Abstract
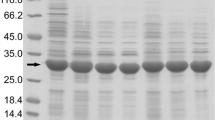
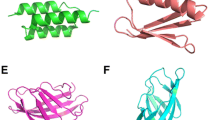
Recombinant expression of proteins in the periplasm of E. coli is frequently used for proteins containing disulfide bonds that are essential for protein folding and activity, as the cytosol of E. coli constitutes a reducing environment. The periplasm in contrast is an oxidative environment which supports proper protein folding. However, yields can be limited compared with cytoplasmic expression, and protocols must be adjusted to avoid overloading the periplasmic transportation machinery. Another less-appreciated issue with periplasmic expression is the potential generation of unwanted N-terminal cleavage products, a persistent issue which we encountered when expressing the disulfide bond containing extracellular regions of several Helicobacter pylori adhesins (BabA, BabB, BabC, and LabA) in the periplasm of E. coli XL10 GOLD, a strain traditionally not used for proteins expression. Here, we describe how introducing a C-terminal hexa-lysine (6 K) tag enhanced solubility and protected BabA from N-terminal proteolytic degradation (BabA), enabling crystallization and subsequent X-ray structural analysis. However. the same strategy had no advantageous effect for LabA, which using this protocol could be retrieved from the periplasm in relatively high yields (20–40 mg/L).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thornton JM (1981) Disulphide bridges in globular proteins. J Mol Biol 151:261–287
Lobstein J, Emrich CA, Jeans C et al (2012) SHuffle, a novel Escherichia coli protein expression strain capable of correctly folding disulfide bonded proteins in its cytoplasm. Microb Cell Fact 11:56
Gaciarz A, Khatri NK, Velez-Suberbie ML et al (2017) Efficient soluble expression of disulfide bonded proteins in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli in fed-batch fermentations on chemically defined minimal media. Microb Cell Fact 16:108
Berkmen M (2012) Production of disulfide-bonded proteins in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 82:240–251
de Marco A (2009) Strategies for successful recombinant expression of disulfide bond-dependent proteins in Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Fact 8:26
Merdanovic M, Clausen T, Kaiser M et al (2011) Protein quality control in the bacterial periplasm. Annu Rev Microbiol 65:149–168
Kadokura H, Tian H, Zander T et al (2004) Snapshots of DsbA in action: detection of proteins in the process of oxidative folding. Science 303:534–537
Berkmen M, Boyd D, Beckwith J (2005) The nonconsecutive disulfide bond of Escherichia coli phytase (AppA) renders it dependent on the protein-disulfide isomerase, DsbC. J Biol Chem 280:11387–11394
Messens J, Collet JF, Van Belle K et al (2007) The oxidase DsbA folds a protein with a nonconsecutive disulfide. J Biol Chem 282:31302–31307
Lei SP, Lin HC, Wang SS et al (1987) Characterization of the Erwinia carotovora pelB gene and its product pectate lyase. J Bacteriol 169:4379–4383
Singh P, Sharma L, Kulothungan SR et al (2013) Effect of signal peptide on stability and folding of Escherichia coli Thioredoxin. PLoS One 8:e63442
Auclair SM, Bhanu MK, Kendall DA (2012) Signal peptidase I: cleaving the way to mature proteins. Protein Sci 21:13–25
Graham LL, Beveridge TJ, Nanninga N (1991) Periplasmic space and the concept of the periplasm. Trends Biochem Sci 16:328–329
Schlegel S, Rujas E, Ytterberg AJ et al (2013) Optimizing heterologous protein production in the periplasm of E. coli by regulating gene expression levels. Microb Cell Fact 12:24
Paraskevopoulou V, Falcone F (2018) Polyionic tags as enhancers of protein solubility in recombinant protein expression. Microorganisms 6:47
Hage N, Renshaw JG, Winkler GS et al (2015) Improved expression and purification of the Helicobacter pylori adhesin BabA through the incorporation of a hexa-lysine tag. Protein Expr Purif 106:25–30
Paraskevopoulou V, Artiaga VG, Rowlinson R et al (2019) Introduction of a C-terminal hexa-lysine tag increases thermal stability of the LacDiNac binding adhesin (LabA) exodomain from Helicobacter pylori. Protein Expr Purif 163:105446
Hage N, Howard T, Phillips C et al (2015) Molecular basis of blood group antigen recognition by the Helicobacter pylori adhesin BabA. Sci Adv 1(e1500315):14
Moonens K, Gideonsson P, Subedi S et al (2016) Structural insights into polymorphic ABO glycan binding by Helicobacter pylori. Cell Host Microbe 19:55–66
Bertani G (1951) Studies on lysogenesis. I. The mode of phage liberation by lysogenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 62:293–300
Miller JH, Miller JB (1972) Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Lennox ES (1955) Transduction of linked genetic characters of the host by bacteriophage P1. Virology 1:190–206
Gibson DG, Young L, Chuang RY et al (2009) Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nat Methods 6:343–345
Yallapragada VVB, Gowda U, Wong D et al (2019) ODX: a fitness tracker-based device for continuous bacterial growth monitoring. Anal Chem 91:12329–12335
Acknowledgments
Work leading to the protocols described in this chapter was funded by the EPSRC (Grants EP/I01375X/1 and EP/L01646X) and AstraZeneca R&D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Paraskevopoulou, V., Alissa, M., Hage, N., Falcone, F.H. (2022). Introduction of a Hexalysine (6 K) Tag Can Protect from N-Terminal Cleavage and Increase Yield of Recombinant Proteins Expressed in the Periplasm of E. coli. In: Garcia Fruitós, E., Arís Giralt, A. (eds) Insoluble Proteins. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2406. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1859-2_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1859-2_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1858-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1859-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols