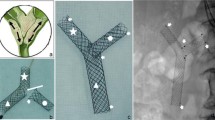
Abstract
Objective
To assess the feasibility, safety, and efficacy of Y-shaped jogged stent in patients with malignant hilar biliary obstruction.
Methods
A total of 196 patients with malignant hilar biliary obstruction treated by biliary tract stent implantation from August 2010 to August 2017 were retrospectively reviewed. Seventeen consecutive patients who were treated with Y-shaped jogged stent implantation were identified as the Y-shaped jogged stent implantation group. Seventeen matched patients undergoing unilateral stent placement combined with percutaneous transhepatic cholangial drainage (PTCD) were enrolled as the control group. Baseline characteristics of patients, stent patency time, and survival time were compared.
Results
There was no significant difference in the age, gender, tumor type and stage, biliary obstruction classification, bilirubin level at diagnosis, presence of metastasis, or chemotherapy between the Y-stent group and the control group (P > 0.05). One week after surgery, the reduction rate of bilirubin was significantly higher in the Y-stent group (88.2% vs 53.0%, P < 0.05). The mean stent patency time was longer in the Y-stent group (7.3 ± 1.0 months vs 5.7 ± 0.9 months, P < 0.05). The mean survival time of the Y-stent group (9.1 ± 1.5 months) was longer than the control group (7.2 ± 1.1 months, P > 0.05). There was no severe complication occurred in both two groups.
Conclusion
Y-shaped jogged stent implantation was a safe, feasible, and effective approach in the treatment of patients with malignant hilar biliary obstruction, with the significantly prolonged stent patency time and survival time.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boulay, B.R. and M. Parepally, Managing malignant biliary obstruction in pancreas cancer: choosing the appropriate strategy. World J Gastroenterol, 2014. 20(28): p. 9345–53.
Boulay, B.R. and A. Birg, Malignant biliary obstruction: From palliation to treatment. World J Gastrointest Oncol, 2016. 8(6): p. 498–508.
Pu, L.Z., et al., Malignant Biliary Obstruction: Evidence for Best Practice. Gastroenterol Res Pract, 2016. 2016: p. 3296801.
Mangiavillano, B., et al., Biliary and pancreatic stenting: Devices and insertion techniques in therapeutic endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic ultrasonography. World J Gastrointest Endosc, 2016. 8(3): p. 143–56.
Menon, S., Hilar stenting for malignant biliary obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc, 2016. 83(2): p. 478–9.
Fu, Y.F., et al., Subcarinal ventilation-assisted Y-shaped stent insertion under local anesthesia for patients with complex tracheobronchial stenosis: initial clinical experience. Diagn Interv Radiol, 2014. 20(4): p. 330–4.
Li, T.F., et al., Application of Y-shaped, coated self-expandable metallic stents for anastomotic stenosis after gastrojejunostomy (Billroth II). Acta Radiol, 2017. 58(1): p. 41–45.
Shin, M. and J.W. Joh, Advances in endoscopic management of biliary complications after living donor liver transplantation: Comprehensive review of the literature. World J Gastroenterol, 2016. 22(27): p. 6173–91.
Singhal, D., T.M. van Gulik, and D.J. Gouma, Palliative management of hilar cholangiocarcinoma. Surg Oncol, 2005. 14(2): p. 59–74.
Lorenz, J.M., Management of Malignant Biliary Obstruction. Semin Intervent Radiol, 2016. 33(4): p. 259–267.
Rerknimitr, R., et al., Asia-Pacific consensus recommendations for endoscopic and interventional management of hilar cholangiocarcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013. 28(4): p. 593–607.
Dumonceau, J.M., et al., Biliary stenting: indications, choice of stents and results: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) clinical guideline. Endoscopy, 2012. 44(3): p. 277–98.
Venkatanarasimha, N., et al., Diagnosis and Management of Complications from Percutaneous Biliary Tract Interventions-Erratum. Radiographics, 2017. 37(3): p. 1004.
Luo, D.C., et al., Clinical value and indication for the dissection of lymph nodes posterior to the right recurrent laryngeal nerve in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Oncotarget, 2017. 8(45): p. 79897–79905.
Chandrashekhara, S.H., et al., Current Status of Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage in Palliation of Malignant Obstructive Jaundice: A Review. Indian J Palliat Care, 2016. 22(4): p. 378–387.
Gamanagatti, S., et al., Unilobar Versus Bilobar Biliary Drainage: Effect on Quality of Life and Bilirubin Level Reduction. Indian J Palliat Care, 2016. 22(1): p. 50–62.
Kato, H., et al., Current status of endoscopic biliary drainage for unresectable malignant hilar biliary strictures. World J Gastrointest Endosc, 2015. 7(11): p. 1032–8.
De Palma, G.D., et al., Unilateral versus bilateral endoscopic hepatic duct drainage in patients with malignant hilar biliary obstruction: results of a prospective, randomized, and controlled study. Gastrointest Endosc, 2001. 53(6): p. 547–53.
Naitoh, I., et al., Unilateral versus bilateral endoscopic metal stenting for malignant hilar biliary obstruction. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2009. 24(4): p. 552–7.
Liberato, M.J. and J.M. Canena, Endoscopic stenting for hilar cholangiocarcinoma: efficacy of unilateral and bilateral placement of plastic and metal stents in a retrospective review of 480 patients. BMC Gastroenterol, 2012. 12: p. 103.
Naitoh, I., et al., Side-by-side versus stent-in-stent deployment in bilateral endoscopic metal stenting for malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Dig Dis Sci, 2012. 57(12): p. 3279–85.
Nam, H.S. and D.H. Kang, Current Status of Biliary Metal Stents. Clin Endosc, 2016. 49(2): p. 124–30.
Jang, S., et al., Association of covered metallic stents with cholecystitis and stent migration in malignant biliary stricture. Gastrointest Endosc, 2018. 87(4): p. 1061–1070.
Hwang, J.C., et al., Y-shaped endoscopic bilateral metal stent placement for malignant hilar biliary obstruction: prospective long-term study. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 2011. 46(3): p. 326–332.
Funding
This work was supported by the Zhejiang Province Natural Science Funding of China (no. LQ17H180001), Zhejiang Province Medical and Health Technology Projects (no. 2017KY724, 2017KY728) and Zhejiang Province Lishui City High-level Talents Development Project (no. 2016RC29, 2017RC08 and 2017RC09), Zhejiang Province Ministry of Construction Project (no. WKJZJ-1629) and Zhejiang Province Lishui City Science and Technology Bureau Social Welfare Project (no. 2016GYX36).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhongwei Zhao: Substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; final approval of the version to be published; agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Jingjing Song: Substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; final approval of the version to be published; agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Xiaoxi Fan: Substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; final approval of the version to be published; agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Shiji Fang: The acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work; final approval of the version to be published; agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Minjiang Chen: The acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work; final approval of the version to be published; agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Weiqian Chen: The acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work; final approval of the version to be published; agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Fazong Wu: The acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work; final approval of the version to be published; agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Liyun Zheng: The acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work; final approval of the version to be published; agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Jianfei Tu: The acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work; final approval of the version to be published; agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Jiansong Ji: Drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content; final approval of the version to be published; agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclaimer
The process and results of this study were not affected by relevant equipments, materials, or pharmaceutical companies.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Z., Song, J., Fan, X. et al. Primary Clinical Application of Y-Shaped Jogged Stent Implantation in Patients with Malignant Hilar Biliary Obstruction. J Gastrointest Surg 23, 745–750 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-019-04131-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-019-04131-1