Abstract
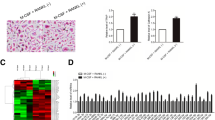
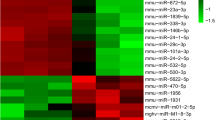
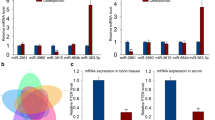
This study determined the effects of miR-338-3p on osteoclast (OC) differentiation and activation. The change levels of miR-338-3p in differentiated OCs were investigated by microRNA microarray assay and quantitative real-time PCR analysis. The effects of miR-338-3p on the differentiation and activation of OCs were determined by tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase staining resorption activity assay and Western blot. Target genes of miR-338-3p were identified by target gene prediction and dual-luciferase reporter gene detection assay as well as Western blot. Results showed that miR-338-3p was markedly downregulated in differentiated OCs. miR-338-3p could inhibit the formation and absorption activity of OCs. Western blot showed that miR-338-3p could influence the change levels of OC differentiation–related proteins. Dual-luciferase reporter gene detection assay and Western blot both showed that miR-338-3p directly targeted IKKβ gene. In conclusion, miR-338-3p may affect the formation and activity of OCs by targeting the IKKβ gene.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Amer Y (2013) NF-kappaB signaling and bone resorption. Osteoporos Int 24:2377–2386
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Chen C, Cheng P, Xie H, Zhou HD, Wu XP, Liao EY, Luo XH (2014) MiR-503 regulates osteoclastogenesis via targeting RANK. J Bone Miner Res 29:338–347
Detsch R, Boccaccini AR (2015) The role of osteoclasts in bone tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 9:1133–1149
Dole NS, Delany AM (2016) MicroRNA variants as genetic determinants of bone mass. Bone 84:57–68
Horne WC, Duong L, Sanjay A, Baron R (2008) Regulating bone resorption: targeting Integrins, calcitonin receptor, and cathepsin K, Principles of Bone Biology, 3rd edn. Academic Press, pp 221–236
Iotsova V, Caamano J, Loy J, Yang Y, Lewin A, Bravo R (1997) Osteopetrosis in mice lacking NF-κB1 and NF-κB2. Nat Med 3:1285–1289
Khandaker M, Riahinezhad S, Sultana F, Vaughan MB, Knight J, Morris TL (2016) Peen treatment on a titanium implant: effect of roughness, osteoblast cell functions, and bonding with bone cement. Int J Nanomed 11:585–595
Kim JH, Kim N (2016) Signaling pathways in osteoclast differentiation. Chonnam Med J 52:12–17
Liu H, Sun Q, Wan C, Li L, Zhang L, Chen Z (2014) MicroRNA-338-3p regulates osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow stromal stem cells by targeting Runx2 and Fgfr2. J Cell Physiol 229:1494–1502
Ono T, Nakashima T (2018) Recent advances in osteoclast biology. Histochem Cell Biol 149:325–341
Otero JE, Dai S, Alhawagri MA, Darwech I, Abu-Amer Y (2010) IKKbeta activation is sufficient for RANK-independent osteoclast differentiation and osteolysis. J Bone Miner Res 25:1282–1294
Shigeru K, Toru Y, Manabu K, Yuki N (2012) Human receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL) induces osteoclastogenesis of primates in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 48:593–598
Soo-Jin K, So-Young K, Hyun-Hee S, Hye-Seon C (2005) Sulforaphane inhibits osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting nuclear factor-κ B. Mol Cells 20:364–370
Tang P, Xiong Q, Ge W, Zhang L (2014) The role of microRNAs in osteoclasts and osteoporosis. RNA Biol 11:1355–1363
Xia Z, Chen C, Chen P, Xie H, Luo X (2011) MicroRNAs and their roles in osteoclast differentiation. Front Med 5:414–419
Yong X, Lihai Z, Yanpan G, Wei G, Peifu T (2015) The Multiple Roles of Microrna-223 in Regulating Bone Metabolism. Molecules 20:19433–19448
Zhang XH, Geng GL, Su B, Liang CP, Wang F, Bao JC (2016) MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits glucocorticoid-induced osteoclast formation through RANKL targeting. Genet Mol Res 15:1–9
Zhao QX, Wang X, Liu Y, He A, Jia R (2010) NFATc1: functions in osteoclasts. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 42:576–579
Funding
This study was supported by the Project of Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (1508085QH172), the Natural Science Research Project of Universities in Anhui (KJ2017A225, KJ2018A1011, and KJ2017A237), the Natural Science Foundation of Bengbu Medical College (BYKY1614ZD), and the National Training Programs of Innovation and Entrepreneurship for Undergraduate (201410367029, 201610367004, 201810367019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, D., Gong, Z., Sun, X. et al. miR-338-3p regulates osteoclastogenesis via targeting IKKβ gene. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 55, 243–251 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-019-00325-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-019-00325-8