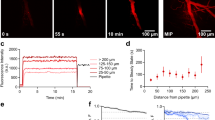
Abstract
We report here the method of visualization of brain microcirculation and assessment of blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability changes using the miniature integrated fluorescence microscope (i.e., miniscope) technology in awake, freely moving rats. The imaging cannula is implanted in the brain area of interest of anesthetized adult rats. After recovery and habituation, sodium fluorescein, a low-molecular-weight tracer, is injected i.v. Fluorescence intensity in the vicinity of microvessels, as an indicator of BBB permeability, is then recorded in vivo via the miniscope for extended periods of time. The method can be used to assess the changes in BBB permeability produced by pharmacologic agents; in this case, the drug of interest is administered after sodium fluorescein. An increase in the sodium fluorescein extravasation in brain microcirculation demonstrates an increase in BBB permeability. The method described here allows a high-resolution visualization of real-time changes in BBB permeability in awake, freely moving rats.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott NJ, Patabendige AA, Dolman DE, Yusof SR, Begley DJ (2010) Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol Dis 37(1):13–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2009.07.030
Sweeney MD, Zhao Z, Montagne A, Nelson AR, Zlokovic BV (2019) Blood-brain barrier: from physiology to disease and back. Physiol Rev 99(1):21–78. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00050.2017
Deli MA, Abraham CS, Kataoka Y, Niwa M (2005) Permeability studies on in vitro blood-brain barrier models: physiology, pathology, and pharmacology. Cell Mol Neurobiol 25(1):59–127
Nag S (2003) Blood-brain barrier permeability using tracers and immunohistochemistry. Methods Mol Med 89:133–144. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-419-0:133
Wunder A, Schoknecht K, Stanimirovic DB, Prager O, Chassidim Y (2012) Imaging blood-brain barrier dysfunction in animal disease models. Epilepsia 53(Suppl 6):14–21. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2012.03698.x
Yen LF, Wei VC, Kuo EY, Lai TW (2013) Distinct patterns of cerebral extravasation by Evans blue and sodium fluorescein in rats. PLoS One 8(7):e68595. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068595
Brailoiu E, Barlow CL, Ramirez SH, Abood ME, Brailoiu GC (2018) Effects of platelet-activating factor on brain microvascular endothelial cells. Neuroscience 377:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.02.039
Leo LM, Familusi B, Hoang M, Smith R, Lindenau K, Sporici KT, Brailoiu E, Abood ME, Brailoiu GC (2019) GPR55-mediated effects on brain microvascular endothelial cells and the blood-brain barrier. Neuroscience 414:88–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.06.039
Nishimura N, Schaffer CB, Friedman B, Tsai PS, Lyden PD, Kleinfeld D (2006) Targeted insult to subsurface cortical blood vessels using ultrashort laser pulses: three models of stroke. Nat Methods 3(2):99–108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth844
Prager O, Chassidim Y, Klein C, Levi H, Shelef I, Friedman A (2010) Dynamic in vivo imaging of cerebral blood flow and blood-brain barrier permeability. NeuroImage 49(1):337–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.08.009
Zhang S, Murphy TH (2007) Imaging the impact of cortical microcirculation on synaptic structure and sensory-evoked hemodynamic responses in vivo. PLoS Biol 5(5):e119. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0050119
Takano T, Han X, Deane R, Zlokovic B, Nedergaard M (2007) Two-photon imaging of astrocytic Ca2+ signaling and the microvasculature in experimental mice models of Alzheimer's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1097:40–50. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1379.004
Abulrob A, Brunette E, Slinn J, Baumann E, Stanimirovic D (2008) Dynamic analysis of the blood-brain barrier disruption in experimental stroke using time domain in vivo fluorescence imaging. Mol Imaging 7(6):248–262
Piper S, Bahmani P, Klohs J, Bourayou R, Brunecker P, Muller J, Harhausen D, Lindauer U, Dirnagl U, Steinbrink J, Wunder A (2010) Non-invasive surface-stripping for epifluorescence small animal imaging. Biomed Opt Express 1(1):97–105. https://doi.org/10.1364/BOE.1.000097
Rowland DJ, Cherry SR (2008) Small-animal preclinical nuclear medicine instrumentation and methodology. Semin Nucl Med 38(3):209–222. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2008.01.004
Nagaraja TN, Ewing JR, Karki K, Jacobs PE, Divine GW, Fenstermacher JD, Patlak CS, Knight RA (2011) MRI and quantitative autoradiographic studies following bolus injections of unlabeled and (14)C-labeled gadolinium-diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid in a rat model of stroke yield similar distribution volumes and blood-to-brain influx rate constants. NMR Biomed 24(5):547–558. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.1625
Jelescu IO, Leppert IR, Narayanan S, Araujo D, Arnold DL, Pike GB (2011) Dual-temporal resolution dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI protocol for blood-brain barrier permeability measurement in enhancing multiple sclerosis lesions. Journal of magnetic resonance imaging 33(6):1291–1300. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.22565
Sharma HS, Muresanu DF, Nozari A, Castellani RJ, Dey PK, Wiklund L, Sharma A (2019) Anesthetics influence concussive head injury induced blood-brain barrier breakdown, brain edema formation, cerebral blood flow, serotonin levels, brain pathology and functional outcome. Int Rev Neurobiol 146:45–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.irn.2019.06.006
Barr JL, Brailoiu GC, Abood ME, Rawls SM, Unterwald EM, Brailoiu E (2020) Acute cocaine administration alters permeability of blood-brain barrier in freely-moving rats-evidence using miniaturized fluorescence microscopy. Drug Alcohol Depend 206:107637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2019.107637
Ghosh KK, Burns LD, Cocker ED, Nimmerjahn A, Ziv Y, Gamal AE, Schnitzer MJ (2011) Miniaturized integration of a fluorescence microscope. Nat Methods 8(10):871–878. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1694
Paxinos G, Watson C (2013) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 7th edn. Academic Press
Sharma HS, Muresanu D, Sharma A, Patnaik R (2009) Cocaine-induced breakdown of the blood-brain barrier and neurotoxicity. Int Rev Neurobiol 88:297–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0074-7742(09)88011-2
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health grant P30DA013429.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic Supplementary Material
(MOV 59117 kb)
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Barr, J.L., Brailoiu, G.C., Unterwald, E.M., Brailoiu, E. (2021). Assessment of Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability Using Miniaturized Fluorescence Microscopy in Freely Moving Rats. In: Turksen, K. (eds) Permeability Barrier. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2367. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/7651_2020_315
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/7651_2020_315
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1672-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1673-4
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols