7488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.10.011
Gullingsrud J, Milman N, Saveria T, Chesnokov O, Williamson K, Srivastava A, Gamain B, Duffy PE, Oleinikov AV (2015) High throughput screening platform identifies small molecules that prevent sequestration of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. J Infect Dis 211(7):1134–1143
Hughes KR, Biagini GA, Craig AG (2010) Continued cytoadherence of Plasmodium falciparum infected red blood cells after antimalarial treatment. Mol Biochem Parasitol 169(2):71–78. Epub 2009 Oct 2001
Chesnokov O, Visitdesotrakul P, Kalani K, Nefzi A, Oleinikov AV (2021) Small molecule compounds identified from mixture-based library inhibit binding between Plasmodium falciparum infected erythrocytes and endothelial receptor ICAM-1. Int J Mol Sci 22(11):5659. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115659
Oleinikov AV, Rossnagle E, Francis S, Mutabingwa TK, Fried M, Duffy PE (2007) Effects of sex, parity, and sequence variation on seroreactivity to candidate pregnancy malaria vaccine antigens. J Infect Dis 196(1):155–164. Epub 2007 May 2023
Oleinikov AV, Amos E, Frye IT, Rossnagle E, Mutabingwa TK, Fried M, Duffy PE (2009) High throughput functional assays of the variant antigen PfEMP1 reveal a single domain in the 3D7 Plasmodium falciparum genome that binds ICAM1 with high affinity and is targeted by naturally acquired neutralizing antibodies. PLoS Pathog 5(4):e1000386. Epub 1002009 Apr 1000317
Oleinikov AV, Voronkova VV, Frye IT, Amos E, Morrison R, Fried M, Duffy PE (2012) A plasma survey using 38 PfEMP1 domains reveals frequent recognition of the Plasmodium falciparum antigen VAR2CSA among young Tanzanian children. PLoS One 7(1):e31011. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0031011
Gullingsrud J, Saveria T, Amos E, Duffy PE, Oleinikov AV (2013) Structure-function-immunogenicity studies of PfEMP1 domain DBL2betaPF11_0521, a malaria parasite ligand for ICAM-1. PLoS One 8(4):e61323
Quintana MDP, Ecklu-Mensah G, Tcherniuk SO, Ditlev SB, Oleinikov AV, Hviid L, Lopez-Perez M (2019) Comprehensive analysis of Fc-mediated IgM binding to the Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1 family in three parasite clones. Sci Rep 9(1):6050. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-42585-0
Raj DK, Das Mohapatra A, Jnawali A, Zuromski J, Jha A, Cham-Kpu G, Sherman B, Rudlaff RM, Nixon CE, Hilton N, Oleinikov AV, Chesnokov O, Merritt J, Pond-Tor S, Burns L, Jolly G, Ben Mamoun C, Kabyemela E, Muehlenbachs A, Lambert L, Orr-Gonzalez S, Gnädig NF, Fidock DA, Park S, Dvorin JD, Pardi N, Weissman D, Mui BL, Tam YK, Friedman JF, Fried M, Duffy PE, Kurtis JD (2020) Anti-PfGARP activates programmed cell death of parasites and reduces severe malaria. Nature 582(7810):104–108. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2220-1
Drew DE, von Heijne G, Nordlund P, de Gier JW (2001) Green fluorescent protein as an indicator to monitor membrane protein overexpression in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett 507(2):220–224
Acknowledgments
I am truly thankful to a number of people, who contributed hands-on to the development, testing, and using these protocols, these are Eddy Rossnagle, Emily Amos, Tyler I. Frey, Valentina Voronkova, Tracy Saveria, Justin Gullingsrud, Olga Chesnokov, and Sergey O. Tcherniuk. I especially grateful to Emily Amos and Justin Gullingsrud who prepared a number of detailed notes for the lab protocols that I have used in preparation of this chapter. I am also thankful to Jonathan Kurtis, who convinced me long time ago to switch to BioPlex protein array system from a planar format, and to Patrick Duffy for his constant support (intellectual and financial) of the development of this functional protein array system for studies of surface antigens of malarial parasites.
Funding was provided by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (grants 29202 and 1634); NIH (grants 1R21AI064503, 1R56AI083668, 1R01AI092120, 1R21AI137721), and Florida Atlantic University start-up fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Oleinikov, A.V. (2022). High-Throughput BioPlex Assay for the Study of Functionally Active Plasmodium Falciparum Antigens That Are Expressed on the Surface of Infected Erythrocytes. In: Jensen, A.T.R., Hviid, L. (eds) Malaria Immunology. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2470. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2189-9_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2189-9_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-2188-2
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-2189-9
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols