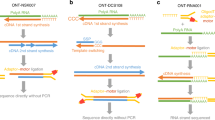
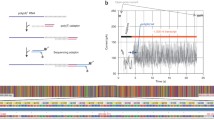
Abstract
The recent advent of Nanopore sequencing allows for the sequencing of full-length RNA or cDNA molecules. This new type of data introduces new challenges from the computational point of view, and requires new software as well as dedicated analysis pipelines. In this chapter, we guide the reader through the typical analysis steps required to process the raw data produced by the instrument into a table of counts suitable for downstream analyses. We first describe the procedure to convert raw direct RNA-Seq and cDNA-Seq data into sequences in fastq format. We then outline how to perform quality control and filtering steps and how to map the filtered long reads to a reference transcriptome or genome.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garalde DR, Snell EA, Jachimowicz D et al (2018) Highly parallel direct RNA sequencing on an array of nanopores. Nat Methods 15:201–206. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4577
Leonardi T (2019) Bedparse: feature extraction from BED files. J Open Source Softw 4:1228. https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.01228
Leger A, Leonardi T (2019) pycoQC, interactive quality control for Oxford Nanopore Sequencing. J Open Source Softw 4:1236. https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.01236
Quinlan AR (2014) BEDTools: the Swiss-Army tool for genome feature analysis: BEDTools: the Swiss-Army tool for genome feature analysis. Curr Protoc Bioinforma 47:11.12.1–11.12.34. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471250953.bi1112s47
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A et al (2009) The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25:2078–2079. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Li H (2018) Minimap2: pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 34:3094–3100. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty191
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Leonardi, T., Leger, A. (2021). Nanopore RNA Sequencing Analysis. In: Picardi, E. (eds) RNA Bioinformatics. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2284. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1307-8_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1307-8_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1306-1
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1307-8
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols