Abstract
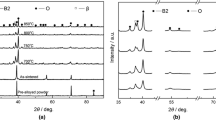
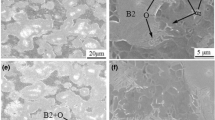
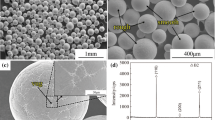
The W-modified Ti2AlNb-based alloys synthesized at 1100 °C by spark plasma sintering were solution treated at 1300 °C for 4 h and then aged at 800–1000 °C for 1 h. The phase composition, microstructure evolution, and microhardness of the aged alloys are investigated in this study. A significant enhancement of hardness, ~ 750 HV, is obtained in the alloy aged at 900 °C, while that of the one without W addition is only ~ 470 HV. The hardness is also higher than that of common β-Ti and Ti–6Al–4V alloys. As the ageing temperature increases, the B2/O structure evolves from B2 + O colonies to Widmannstätten structure, followed by a “disordering to ordering” procedure. This process also involves the variation of the angle between adjacent O phase from 90° to 60°. Specifically, a herringbone Widmannstätten B2 + O structure is constructed in the alloys aged in the α2 + B2 + O phase region, which is related to the diffusion of W and the substitution of W for Nb in the lattice of B2 or O.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Banerjee, A.K. Gogia, T.K. Nandi, V.A. Joshi, A new ordered orthorhombic phase in a Ti3Al–Nb alloy. Acta Metall. 36, 871–882 (1988)
J. Kumpfert, Intermetallic alloys based on orthorhombic titanium aluminide. Adv. Eng. Mater. 3, 851–864 (2001)
T.K. Nandy, R.S. Mishra, D. Banerjee, Creep behaviour of an orthorhombic phase in a Ti–Al–Nb alloy. Scripta Mater. 28, 569–574 (1993)
H. Song, Z.J. Wang, X.D. He, Improving in plasticity of orthorhombic Ti2AlNb-based alloys sheet by high density electropulsing. Trans. Nonferrous Metal. Soc. 23, 32–37 (2013)
B. Wu, M. Zinkevich, F. Aldinger, M. Chu, J. Shen, Prediction of the ordering behaviours of the orthorhombic phase based on Ti2AlNb alloys by combining thermodynamic model with ab initio calculation. Intermetallics 16, 42–51 (2008)
D. Banerjee, The intermetallic Ti2AlNb. Prog. Mater Sci. 42, 135–158 (1997)
P.M. Sarosi, J.A. Hriljac, I.P. Jones, Atom location by channelling-enhanced microanalysis and the ordering of Ti2AlNb. Philos. Mag. 83, 4031–4044 (2003)
K. Muraleedharan, T.K. Nandy, D. Banerjee, S. Lele, Phase stability and ordering behaviour of the O phase in Ti–Al–Nb alloys. Intermetallics 3, 187–199 (1995)
W. Wang, W.D. Zeng, Y.T. Liu, G.X. Xie, X.B. Liang, Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of Ti–22Al–25Nb (At.%) orthorhombic alloy with three typical microstructures. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 27, 293–303 (2018)
W. Wang, W. Zeng, D. Li, B. Zhu, Y. Zheng, X. Liang, Microstructural evolution and tensile behavior of Ti2AlNb alloys based α2-phase decomposition. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 662, 120–128 (2016)
C.J. Boehlert, C.J. Cowen, C.R. Jaeger, M. Niinomi, T. Akahori, Tensile and fatigue evaluation of Ti–15Al–33Nb (at.%) and Ti–21Al–29Nb (at.%) alloys for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 25, 263–275 (2005)
S.L. Semiatin, P.R. Smith, Microstructural evolution during rolling of Ti–22Al–23Nb sheet. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 202, 26–35 (1995)
Y.T. Wu, C.T. Yang, C.H. Koo, A.K. Singh, A study of texture and temperature dependence of mechanical properties in hot rolled Ti–25Al–xNb alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 80, 339–347 (2003)
J. Yang, G. Wang, X. Jiao, X. Li, C. Yang, Hot deformation behavior and microstructural evolution of Ti–22Al–25Nb–1.0B alloy prepared by elemental powder metallurgy. J. Alloy. Compd. 695, 1038–1044 (2017)
J. Wu, R. Guo, L. Xu, Z. Lu, Y. Cui, R. Yang, Effect of hot isostatic pressing loading route on microstructure and mechanical properties of powder metallurgy Ti2AlNb alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 33, 172–178 (2017)
H.Z. Niu, Y.F. Chen, D.L. Zhang, Y.S. Zhang, J.W. Lu, W. Zhang, P.X. Zhang, Fabrication of a powder metallurgy Ti2AlNb-based alloy by spark plasma sintering and associated microstructure optimization. Mater. Design 89, 823–829 (2016)
S. Emura, K. Tsuzaki, K. Tsuchiya, Improvement of room temperature ductility for Mo and Fe modified Ti2AlNb alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 355–362 (2010)
