Abstract
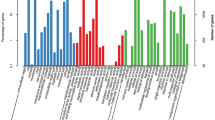
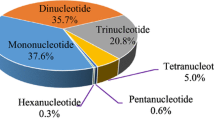
As the largest genus in the family Salicaceae, Salix L. has great potential in industrial, ornamental, and bioenergy-related applications. Despite their comprehensive importance, the genetic and genomic resources available for various willow species are still insufficient. In the present study, the transcriptomes of S. babylonica and S. suchowensis were sequenced using Roche 454 pyrosequencing and screened for expressed sequence tagged simple sequence repeat (EST-SSR) markers. A total of 280,074 and 267,030 reads with an average length of 432 bp and 398 bp were obtained for S. babylonica and S. suchowensis, respectively. The de novo assemblies yielded 40,271 unigenes for S. babylonica and 55,083 unigenes for S. suchowensis, of which 32,506 and 42,482 unigenes were respectively annotated in at least one of the four reference databases. A total of 1479 differentially expressed genes were identified between the two species. A set of 1083 SSR markers (424 for S. babylonica and 659 for S. suchowensis) were developed from the expressed sequence assemblies. Of the 300 randomly selected EST-SSR markers, 295 (98.3%) were polymorphic among different individuals of S. babylonica and of S. eriocephala. High rates of cross-species/genus amplification were also observed within 16 different species. In conclusion, this transcriptomic analysis provides novel resources for functional genomic research and can be used to improve the efficiency of genetics and breeding applications for these Salix species.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
An M, Deng M, Zheng SS, Song YG (2016) De novo transcriptome assembly and development of SSR markers of oaks Quercus austrocochinchinensis and Q. kerrii (Fagaceae). Tree Genet Genomes 12:103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-016-1060-5
Berlin S, Lagercrantz U, von Arnold S, Ost T, Rönnberg-Wästljung AC (2010) High-density linkage mapping and evolution of paralogs and orthologs in Salix and Populus. BMC Genomics 11:129. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-11-129
Berlin S, Trybush SO, Fogelqvist J, Gyllenstrand N, Hallinbäck HR, Åhman I, Nordh NE, Shield I, Powers SJ, Weih M, Lagercrantz U, Rönnberg-Wästljung AC, Karp A, Hanley SJ (2014) Genetic diversity, population structure and phenotypic variation in European Salix viminalis L. (Salicaceae). Tree Genet Genomes 10:1595–1610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-014-0782-5
Bi C, Xu QY, Ye QL, Yin TM, Ye N (2016) Genome-wide identification and characterization of WRKY gene family in Salix suchowensis. PeerJ 4:e2437. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.2437
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Bozzi JA, Liepelt S, Ohneiser S, Gallo LA, Marchelli P, Leyer I, Ziegenhagen B, Mengel C (2015) Characterization of 23 polymorphic SSR markers in Salix humboldtiana (Salicaceae) using next-generation sequencing and cross-amplification from related species. Appl Plant Sci 3:1–4. https://doi.org/10.3732/apps.1400120
Chou HH, Holmes MH (2001) DNA sequence quality trimming and vector removal. Bioinformatics 17:1093–1094. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/17.12.1093
Dai XG, Hu QJ, Cai QL, Feng K, Ye N, Tuskan GA, Milne R, Chen YN, Wan ZB, Wang ZF, Luo WC, Wang K, Wan DS, Wang MX, Wang J, Liu JQ, Yin TM (2014) The willow genome and divergent evolution from poplar after the common genome duplication. Cell Res 24:1274–1277. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2014.83
Dai XG, Zhu TW, Li XP, Yin TM (2017) Gene discovery and marker resource development by transcriptome sequencing from a short-rotation coppice willow, Salix suchowensis. Plant Breed 136:279–286. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.12458
Davey JW, Hohenlohe PA, Etter PD, Boone JQ, Catchen JM, Blaxter ML (2011) Genome-wide genetic marker discovery and genotyping using next-generation sequencing. Nat Rev Genet 12:499–510. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3012
Dong SB, Liu YL, Niu J, Ning Y, Lin SZ, Zhang ZX (2014) De novo transcriptome analysis of the Siberian apricot (Prunus sibirica L.) and search for potential SSR markers by 454 pyrosequencing. Gene 544:220–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2014.04.031
Du FK, Xu F, Qu H, Feng SS, Tang JJ, Wu RL (2013) Exploiting the transcriptome of Euphrates poplar, Populus euphratica (Salicaceae) to develop and characterize new EST-SSR markers and construct an EST-SSR database. PLoS One 8:e61337. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0061337
Ellis JR, Burke JM (2007) EST-SSRs as a resource for population genetic analyses. Heredity 99:125–132. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.hdy.6801001
Gasic K, Han Y, Kertbundit S, Shulaev V, Iezzoni AF, Stover EW, Bell RL, Wisniewski ME, Korban SS (2009) Characteristics and transferability of new apple EST-derived SSRs to other Rosaceae species. Mol Breed 23:397–411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-008-9243-x
Ghelardini L, Berlin S, Weih M, Lagercrantz U, Gyllenstrand N, Rönnberg-Wästljung AC (2014) Genetic architecture of spring and autumn phenology in Salix. BMC Plant Biol 14:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-14-31
Hallingbäck HR, Fogelqvist J, Powers SJ, Turrion-Gomez J, Rossiter R, Amey J, Martin T, Weih M, Gyllenstrand N, Karp A, Lagercrantz U, Hanley SJ, Berlin S, Rönnberg-Wästljung AC (2016) Association mapping in Salix viminalis L. (Salicaceae)—identification of candidate genes associated with growth and phenology. Glob Change Biol Bioenergy 8:670–685. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcbb.12280
Han SM, Wu ZJ, Jin Y, Yang WN, Shi HZ (2015) RNA-Seq analysis for transcriptome assembly, gene identification, and SSR mining in ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba L.). Tree Genet Genomes 11:37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-015-0868-8
Hanley SJ, Karp A (2014) Genetic strategies for dissecting complex traits in biomass willows (Salix spp.). Tree Physiol 34:1167–1180. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpt089
He Q, Marjamäki M, Soini H, Mertsola J, Viljanen MK (1994) Primers are decisive for sensitivity of PCR. BioTechniques 17:82–87
He XD, Wang Y, Li FG, Weng QJ, Li M, Xu LA, Shi JS, Gan SM (2012) Development of 198 novel EST-derived microsatellites in Eucalyptus (Myrtaceae). Am J Bot 99:e134–e148. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1100442
He XD, Zheng JW, Serapiglia M, Smart L, Shi SZ, Wang BS (2014) Short note: development, characterization and cross-amplification of eight EST-derived microsatellites in Salix. Silvae Genet 63:113–115. https://doi.org/10.1515/sg-2014-0015
Huang CL, Chang CT, Huang BH, Chung JD, Chen JH, Chiang YC, Hwang SY (2015) Genetic relationships and ecological divergence in Salix species and populations in Taiwan. Tree Genet Genomes 11:39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-015-0862-1
Huang HH, Xu LL, Tong ZK, Lin EP, Liu QP, Cheng LJ, Zhu MY (2012) De novo characterization of the Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) transcriptome and analysis of candidate genes involved in cellulose and lignin biosynthesis. BMC Genomics 13(1):648. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-648
Jia HX, Yang HF, Sun P, Li JB, Zhang J, Guo YH, Han XJ, Zhang GS, Lu MZ, Hu JJ (2016) De novo transcriptome assembly, development of EST-SSR markers and population genetic analyses for the desert biomass willow, Salix psammophila. Sci Rep 6:39591. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep39591
Kalia RK, Rai MK, Kalia S, Singh R, Dhawan AK (2011) Microsatellite markers: an overview of the recent progress in plants. Euphytica 177:309–334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-010-0286-9
Kunkel TA, Bebenik K (2000) DNA replication fidelity. Annu Rev Biochem 69:497–529. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.497
Larsson G, Bremer B (1991) Osier willows—useful plants then and now. Sven Bot Tidskr 85:185–200
Lauron-Moreau A, Pitre FE, Argus GW, Labrecque M, Brouillet L (2015) Phylogenetic relationships of American willows (Salix L., Salicaceae). PLoS One 10:e0121965. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0121965
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25:1754–1760. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324
Lindegaard KN, Barker JHA (1997) Breeding willows for biomass. Asp Appl Biol 1997:155–162
Liu JJ, Yin TM, Ye N, Chen YN, Yin TT, Liu M, Hassani D (2013) Transcriptome analysis of the differentially expressed genes in the male and female shrub willows (Salix suchowensis). PLoS One 8:e60181. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060181
Ma T, Wang JY, Zhou GK, Yue Z, Hu QJ, Chen Y, Liu BB, Qiu Q, Wang Z, Zhang J, Wang K, Jiang D, Gou C, Yu LL, Zhan DL, Zhou R, Luo WC, Ma H, Yang YZ, Pan SK, Fang DM, Luo YD, Wang X, Wang GN, Wang J, Wang Q, Lu X, Chen Z, Liu JC, Lu Y, Yin Y, Yang HM, Abbott RJ, Wu YX, Wan DS, Li J, Yin TM, Lascoux M, Difazio SP, Tuskan GA, Wang J, Liu JQ (2013) Genomic insights into salt adaptation in a desert poplar. Nat Commun 4:2797. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3797
Mardis ER (2008) The impact of next-generation sequencing technology on genetics. Trends Genet 24:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2007.12.007
Mirski P, Brzosko E, Jędrzejczyk I, Kotowicz J, Ostrowiecka B, Wróblewska A (2017) Genetic structure of dioecious and trioecious Salix myrsinifolia populations at the border of geographic range. Tree Genet Genomes 13:15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-016-1096-6
Morozova O, Marra MA (2008) Applications of next-generation sequencing technologies in functional genomics. Genomics 92:255–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2008.07.001
Morozova O, Hirst M, Marra MA (2009) Applications of new sequencing technologies for transcriptome analysis. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 10:135–151. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genom-082908-145957
Munoz-Merida A, Gonzalez-Plaza JJ, Canada A, Blanco AM, Garcia-Lopez MdC, Rodriguez JM, Pedrola L, Sicardo MD, Hernandez ML, De la Rosa R, Belaj A, Gil-Borja M, Luque F, Martinez-Rivas JM, Pisano DG, Trelles O, Valpuesta V, Beuzon CR (2013) De Novo assembly and functional annotation of the Olive (Olea europaea) transcriptome. DNA Res 20(1):93–108. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dss036
Ozsolak F, Milos PM (2011) RNA sequencing: advances, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Genet 12:87–98. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2934
Puschenreiter M, Türktaş M, Sommer P, Wieshammer G, Laaha G, Wenzel WW, Hauser MT (2010) Differentiation of metallicolous and non-metallicolous Salix caprea populations based on phenotypic characteristics and nuclear microsatellite (SSR) markers. Plant Cell Environ 33:1641–1655. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2010.02170.x
Qiu Q, Ma T, Hu QJ, Liu BB, Wu YX, Zhou HH, Wang Q, Wang J, Liu JQ (2011) Genome-scale transcriptome analysis of the desert poplar, Populus euphratica. Tree Physiol 31:452–461. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpr015
Rao GD, Sui JK, Zeng YF, He CY, Duan AG, Zhang JG (2014) De novo transcriptome and small RNA analysis of two Chinese willow cultivars reveals stress response genes in Salix matsudana. PLoS One 9:e109122. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0109122
Rao GD, Zeng YF, Sui JK, Zhang JG (2016) De novo transcriptome analysis reveals tissue-specific differences in gene expression in Salix arbutifolia. Trees 30:1647–1655. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-016-1397-2
Rozen S, Skaletsky H (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol Biol 132:365–386. https://doi.org/10.1385/1-59259-192-2:365
Savadi SB, Fakrudin B, Nadaf HL, Gowda MVC (2012) Transferability of sorghum genic microsatellite markers to peanut. Am J Plant Sci 3:1169–1180. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2012.39142
Serapiglia MJ, Gouker FE, Smart LB (2014) Early selection of novel triploid hybrids of shrub willow with improved biomass yield relative to diploids. BMC Plant Biol 14:74. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-14-74
Shi X, Sun HJ, Chen YT, Pan HW, Wang SF (2016) Transcriptome sequencing and expression analysis of cadmium (Cd) transport and detoxification related genes in cd-accumulating Salix integra. Front Plant Sci 7:1577. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01577
Smart LB, Cameron KD (2008) Genetic improvement of willow (Salix spp.) as a dedicated bioenergy crop. In: Vermerris W (ed) Genetic improvement of bioenergy crops. Springer, New York, pp 347–370
Torales SL, Rivarola M, Pomponio MF, Gonzalez S, Acuña CV, Fernández P, Lauenstein DL, Verga AR, Hopp HE, Paniego NB, Poltri SN (2013) De novo assembly and characterization of leaf transcriptome for the development of functional molecular markers of the extremophile multipurpose tree species Prosopis alba. BMC Genomics 14:705. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-705
Tu ZY (1982) Breeding and cultivation of Salix. Jiangsu Science and Technology Press, Nanjing
Tuskan GA, Gunter LE, Yang ZK, Yin TM, Sewell MM, DiFazio SP (2004) Characterization of microsatellites revealed by genomic sequencing of Populus trichocarpa. Can J For Res 34:85–93. https://doi.org/10.1139/x03-283
Tuskan GA, DiFazio S, Jansson S, Bohlmann J, Grigoriev I, Hellsten U, Putnam N, Ralph S, Rombauts S, Salamov A, Schein J, Sterck L, Aerts A, Bhalerao RR, Bhalerao RP, Blaudez D, Boerjan W, Brun A, Brunner A, Busov V, Campbell M, Carlson J, Chalot M, Chapman J, Chen GL, Cooper D, Coutinho PM, Couturier J, Covert S, Cronk Q, Cunningham R, Davis J, Degroeve S, Déjardin A, Depamphilis C, Detter J, Dirks B, Dubchak I, Duplessis S, Ehlting J, Ellis B, Gendler K, Goodstein D, Gribskov M, Grimwood J, Groover A, Gunter L, Hamberger B, Heinze B, Helariutta Y, Henrissat B, Holligan D, Holt R, Huang W, Islam-Faridi N, Jones S, Jones-Rhoades M, Jorgensen R, Joshi C, Kangasjärvi J, Karlsson J, Kelleher C, Kirkpatrick R, Kirst M, Kohler A, Kalluri U, Larimer F, Leebens-Mack J, Leplé JC, Locascio P, Lou Y, Lucas S, Martin F, Montanini B, Napoli C, Nelson DR, Nelson C, Nieminen K, Nilsson O, Pereda V, Peter G, Philippe R, Pilate G, Poliakov A, Razumovskaya J, Richardson P, Rinaldi C, Ritland K, Rouzé P, Ryaboy D, Schmutz J, Schrader J, Segerman B, Shin H, Siddiqui A, Sterky F, Terry A, Tsai CJ, Uberbacher E, Unneberg P, Vahala J, Wall K, Wessler S, Yang G, Yin T, Douglas C, Marra M, Sandberg G, Van de Peer Y, Rokhsar D (2006) The genome of black cottonwood, Populus trichocarpa (Torr. & Gray). Science 313:1596–1604. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1128691
Varshney RK, Nayak SN, May GD, Jackson SA (2009) Next-generation sequencing technologies and their implications for crop genetics and breeding. Trends Biotechnol 27:522–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2009.05.006
Wang Z, Gerstein M, Snyder M (2009) RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet 10:57–63. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2484
