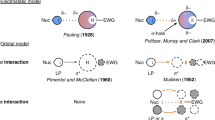
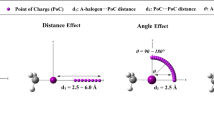
Abstract
Because of its expected applicability for modulation of molecular recognition phenomena in chemistry and biology, halogen bonding has lately attracted rapidly increasing interest. As most of these processes proceed in solution, the understanding of the influence of solvents on the interaction is of utmost importance. In addition, solution studies provide fundamental insights into the nature of halogen bonding, including, for example, the relative importance of charge transfer, dispersion, and electrostatics forces. Herein, a selection of halogen bonding literature is reviewed with the discussion focusing on the solvent effect and the electronic characteristics of halogen bonded complexes. Hence, charged and neutral systems together with two- and three-center bonds are presented in separate sub-sections. Solvent polarity is shown to have a slight stabilizing effect on neutral, two-center halogen bonds while strongly destabilizes charged, two-center complexes. It does not greatly influence the geometry of three-center halogen bonds, even though polar solvents facilitate dissociation of the counter-ion of charged three-center bonds. The charged three-center bonds are strengthened by increased environment polarity. Solvents possessing hydrogen bond donor functionalities efficiently destabilize all types of halogen bonds, primarily because of halogen vs hydrogen bond competition. A purely electrostatic model is insufficient for the description of halogen bonds in polar systems whereas it may give reasonable correlation to experimental data obtained in noninteracting, apolar solvents. Whereas dispersion plays a significant role for neutral, two-center halogen bonds, charged halogen bond complexes possess a significant charge transfer characteristic.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guthrie F (1863) On the iodide of iodammonium. J Chem Soc 16:239–244
Lachman A (1903) A probable cause of the different colors of iodine solutions. J Am Chem Soc 25:50–55
Kleinberg J, Davidson AW (1948) The nature of iodine solutions. Chem Rev 42:601–609
Walker OJ (1935) Absorption spectra of iodine solutions and the influence of the solvent. Trans Faraday Soc 31:1432–1438
Benesi HA, Hildebrand JH (1949) A spectrophotometric investigation of the interaction of iodine with aromatic hydrocarbons. J Am Chem Soc 71:2703–2707
Mulliken RS (1950) Structures of complexes formed by halogen molecules with aromatic and with oxygenated solvents. J Am Chem Soc 72:600–608
Hassel O, Hvoslef J (1954) The structure of bromine 1,4-dioxanate. Acta Chem Scand 8:873
Hassel O (1970) Structural aspects of interatomic charge transfer bonding. Science 170:497–502
Bertran JF, Rodriguez M (1979) Detection of halogen bond formation by correlation of proton solvent shifts. 1. Haloforms in normal-electron donor solvents. Org Magn Resonance 12:92–94
Blackstock SC, Lorand JP, Kochi JK (1987) Charge transfer interactions of amines with tetrahalomethanes - X-ray crystal-structures of the donor-acceptor complexes of quinuclidine and diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane with carbon tetrabromide. J Org Chem 52:1451–1460
Legon AC (1999) Prereactive complexes of dihalogens XY with Lewis bases B in the gas phase: a systematic case for the halogen analogue B–XY of the hydrogen bond B–HX. Angew Chem Int Ed 38:2687–2714
Metrangolo P, Neukirch H, Pilati T et al (2005) Halogen bonding based recognition processes: a world parallel to hydrogen bonding. Acc Chem Res 38:386–395
Erdelyi M (2012) Halogen bonding in solution. Chem Soc Rev 41:3547–3557
Beale TM, Chudzinski MG, Sarwar MG et al (2013) Halogen bonding in solution: thermodynamics and applications. Chem Soc Rev 42:1667–1680
Bertran JF, Rodriguez M (1981) On the nature of haloform-aromatic complexes. Org Magn Resonance 16:79–81
Bertran JF, Rodriguez M (1980) Detection of halogen bond formation by correlation of proton solvent shifts. 2. Methylene halides in N-electron donor solvents. Org Magn Resonance 14:244–246
Metrangolo P, Panzeri W, Recupero F et al (2002) Perfluorocarbon-hydrocarbon self-assembly – Part 16. 19F NMR study of the halogen bonding between halo-perfluorocarbons and heteroatom containing hydrocarbons. J Fluor Chem 114:27–33
McKinney WJ, Popov AI (1969) Studies on chemistry of halogens and of polyhalides. 30. Influence of solvent properties on formation of pyridine-iodine charge transfer complexes. J Am Chem Soc 91:5215–5218
Bhaskar KR, Singh S (1967) Spectroscopic studies of N-donor-sigma-acceptor systems – pyridines. Spectrochim Acta A 23:1155–1159
Laurence C, Queigneccabanetos M, Wojtkowiak B (1983) 1-Iodoacetylenes. 4. Structure-reactivity relationships for the complexation of substituted 1-iodoacetylenes with Lewis-bases. Can J Chem 61:135–138
Laurence C, Queigneccabanetos M, Dziembowska T et al (1981) 1-Iodoacetylenes. 1. Spectroscopic evidence of their complexes with Lewis-bases - a spectroscopic scale of soft basicity. J Am Chem Soc 103:2567–2573
Laurence C, Queigneccabanetos M, Wojtkowiak B (1982) 1-Iodoacetylenes. 2. Formation-constants of their complexes with Lewis-bases. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 2:1605–1610
Webb JA, Klijn JE, Hill PA et al (2004) Experimental studies of the 13C NMR of iodoalkynes in Lewis-basic solvents. J Org Chem 69:660–664
Cabot R, Hunter CA (2009) Non-covalent interactions between iodo-perfluorocarbons and hydrogen bond acceptors. Chem Commun 2005–2007
Sarwar MG, Dragisic B, Salsberg LJ et al (2010) Thermodynamics of halogen bonding in solution: substituent, structural, and solvent effects. J Am Chem Soc 132:1646–1653
Hunter CA (2004) Quantifying intermolecular interactions: guidelines for the molecular recognition toolbox. Angew Chem Int Ed 43:5310–5324
Dimroth K, Bohlmann F, Reichard C et al (1963) Über Pyridinium-N-phenol-betaine und ihre Verwendung zur Charakterisierung der polarität von Losungsmitteln. Liebigs Ann Chem 661:1–37
Kamlet MJ, Abboud JL, Taft RW (1977) Solvatochromic comparison method. 6. π* scale of solvent polarities. J Am Chem Soc 99:6027–6038
Dong DC, Winnik MA (1982) The Py scale of solvent polarities - solvent effects on the vibronic fine-structure of pyrene fluorescence and empirical correlations with E T-value and Y-value. Photochem Photobiol 35:17–21
Li QZ, Li R, Zhou ZJ et al (2012) S…X halogen bonds and H …X hydrogen bonds in H2CS-XY (XY=FF, ClF, ClCl, BrF, BrCl, and BrBr) complexes: cooperativity and solvent effect. J Chem Phys 136:014302
Lu YX, Li HY, Zhu X et al (2011) How does halogen bonding behave in solution? A theoretical study using implicit solvation model. J Phys Chem A 115:4467–4475
Lu YX, Li HY, Zhu X et al (2012) Effects of solvent on weak halogen bonds: density functional theory calculations. Int J Quantum Chem 112:1421–1430
Hawthorne B, Fan-Hagenstein H, Wood ER et al (2013) Study of the halogen bonding between pyridine and perfluoroalkyl iodide in solution phase using the combination of FTIR and 19F NMR. Int J Spectrosc 2013:216518
Libri S, Jasim NA, Perutz RN et al (2008) Metal fluorides form strong hydrogen bonds and halogen bonds: measuring interaction enthalpies and entropies in solution. J Am Chem Soc 130:7842–7844
Forni A, Rendine S, Pieraccini S et al (2012) Solvent effect on halogen bonding: the case of the I…O interaction. J Mol Graph Model 38:31–39
Ma N, Zhang Y, Ji B et al (2012) Structural competition between halogen bonds and lone-pair…pi interactions in solution. Chemphyschem 13:1411–1414
Li QZ, Xu XS, Liu T et al (2010) Competition between hydrogen bond and halogen bond in complexes of formaldehyde with hypohalous acids. Phys Chem Chem Phys 12:6837–6843
Zhang Y, Ji BM, Tian AM et al (2012) Communication: competition between π…π interaction and halogen bond in solution: a combined 13C NMR and density functional theory study. J Chem Phys 136:141101
Zou WS, Han J, Jin WJ (2009) Concentration-dependent Br…O halogen bonding between carbon tetrabromide and oxygen-containing organic solvents. J Phys Chem A 113:10125–10132
Sarwar MG, Dragisic B, Sagoo S et al (2010) A tridentate halogen-bonding receptor for tight binding of halide anions. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:1674–1677
Kilah NL, Wise MD, Serpell CJ et al (2010) Enhancement of anion recognition exhibited by a halogen-bonding rotaxane host system. J Am Chem Soc 132:11893–11895
Sarwar MG, Dragisic B, Dimitrijevic E et al (2013) Halogen bonding between anions and iodoperfluoroorganics: solution-phase thermodynamics and multidentate-receptor design. Chem Eur J 19:2050–2058
Walter SM, Kniep F, Rout L et al (2012) Isothermal calorimetric titrations on charge-assisted halogen bonds: role of entropy, counterions, solvent, and temperature. J Am Chem Soc 134:8507–8512
Parra RD (2012) Dimers and trimers of formamidine and its mono-halogenated analogues HN=CHNHX, (X=H, Cl, Br, or I): a comparative study of resonance-assisted hydrogen and halogen bonds. Comput Theor Chem 998:183–192
Waentig P (1910) On the state of dissolved iodine. Z Phys Chem 68:513–571
Popov AI, Rygg RH (1957) Studies on the chemistry of halogens and of polyhalides. XI. Molecular complexes of pyridine, 2-picoline and 2,6-lutidine with iodine and iodine halides. J Am Chem Soc 79:4622–4625
Haque I, Wood JL (1967) The infra-red spectra of pyridine-halogen complexes. Spectrochim Acta A 23:959–967
Tassaing T, Besnard M (1997) Ionization reaction in iodine/pyridine solutions: what can we learn from conductivity measurements, far-infrared spectroscopy, and Raman scattering? J Phys Chem A 101:2803–2808
Tassaing T, Besnard M (1997) Vibrational spectroscopic studies of the chemical dynamics in charge transfer complexeses of the type iodine-pyridine 1. Experimental results. Mol Phys 92:271–280
Zingaro RA, VanderWerf CA, Kleinberg J (1951) Evidence for the existence of unipositive iodine ion in solutions of iodine in pyridine. J Am Chem Soc 73:88–90
Reid C, Mulliken RS (1954) Molecular compounds and their spectra. IV. The pyridine-iodine system. J Am Chem Soc 76:3869–3874
Popov AI, Pflaum RT (1957) Studies on the chemistry of halogens and of polyhalides. X. The reactions of iodine monochloride with pyridine and with 2,2′-bipyridine. J Am Chem Soc 79:570–572
Creighton JA, Haque I, Wood JL (1966) The iododipyridinium ion. Chem Commun 229
Audrieth LF, Birr EJ (1933) Anomalous electrolytes. I. The electrical conductivity of solutions of iodine and cyanogen iodide in pyridine. J Am Chem Soc 55:668–673
Kleinberg J, Colton E, Sattizahn J et al (1953) The behavior of iodine species in pyridine and quinoline. J Am Chem Soc 75:442–445
Kortüm G, Wilski H (1953) Über die elektrische Leitfähigkeit von Jod-Pyridin-Lösungen. Z Phys Chem 202:35–55
Ginn SGW, Wood JL (1965) The structure of the triiodide ion. Chem Commun 262–263
Ginn SGW, Wood JL (1966) Intermolecular vibrations of charge transfer complexes. Trans Faraday Soc 62:777–787
Haque I, Wood JL (1967) The infra-red spectra of γ-picoline-halogen complexes. Spectrochim Acta A 23:2523–2533
Bell RP, Gelles E (1951) The halogen cations in aqueous solution. J Chem Soc 2734–2740
Larsen DW, Allred AL (1965) Halogen complexes. II. The types and mean lifetimes of complexes formed by iodine and 2,4,6-trimethylpyridine. J Am Chem Soc 87:1219–1226
Schuster II, Roberts JD (1979) Halogen complexes of pyridines: a proton and carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance study. J Org Chem 44:2658–2662
Carlsohn H (1932) Habilitationsschrift: Über eine neue Klasse von Verbindungen des positive Einwertigen Jod. Verlag von S. Hirzel, Liepzig
Carlsohn H (1935) Beiträge zur Chemie des Broms, I. Mitteil.: Darstellung von Brom (I)-dipyridin-perchlorat und Brom (I)-dipyridin-nitrat. Chem Ber 68B:2209–2211
Uschakow MI, Tchistow WO (1935) Über salzartige Eigenschaften der Halogene. Einwerkungsprodukte von Brom auf Silbersalze. Chem Ber 68B:824–830
Kleinberg J (1946) The positive character of the halogens. J Chem Educ 23:559–562
Zingaro RA, Goodrich JE, Keinberg J et al (1949) Reactions of the silver salts of carboxylic acids with iodine in the presence of some tertiary amines. J Am Chem Soc 71:575–576
Zingaro RA, Van der Werf CA, Kleinberg J (1950) Further observation on the preparation and reactions of positive iodine salts. J Am Chem Soc 72:5341–5342
Schmidt H, Meinert H (1959) Zur Darstellung von Salzen mit positiv einwertigen Halogen-Kationen. Angew Chem 71:126–127
Kleinberg J (1963) Unipositive halogen complexes. Inorg Synth 7:169–176
Hassel O, Hope H (1961) Structure of the solid compound formed by addition of two molecules of iodine to one molecule of pyridine. Acta Chem Scand 15:407–416
Haque I, Wood JL (1968) The vibrational spectra and structure of the bis(pyridine)iodine(I), bis(pyridine)bromine(I), bis(γ-picoline)iodine(I) and bis(γ-picoline)bromine(I) cations. J Mol Struct 2:217–238
Sabin JR (1971) A theoretical study of the bis(pyridine)iodine(I) cation. J Mol Struct 7:407–419
Carter S, Gray NAB, Wood JL (1971) The electronic spectra of the bis(pyridine)iodine(I) and related cations. J Mol Struct 7:481–485
Baruah SK (2004) Infrared studies of some sensitive vibrational modes of pyridines on complex formation with halogens and interhalogens. Asian J Chem 16:706–710
Okitsu T, Yumitate S, Sato K et al (2013) Substituent effect of bis(pyridines)iodonium complexes as iodinating reagents: control of the iodocyclization/oxidation process. Chem Eur J 19:4992–4996
Baruah SK, Baruah PK (2004) Studies of nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of positive halogen salts of pyridine and substituted pyridines. Asian J Chem 16:688–694
Perrin CL (2009) Symmetry of hydrogen bonds in solution. Pure Appl Chem 81:571–583
Perrin CL (2010) Are short, low-barrier hydrogen bonds unusually strong? Acc Chem Res 43:1550–1557
Carlsson A-CC, Gräfenstein J, Laurila JL et al (2012) Symmetry of [N-X-N]+ halogen bonds in solution. Chem Commun 48:1458–1460
Carlsson A-CC, Gräfenstein J, Budnjo A et al (2012) Symmetric halogen bonding is preferred in solution. J Am Chem Soc 134:5706–5715
Carlsson A-CC, Uhrbom M, Karim A et al (2013) Solvent effects on halogen bond symmetry. CrystEngComm 15:3087–3092
Saunders M, Jaffe MH, Vogel P (1971) A new method for measuring equilibrium deuterium isotope effects. Isomerization of 3-deuterio-2,3-dimethylbutyl-2-ium ion. J Am Chem Soc 93:2558–2559
Siehl H-U (1987) Isotope effects on NMR spectra of equilibrating systems. Adv Phys Org Chem 23:63–163
Georgiuo DC, Butler P, Browne EC et al (2013) On the bonding in bis-pyridine iodonium cations. Aust J Chem 66:1179–1188
Anderson GM, Winfield JM (1986) Preparation and properties of bis(acetonitrile)iodine(I) hexafluoromolybdate(V) and hexafluorouranate(V). J Chem Soc Dalton Trans 337–340
Tytko K-H, Schmeisser M (1973) Chemische Charakterisierung des [py2X]+-Ions (X=Br, J). Z Naturforsch B Chem Sci 28:731–735
Tornieporth-Oetting I, Klapötke T (1990) Die Reaktivität des I3 +-Kations gegenüber Ammoniak, Nitrilen und Pyridin. Z Anorg Allg Chem 586:93–98
Neverov AA, Xiaomei Feng H, Hamilton K et al (2003) Bis(pyridine)-based bromonium ions. Molecular structures of bis(2,4,6-collidine)bromonium perchlorate and bis(pyridine)bromonium triflate and the mechanism of the reactions of 1,2-bis(2′-pyridylethynyl)benzenebrominum triflate and bis(pyridine)bromonium triflate with acceptor olefins. J Org Chem 68:3802–3810
Barluenga J (1999) Transferring iodine: more than a simple functional group exchange in organic synthesis. Pure Appl Chem 71:431–436
Snyder SA, Treitler DS, Brucks AP (2011) Halonium-induced cyclization reactions. Aldrichim Acta 44:27–40
Uschakow MJ, Tschistow WO (1935) Über salzartige Eigenschaften der Halogene. Einwirkungsprodukte von Brom auf Silbersalze. Ber Deutsch Chem Ges A (68):824–830
Diner UE, Lown JW (1971) Addition of iodonium nitrate to unsaturated hydrocarbons. Can J Chem 49:403–415
Barluenga J, Gonzalez JM, Campos PJ et al (1985) I(Py)2BF4, a new reagent in organic-synthesis – general-method for the 1,2-iodofunctionalization of olefins. Angew Chem Int Ed 24:319–320
Lemieux RU, Morgan AR (1965) Synthesis of beta-D-glucopyranosyl 2-deoxy-alpha-D-arabino-hexopyranoside. Can J Chem 43:2190–2197
Simonot B, Rousseau G (1993) Preparation of 7-membered and medium-ring lactones by iodo lactonization. J Org Chem 58:4–5
Chalker JM, Thompson AL, Davis BG (2010) Safe and scalable preparation of Barluenga’s reagent. Org Synth 87:288
Barluenga J, González-Bobes F, Murguía MC et al (2004) Bis(pyridine)iodonium tetrafluoroborate (IPy2BF4): a versatile oxidizing reagent. Chem Eur J 10:4206–4213
Neverov AA, Brown RS (1998) Mechanistic evaluation of the transfer of Br+ from bis(sym-collidine)bromonium triflate to acceptor alkenes. J Org Chem 63:5977–5982
Cui X-L, Brown RS (2000) Mechanistic evaluation of the halocyclization of 4-penten-1-ol by some bis(2-substituted pyridine) and bis(2,6-disubstituted pyridine)bromonium triflates. J Org Chem 65:5653–5658
Grossman RB, Trupp RJ (1998) The first reagent-controlled asymmetric halolactonizations. Dihydroquinidine-halogen complexes as chiral sources of positive halogen ion. Can J Chem 76:1233–1237
Sabin JR (1972) Some calculations on lighter bis(pyridine)halogen(I) cations. J Mol Struct 11:33–55
Wolters LP, Bickelhaupt FM (2012) Halogen bonding versus hydrogen bonding: a molecular orbital perspective. ChemstryOpen 1:96–105
Bakshi PK, James MA, Cameron TS et al (1996) Polyhalide anions in crystals. 1. Triiodides of the Me4N+, Me4P+, quinuclidinium, 1-azoniapropellane, and 1,4-diazoniabicyclo[2.2.2]octane (DabcoH2 2+) cations, and 1,10-phenanthrolinium+ tribromide. Can J Chem 74:559–573
Robertson KN, Cameron TS, Knop O (1996) Polyhalide anions in crystals. 2. I3− asymmetry and N-H…I bonding: triiodides of the Me2NH2+, Ph2I+, tropanium, N, N, N′, N′-Me(4)-1,2-ethanediammonium, N, N, N′, N′-Me(4)-1,3-propanediammo-nium, N-Me-piperazinium2+, and N, N′-Me2-piperazinium2+ cations, and Me2NH2I. Can J Chem 74:1572–1591
Hayward GC, Hendra PJ (1967) Far infra-red and Raman spectra of trihalide ions IBr2 − and I3 −. Spectrochim Acta A 23:2309–2314
Person WB, Anderson GR, Fordemwalt JN et al (1961) Infrared and Raman spectra, force constants, and structures of some polyhalide ions - ICI2 −, ICI4 −, BrCl2 −, and Br3 −. J Chem Phys 35:908–914
Maki AG, Forneris R (1967) Infrared and Raman spectra of some trihalide ions - ICl2 −, IBr2 −, I3 −, I2Br− and BrICl−. Spectrochim Acta A 23:867–880
Pimentel GC (1951) The bonding of trihalide and bifluoride ions by the molecular orbital method. J Chem Phys 19:446–448
Gabes W, Gerding H (1972) Vibrational-spectra and structures of trihalide ions. J Mol Struct 14:267–279
Sasaki K, Aida K (1980) IR-spectra of charge transfer complexes between ICl, IBr and aminopyridines. J Inorg Nucl Chem 42:13–15
Kiefer W, Bernstei HJ (1972) UV-laser excited resonance Raman spectrum of I3 − ion. Chem Phys Lett 16:5–9
Kaya K, Mikami N, Ito M et al (1972) Resonance Raman effect of I3 − ion by ultraviolet laser excitation. Chem Phys Lett 16:151–153
Johnson AE, Myers AB (1995) Emission cross-sections and line-shapes for photodissociating triiodide in ethanol - experimental and computational studies. J Chem Phys 102:3519–3533