Y. Wu, S.K. Hwang, The effect of ageing on microstructure of the O-phase in Ti–24Al–14Nb–3V–0.5Mo alloy. Mater. Lett. 49, 131–136 (2001)
M. Li, Q. Cai, Y. Liu, Z. Ma, Z. Wang, Y. Huang, H. Li, Formation of fine B2/β + O structure and enhancement of hardness in the aged Ti2AlNb-based alloys prepared by spark plasma sintering. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 48, 4365–4371 (2017)
F. Tang, S. Nakazawa, M. Hagiwara, Creep behavior of tungsten-modified orthorhombic Ti–22Al–20Nb–2W alloy. Scr. Mater. 43, 1065–1070 (2000)
F. Tang, S. Emura, M. Hagiwara, Tensile properties of tungsten-modified orthorhombic Ti–22Al–20Nb–2W alloy. Scr. Mater. 44, 671–676 (2001)
S.J. Yang, S.W. Nam, M. Hagiwara, Phase identification and effect of W on the microstructure and micro-hardness of Ti2AlNb-based intermetallic alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 350, 280–287 (2003)
F.A. Sadi, C. Servant, On the B2 → O phase transformation in Ti–Al–Nb alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 346, 19–28 (2003)
A.A. Popov, A.G. Illarionov, S.V. Grib, S.L. Demakov, M.S. Karabanalov, O.A. Elkina, Phase and structural transformations in the alloy on the basis of the orthorhombic titanium aluminide. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 106, 399–410 (2008)
C.J. Boehlert, B.S. Majumdar, V. Seetharaman, D.B. Miracle, Part I. The microstructural evolution in Ti–Al–Nb O + Bcc orthorhombic alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 30, 2305–2323 (1999)
K. Muraleedharan, A.K. Gogia, T.K. Nandy, D. Banerjee, S. Lele, Transformations in a Ti–24Al–15Nb alloy: Part I Phase equilibria and microstructure. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 23, 401–415 (1992)
H.T. Weykamp, D.R. Baker, D.M. Paxton, M.J. Kaufman, Continuous cooling transformations in Ti3Al + Nb alloys. Scr. Mater. 24, 445–450 (1990)
S. Narasimhan, D. Vanderbilt, Elastic stress domains and the herringbone reconstruction on Au(111). Phys. Rev. Lett. 69, 1564–1567 (1992)
W. Wang, W. Zeng, C. Xue, X. Liang, J. Zhang, Quantitative analysis of the effect of heat treatment on microstructural evolution and microhardness of an isothermally forged Ti–22Al–25Nb (at%) orthorhombic alloy. Intermetallics 45, 29–37 (2014)
D. Li, S. Hu, J. Shen, H. Zhang, X. Bu, Microstructure and mechanical properties of laser-welded joints of Ti–22Al–25Nb/TA15 dissimilar titanium alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 25, 1880–1888 (2016)
K.Y. Xie, Y. Wang, Y. Zhao, L. Chang, G. Wang, Z. Chen, Y. Cao, X. Liao, E.J. Lavemia, R.Z. Valiev, B. Sarrafpour, H. Zoellner, S.P. Ringer, Nanocrystalline β-Ti alloy with high hardness, low Young’s modulus and excellent in vitro biocompatibility for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 33, 3530–3536 (2013)
E. Brandl, A. Schoberth, C. Leyens, Morphology, microstructure, and hardness of titanium (Ti–6Al–4V) blocks deposited by wire-feed additive layer manufacturing (ALM). Mater. Sci. Eng., A 532, 295–307 (2012)
Q. Cai, M. Li, Y. Zhang, Y. Liu, Z. Ma, C. Li, H. Li, Precipitation behavior of Widmannstätten O phase associated with interface in aged Ti2AlNb-based alloy. Mater. Charact. 145, 413–422 (2018)
C. Leyens, M. Peters, Titanium and Titanium Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications (Wiley, New York, 2003)
V. Recina, B. Karlsson, Tensile properties and microstructure of Ti–48Al–2W–0.5Si γ-titanium aluminide at temperatures between room temperature and 800 °C. Mater. Sci. Techonl. 15, 57–66 (2013)
Y.I. Frenkel, T. Kontorova, On the theory of plastic deformation and twinning. II. Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 8, 1340–1348 (1938)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Granted Nos. 51474156, 51604193, 51804195, and U1660201), the National High Technology Research and Development Program (“863″ Program) of China (Granted No. 2015AA042504), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2017M621429) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Cai, Q., Liu, Y. et al. Herringbone Structure and Significantly Enhanced Hardness in W-Modified Ti2AlNb Alloys by Spark Plasma Sintering. Met. Mater. Int. 25, 1000–1007 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00251-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00251-0