Wullschleger SD, Weston DJ, DiFazio SP, Tuskan GA (2013) Revisiting the sequencing of the first tree genome: Populus trichocarpa. Tree Physiol 33:357–364. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tps081
Xia ZH, Xu HM, Zhai JL, Li DJ, Luo HL, He CZ, Huang X (2011) RNA-Seq analysis and de novo transcriptome assembly of Hevea brasiliensis. Plant Mol Biol 77:299–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-011-9811-z
Yadav HK, Ranjan A, Asif MH, Mantri S, Sawant SV, Tuli R (2011) EST-derived SSR markers in Jatropha curcas L.: development, characterization, polymorphism, and transferability across the species/genera. Tree Genet Genomes 7:207–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-010-0326-6
Yang YL, Zhang YD, Zhang XY (2008) Transferability analysis of Populous SSR markers in Salix. Mol Plant Breed 6:1134–1138. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-416X.2008.06.018
Zalapa JE, Cuevas H, Zhu H, Steffan S, Senalik D, Zeldin E, McCown B, Harbut R, Simon P (2012) Using next-generation sequencing approaches to isolate simple sequence repeat (SSR) loci in the plant science. Am J Bot 99:193–208. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1100394
Zhang J, Yuan HW, Li M, Li YJ, Wang Y, Ma XJ, Zhang Y, Tan F, Wu RL (2016) A high-density genetic map of tetraploid Salix matsudana using specific length amplified fragment sequencing (SLAF-seq). PLoS One 11:e0157777. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0157777
Zhang YX, Han XJ, Chen SS, Zheng L, He XL, Liu MY, Qiao GR, Wang Y, Zhuo RY (2017) Selection of suitable reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR gene expression analysis in Salix matsudana under different abiotic stresses. Sci Rep 7:40290. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40290
Zheng JW, Sun C, Zhou J, He KY, He XD (2014) A modified method of DNA extraction from Salix. J Jiangsu Fore Sci Technol 41:4–6. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-7380.2014.06.002
Zhou CP, He XD, Li FG, Weng QJ, Yu XL, Wang Y, Li M, Shi JS, Gan SM (2013) Development of 240 novel EST-SSRs in Eucalyptus L’Herit. Mol Breed 33:221–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-013-9923-z
Zorrilla-Fontanesi Y, Cabeza A, Torres AM, Botella MA, Valpuesta V, Monfort A, Sánchez-Sevilla JF, Amaya I (2011) Development and bin mapping of strawberry genic-SSRs in diploid Fragaria and their transferability across the Rosoideae subfamily. Mol Breed 27:137–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-010-9417-1
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Shanghai BIOZERON Biotechnology Co., Ltd. for their assistance with the bioinformatics analysis.
Data archiving statement
All 454 pyrosequencing reads obtained for S. babylonica and S. suchowensis were submitted to the sequence read archive (SRA) database at NCBI (accession numbers: SRX389383 and SRX388824, respectively). The primer sequences for the 1083 EST-SSRs have also been deposited in the Probe database of GenBank (IDs Pr032826580-Pr032827662).
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Fund for Independent Innovation of Agricultural Sciences and Technology in Jiangsu Province (No. CX(14)2024), Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation (BK20141039), Six Talent Peak project in Jiangsu Province (2016-NY-036), and 333 High-level Personnel Training Project in Jiangsu Province (No. BRA2017518).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by P. Ingvarsson
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, X., Zheng, J., Jiao, Z. et al. Transcriptome sequencing and EST-SSR marker development in Salix babylonica and S. suchowensis. Tree Genetics & Genomes 15, 9 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-018-1315-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-018-1315-4