Johnson AE, Myers AB (1996) A comparison of time- and frequency-domain resonance Raman spectroscopy in triiodide. J Chem Phys 104:2497–2507
Johnson AE, Myers AB (1996) Solvent effects in the Raman spectra of the triiodide ion: observation of dynamic symmetry breaking and solvent degrees of freedom. J Phys Chem 100:7778–7788
Al-Hashimi NA (2004) Spectroscopic studies of the reaction of iodine with 2,3-diaminopyridine. Spectrochim Acta A 60:2181–2184
Margulis CJ, Coker DF, Lynden-Bell RM (2001) Symmetry breaking of the triiodide ion in acetonitrile solution. Chem Phys Lett 341:557–560
Sato H, Hirata F, Myers AB (1998) Theoretical study of the solvent effect on triiodide ion in solutions. J Phys Chem A 102:2065–2071
Zhang FS, Lynden-Bell RM (2003) Solvent-induced symmetry breaking. Phys Rev Lett 90:185505
Zhang FS, Lynden-Bell RM (2003) Temperature and solvent dependence of vibrational relaxation of triiodide: a simulation study. J Chem Phys 119:6119–6131
Zhang FS, Lynden-Bell RM (2005) Solvent-induced symmetry breaking: varying solvent strength. Phys Rev E 71:021502
Zhang FS, Lynden-Bell RM (2005) Interactions of triiodide cluster ion with solvents. Eur Phys J D 34:129–132
Karm A, Reitti M, Carlsson A-CC et al (2014) The nature of the [N-Cl-N]+ and [N-F-N]+ halogen bonds in solution. Chem Sci 5:3226–3233
Suzaki Y, Saito T, Ide T et al (2014) A rhomboid-shaped organic host molecule with small binding space. Unsymmetrical and symmetrical inclusion of halonium ions. Dalton Trans 43:6643–6649
Koskinen L, Hirva P, Kalenius E et al (2015) Halogen bonds with coordinative nature: halogen bonding in a S-I+-S iodonium complex. CrystEngComm 17:1231–1236
Hakkert SB, Erdelyi M (2015) Halogen bond symmetry: the N-X-N bond. J Phys Org Chem 28:226–233
Robinson SW, Mustoe CL, White NG et al (2015) Evidence for halogen bond covalency in acyclic and interlocked halogen-bonding receptor anion recognition. J Am Chem Soc 137:499–507
Jungbauer SH, Bulfield D, Kniep F et al (2014) Toward molecular recognition: three-point halogen bonding in the solid state and in solution. J Am Chem Soc 136:16740–16743
Lim JY, Beer PB (2015) Superior perrhenate anion recognition in water by a halogen bonding acyclic receptor. Chem Commun 51:3686–3688
Robertson CC, Perutz RN, Brammer L et al (2014) A solvent-resistant halogen bond. Chem Sci 5:4179–4183
Kodiah BN, Arto V, Sandip B, Fangfang P, Rissanen K (2015) Org Chem Frontiers doi:10.1039/C4QO00326H
Dumele O, Wu D, Trapp N, Goroff N, Diedrich F (2014) Halogen bonding of (iodoethynyl)benzene derivatives in solution. 16:4722–4725
Thorson RA, Woller GR, Driscoll ZL, Geiger BE, Moss CA, Schlapper AL, Speetzen ED, Bosch E, Erdelyi M, Bowling NP (2015) Intramolecular halogen bonding in solution: 15N, 13C and 19F NMR studies of temperature and solvent effects. doi:10.1002/ejoc.201403671
Vargas Jetzsch A (2015) Applications of halogen bonding in solution. Pure Appl Chem 87:15–41
Acknowledgments
The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Union Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007–2013) under grant agreement no. 259638, and from the Swedish Research Council (VR 2012–3819). Jenny Mattsson (University of Gothenburg) is gratefully acknowledged for linguistic improvement of the text.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Carlsson, AC.C., Veiga, A.X., Erdélyi, M. (2014). Halogen Bonding in Solution. In: Metrangolo, P., Resnati, G. (eds) Halogen Bonding II. Topics in Current Chemistry, vol 359. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/128_2014_607
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/128_2014_607
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-15731-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-15732-0
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)