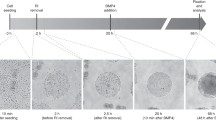
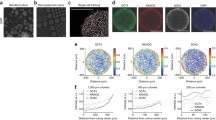
Abstract
In the developing mammalian embryo, intercellular signaling allows cells to self-organize to create spatial patterns of different cell fates. This process is challenging to study because of the difficulty of observing or manipulating embryos on the spatial and temporal scales required. In vitro models can provide a complement to in vivo systems for addressing these issues. These models are also the only windows we have into early human development. Here we provide protocols for two systems based on differentiating human pluripotent stem cells in micropatterned colonies on defined size and shape. The first model replicates the patterning of the germ layers at gastrulation, while the second replicates the medial-lateral patterning of the ectoderm. These systems allow study of how signaling underlies self-organized patterning at stages of development which are otherwise inaccessible.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Théry M (2010) Micropatterning as a tool to decipher cell morphogenesis and functions. J Cell Sci 123:4201–4213
Warmflash A, Sorre B, Etoc F et al (2014) A method to recapitulate early embryonic spatial patterning in human embryonic stem cells. Nat Methods 11:847–854. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3016
Britton G, Heemskerk I, Hodge R et al (2019) A novel self-organizing embryonic stem cell system reveals signaling logic underlying the patterning of human ectoderm. Development 146(20):dev179093. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.179093
Chhabra S, Liu L, Goh R et al (2019) Dissecting the dynamics of signaling events in the BMP, WNT, and NODAL cascade during self-organized fate patterning in human gastruloids. PLoS Biol 17:e3000498. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000498
Tewary M, Ostblom J, Prochazka L et al (2017) A stepwise model of reaction-diffusion and positional information governs self-organized human peri-gastrulation-like patterning. Development 144:4298–4312. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.149658
Manfrin A, Tabata Y, Paquet ER et al (2019) Engineered signaling centers for the spatially controlled patterning of human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Methods 16:640–648. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-019-0455-2
Morgani SM, Metzger JJ, Nichols J et al (2018) Micropattern differentiation of mouse pluripotent stem cells recapitulates embryo regionalized cell fate patterning. elife 7:e32839. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.32839
Martyn I, Kanno TY, Ruzo A et al (2018) Self-organization of a human organizer by combined Wnt and Nodal signalling. Nature 558:132–135. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0150-y
Arnold SJ, Robertson EJ (2009) Making a commitment: cell lineage allocation and axis patterning in the early mouse embryo. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:91–103. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2618
Heemskerk I, Burt K, Miller M et al (2019) Rapid changes in morphogen concentration control self-organized patterning in human embryonic stem cells. elife 8:e40526. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.40526.001
Deglincerti A, Etoc F, Guerra MC et al (2016) Self-organization of human embryonic stem cells on micropatterns. Nat Protoc 11:2223–2232. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2016.131
Acknowledgments
George Britton, Sapna Chhabra, and Joseph Massey contributed equally to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Britton, G., Chhabra, S., Massey, J., Warmflash, A. (2021). Fate-Patterning of 2D Gastruloids and Ectodermal Colonies Using Micropatterned Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. In: Ebrahimkhani, M.R., Hislop, J. (eds) Programmed Morphogenesis. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2258. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1174-6_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1174-6_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1173-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1174-6
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols