Abstract
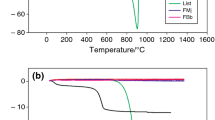
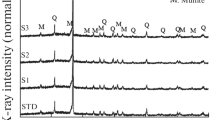
This study was aimed to investigate the key properties, mullite formation and glaze-body fit of sanitary ware bodies, by using pottery stone from Lampang, Thailand as a substitute for kaolin, feldspar, and silica. Seven samples of formulated bodies were prepared by wet milling, formed by plaster mold casting, and fired at 1175 °C, 1200 °C, and 1225 °C. Testings were carried out in accordance with ASTM C373-88, ASTM C326-09, ASTM C689-09, and ASTM C372-94. Phase analysis and microstructure of selected formulations were analyzed by using XRD and SEM. For the formulation having 37.7-20.7-41.6 of C-Q-F ratio and pottery stone in substitute for 100% silica, after firing at 1200 °C showed 9.27% total shrinkage, 0.17% water absorption, and 60 MPa flexure stress. The crystal structure resulted in higher amount of mullite. The linear thermal expansion and thermal expansion coefficient were lower to 0.34 and 7.07 × 10−6/°C, respectively. The difference of linear thermal expansion between the formulated body and commercial white-opaque glaze was − 0.02 at 500 °C. The shrinkage difference of body and glaze showed that the glaze-body fit was under slightly amount of compression. As a result, the formulation with the substitute for 100% silica could be vitrificated at lower temperature and indicated positive trends towards lower dunting during firing.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wattanasiriwech, D., Wattanasiriwech, S.: Fluxing action of illite and microcline in a triaxial porcelain body. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 31, 1371–1376 (2011)
Tuncel, D.Y., Özel, E.: Evaluation of pyroplastic deformation in sanitary ware porcelain bodies. Ceram. Int. 38, 1399–1407 (2012)
Njoya, D., Hajjaji, M., Baçaoui, A., Njopwouo, D.: Microstructural characterization and influence of manufacturing parameters on technological properties of vitreous ceramic materials. Mater. Charact. 61, 289–295 (2010)
Lee, W.E., Iqbal, Y.: Influence of mixing on mullite formation in porcelain. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 21, 2583–2586 (2001)
Rhodes, D.: Clay and glazes for the potter. A & C Black (Publishers), New York (1973)
Pagani, A., Francescon, F., Pavese, A., Diella, V.: Sanitary-ware vitreous body characterization method by optical microscopy, elemental maps, image processing and X-ray powder diffraction. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 30, 1267–1275 (2010)
Lee, W.E., Souza, G.P., McConville, C.J., Tarvornpanich, T., Iqbal, Y.: Mullite formation in clays and clay-derived vitreous ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 28, 465–471 (2008)
Novaes de Oliveira, A.P., Vilches, E.S., Soler, V.C., Villegas, F.A.G.: Relationship between Young’s modulus and temperature in porcelain tiles. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 33, 2853–2858 (2012)
Kivitz, E., Palm, B., Heinrich, J.G., Blumm, J., Kolb, G.: Reduction of the porcelain firing temperature by preparation of the raw materials. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 29, 2691–2696 (2009)
Mukhopadhyay, T.K., Ghatak, S., Maiti, H.S.: Effect of pyrophyllite incorporation in porcelain composition on mechanical properties and microstructure. Ceram. Int. 35, 2555–2562 (2009)
Higashi, S.: Ammonium-bearing mica and mica/smectite of several pottery stone and pyrophyllite deposits in Japan: their mineralogical properties and utilization. Appl. Clay Sci. 16, 171–184 (2000)
Sirilar, P., Srisukhumbowornchai, N., Thanakijkasem, P., Sirisoonthorn, S., Klein, G.: Utilization of pottery stone as a replacing materials for vitreous ceramic sanitary ware production: a case study in Khon Kaen, Thailand. Key Eng. Mater. 718, 143–147 (2016)
Klein, G.: Ceramics calculation: raw materials, mass and glazes. Koblenz University of Applied Science, Koblenz (2013)
Das, S.K., Dana, K.: Differences in densification behaviour of K- and Na-feldspar-containing porcelain bodies. Thermochim. Acta. 406, 199–206 (2003)
Bernardin, A.M., Souza de Merdeiros, D., Riella, H.G.: Pyroplasticity in porcelain tiles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 427, 316–319 (2006)
Ferrari, S., Gualtieri, A.F.: The use of illite clays in the production of stoneware tiles ceramics. Appl. Clay Sci. 32, 73–81 (2006)
Dinsdale, A.: Pottery Science. Ellis Horwood Limited, Chichester (1986)
Taylor, J.R., Bull, A.C.: Ceramics glaze technology. Wheaton & Co, London (1986)
Ryan, W.: Properties of ceramic raw materials, 2nd edn. Biddles, King's Lynn (1978)
Sirilar, P., Srisukhumbowornchai, N., Thanakijkasem, P., Sirisoonthorn, S., Klein, G.: Thermal and physical properties of white-opaque sanitary glazes using Lampang pottery stone as a raw materials. Mater. Sci. Forum. 872, 118–122 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge Khonkaen Ceramic Co., Ltd., Khonkaen, Thailand and Kiwlom Co. Ltd., Lampang, Thailand for providing raw materials.
Funding
This research was supported by the Office of Higher Education Commission, strategic scholarships for frontier research network program
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sirilar, P., Srisukhumbowornchai, N., Thanakijkasem, P. et al. Influence of Lampang pottery stone: local materials in Thailand on C-Q-F ratio, key properties, mullite formation and glaze-body fit of vitreous ceramic sanitary ware. J Aust Ceram Soc 55, 1153–1160 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-019-00331-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-019-00331-9