Abstract
Aim
Pseudomonas orientalis and Chaetomium cupreum isolated from metal(oid)s-contaminated soil were characterized to evaluate their role in plant growth promotion and enhance the tolerance of Eucalyptus globulus to copper stress.
Methods
We evaluated minimum inhibitory concentration and explored plant-promoting traits under copper stress. Moreover, changes in morphology and the accumulation of metals on the cell surface were determined by scanning electron microscopy images coupled with energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX). The effect of inoculation with P. orientalis and C. cupreum on E. globulus plants established in soils contaminated with copper was determined through root and shoot biomass and antioxidant response.
Results
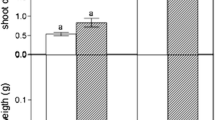
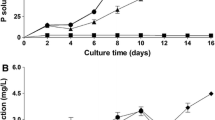
Both strains showed high tolerance to metal(oid)s, whereas phosphate solubilization was only detected in P. orientalis. Under copper stress, C. cupreum presented a higher production rate of siderophores and indole acetic acid (4.5 mm day−1, 15.042 μg mL−1). SEM images and EDX analysis reflected cellular changes in fungus and proved biosorption of copper. Inoculation of P. orientalis and C. cupreum on Eucalyptus globulus plants significantly increased plant growth and mitigated the toxic effects of copper.
Conclusions
According to these results, both microorganisms contribute positively to stimulated plant growth and to decreasing stress caused by high concentrations of copper in soil, especially C. cupreum.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali H, Khan E, Sajad MA (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals--concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91:869–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.075
Almonacid L, Fuentes A, Ortiz J, Salas C, Garcia-Romera I, Ocampo J, Arriagada C (2015) Effect of mixing soil saprophytic fungi with organic residues on the response of Solanum lycopersicum to arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Soil Use Manag 31:155–164. https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12160
Armada E, Probanza A, Roldan A, Azcon R (2016) Native plant growth promoting bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis and mixed or individual mycorrhizal species improved drought tolerance and oxidative metabolism in Lavandula dentata plants. J Plant Physiol 192:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2015.11.007
Arriagada C, Aranda E, Sampedro I, Garcia-Romera I, Ocampo JA (2009a) Contribution of the saprobic fungi Trametes versicolor and Trichoderma harzianum and the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi Glomus deserticola and G. claroideum to arsenic tolerance of Eucalyptus globulus. Bioresour Technol 100:6250–6257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.07.010
Arriagada C, Aranda E, Sampedro I, Garcia-Romera I, Ocampo JA (2009b) Interactions of Trametes versicolor, Coriolopsis rigida and the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus deserticola on the copper tolerance of Eucalyptus globulus. Chemosphere 77:273–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.07.042
Avis TJ, Gravel V, Antoun H, Tweddell RJ (2008) Multifaceted beneficial effects of rhizosphere microorganisms on plant health and productivity. Soil Biol Biochem 40:1733–1740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.02.013
Bensidhoum L, Nabti E, Tabli N, Kupferschmied P, Weiss A, Rothballer M, Schmid M, Keel C, Hartmann A (2016) Heavy metal tolerant Pseudomonas protegens isolates from agricultural well water in northeastern Algeria with plant growth promoting, insecticidal and antifungal activities. Eur J Soil Biol 75:38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2016.04.006
Benyo D et al (2016) Physiological and molecular responses to heavy metal stresses suggest different detoxification mechanism of Populus deltoides and P. x canadensis. J Plant Physiol 201:62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2016.05.025
Chen W-C, Juang R-S, Wei Y-H (2015) Applications of a lipopeptide biosurfactant, surfactin, produced by microorganisms. Biochem Eng J 103:158–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2015.07.009
Chen SH, Ng SL, Cheow YL, Ting ASY (2017) A novel study based on adaptive metal tolerance behavior in fungi and SEM-EDX analysis. J Hazard Mater 334:132–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.04.004
Chiboub M, Saadani O, Fatnassi IC, Abdelkrim S, Abid G, Jebara M, Jebara SH (2016) Characterization of efficient plant-growth-promoting bacteria isolated from Sulla coronaria resistant to cadmium and to other heavy metals. C R Biol 339:391–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crvi.2016.04.015
Dakora FD, Phillips DA (2002) Root exudates asmediators of mineral acquisition in low-nutrient environments. Plant Soil 245:35–47
Du Z, Bramlage WJ (1992) Modified thiobarbituric acid assay for measuring lipid oxidation in sugar-rich plant tissue extracts. J Agric Food Chem 40:1566–1570
Fuentes A, Almonacid L, Ocampo JA, Arriagada C (2016) Synergistic interactions between a saprophytic fungal consortium and Rhizophagus irregularis alleviate oxidative stress in plants grown in heavy metal contaminated soil. Plant Soil 407:355–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2893-2
Gadd GM (2004) Microbial influence on metal mobility and application for bioremediation. Geoderma 122:109–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2004.01.002
Gasser I, Muller H, Berg G (2009) Ecology and characterization of polyhydroxyalkanoate-producing microorganisms on and in plants. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 70:142–150. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2009.00734.x
Ginocchio R (2000) Effects of a copper smelter on a grassland community in the Puchuncaví Valley, Chile. Chemosphere 41:15–23
Ginocchio R, Carvallo G, Toro I, Bustamante E, Silva Y, Sepúlveda N (2004) Micro-spatial variation of soil metal pollution and plant recruitment near a copper smelter in Central Chile. Environ Pollut 127:343–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2003.08.020
Gola D, Dey P, Bhattacharya A, Mishra A, Malik A, Namburath M, Ahammad SZ (2016) Multiple heavy metal removal using an entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana. Bioresour Technol 218:388–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.06.096
Jones DL (1998) Organic acids in the rizosphere - a critical review. Plant Soil 205:25–44
Kamran MA, Syed JH, Eqani SA, Munis MF, Chaudhary HJ (2015) Effect of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria inoculation on cadmium (cd) uptake by Eruca sativa. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:9275–9283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4074-x
Korayem AS, Abdelhafez AA, Zaki MM, Saleh EA (2015) Optimization of biosurfactant production by Streptomyces isolated from Egyptian arid soil using Plackett–Burman design. Ann Agric Sci 60:209–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aoas.2015.09.001
Li WC, Ye ZH, Wong MH (2009) Metal mobilization and production of short-chain organic acids by rhizosphere bacteria associated with a cd/Zn hyperaccumulating plant, Sedum alfredii. Plant Soil 326:453–467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-0025-y
Liu W, Yang C, Shi S, Shu W (2014) Effects of plant growth-promoting bacteria isolated from copper tailings on plants in sterilized and non-sterilized tailings. Chemosphere 97:47–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.10.089
Luo J, Qi S, Peng L, Xie X (2017) Enhanced phytoremediation capacity of a mixed-species plantation of Eucalyptus globulus and Chickpeas. J Geochem Explor 182:201–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.01.006
Ma Y, Prasad MN, Rajkumar M, Freitas H (2011) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and endophytes accelerate phytoremediation of metalliferous soils. Biotechnol Adv 29:248–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2010.12.001
Machuca A, Milagres AMF (2003) Use of CAS-agar plate modified to study the effect of different variables on the siderophore production by Aspergillus. Lett Appl Microbiol 36:177–181
Milagres A, Machuca A, Napoleao D (1999) Detection of siderophore production from several fungi and bacteria by a modification of chrome azurol S (CAS) agar plate assay. J Microbiol Methods 37:1–6
Miransari M (2011) Hyperaccumulators, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and stress of heavy metals. Biotechnol Adv 29:645–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.04.006
Mishra A, Malik A (2012) Simultaneous bioaccumulation of multiple metals from electroplating effluent using Aspergillus lentulus. Water Res 46:4991–4998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.06.035
Moreira H, Pereira SIA, Marques APGC, Rangel AOSS, Castro PML (2016) Selection of metal resistant plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for the growth and metal accumulation of energy maize in a mine soil — effect of the inoculum size. Geoderma 278:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.05.003
Onyia CE, Anyanwu CU, Onuigbo AC, Mbegbu EC (2014) Impact of heavy metals and initial pH variations on the phosphate solubilizing fungi (PSF) isolated from Nsukka pepper and gardenegg plants rhizosphere. IOSR J Pharm Biol Sci 9:33–39. https://doi.org/10.9790/3008-09423339
Plassard C, Fransson P (2009) Regulation of low-molecular weight organic acid production in fungi Fungal. Biol Rev 23:30–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbr.2009.08.002
Rajkumar M, Ae N, Prasad MN, Freitas H (2010) Potential of siderophore-producing bacteria for improving heavy metal phytoextraction. Trends Biotechnol 28:142–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2009.12.002
Rajkumar M, Sandhya S, Prasad MN, Freitas H (2012) Perspectives of plant-associated microbes in heavy metal phytoremediation. Biotechnol Adv 30:1562–1574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2012.04.011
Rashid MI, Mujawar LH, Shahzad T, Almeelbi T, Ismail IM, Oves M (2016) Bacteria and fungi can contribute to nutrients bioavailability and aggregate formation in degraded soils. Microbiol Res 183:26–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2015.11.007
San Keskin NO, Han D, Devrim Ozkan A, Angun P, Onarman Umu OC, Tekinay T (2015) Production and structural characterization of biosurfactant produced by newly isolated Staphylococcus xylosus STF1 from petroleum contaminated soil. J Pet Sci Eng 133:689–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2015.07.011
Sari M, Kusharyoto W, Artika IM (2014) Screening for biosurfactant - producing yeast: confirmation of biosurfactant production. Biotechnology 13:106–111
Schalk IJ, Hannauer M, Braud A (2011) New roles for bacterial siderophores in metal transport and tolerance. Environ Microbiol 13:2844–2854. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02556.x
Singh H, Reddy MS (2011) Effect of inoculation with phosphate solubilizing fungus on growth and nutrient uptake of wheat and maize plants fertilized with rock phosphate in alkaline soils. Eur J Soil Biol 47:30–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2010.10.005
Spaepen S, Vanderleyden J, Remans R (2007) Indole-3-acetic acid in microbial and microorganism-plant signaling. FEMS Microbiol Rev 31:425–448. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00072.x
Sriram MI, Kalishwaralal K, Deepak V, Gracerosepat R, Srisakthi K, Gurunathan S (2011) Biofilm inhibition and antimicrobial action of lipopeptide biosurfactant produced by heavy metal tolerant strain Bacillus cereus NK1. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 85:174–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2011.02.026
Ullah A, Heng S, Munis MFH, Fahad S, Yang X (2015) Phytoremediation of heavy metals assisted by plant growth promoting (PGP) bacteria: a review. Environ Exp Bot 117:28–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2015.05.001
Velioglu Z, Ozturk Urek R (2015) Optimization of cultural conditions for biosurfactant production by Pleurotus djamor in solid state fermentation. J Biosci Bioeng 120:526–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2015.03.007
Wang H, Xu R, You L, Zhong G (2013) Characterization of cu-tolerant bacteria and definition of their role in promotion of growth, cu accumulation and reduction of cu toxicity in Triticum aestivum L. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 94:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.04.005
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, New York, pp 315–322
Widden P, Bisset J (1972) An automatic multichamber soil washing apparatus for removing fungal spores from soil. Can J Microbiol 18:1399–1404
Xie X, Fu J, Wang H, Liu J (2010) Heavy metal resistance by two bacteria strains isolated from a copper mine tailing in China. Afr J Biotechnol 9:4056–4066
Zafar S, Aqil F, Ahmad I (2007) Metal tolerance and biosorption potential of filamentous fungi isolated from metal contaminated agricultural soil. Bioresour Technol 98:2557–2561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.09.051
Zahoor M, Irshad M, Rahman H, Qasim M, Afridi SG, Qadir M, Hussain A (2017) Alleviation of heavy metal toxicity and phytostimulation of Brassica campestris L. by endophytic Mucor sp. MHR-7. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 142:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.04.005
Zaidi S, Usmani S, Singh BR, Musarrat J (2006) Significance of Bacillus subtilis strain SJ-101 as a bioinoculant for concurrent plant growth promotion and nickel accumulation in Brassica juncea. Chemosphere 64:991–997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.12.057
Zengerer V, Schmid M, Bieri M, Muller DC, Remus-Emsermann MNP, Ahrens CH, Pelludat C (2018) Pseudomonas orientalis F9: a potent antagonist against Phytopathogens with phytotoxic effect in the apple flower. Front Microbiol 9:145. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00145
Zhang H, Yang Q (2007) Expressed sequence tags-based identification of genes in the biocontrol agent Chaetomium cupreum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:650–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0701-2
Zouari M, Ben Ahmed C, Elloumi N, Bellassoued K, Delmail D, Labrousse P, Ben Abdallah F, Ben Rouina B (2016) Impact of proline application on cadmium accumulation, mineral nutrition and enzymatic antioxidant defense system of Olea europaea L. cv Chemlali exposed to cadmium stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 128:195–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.02.024
Acknowledgements
Financial support of this study was provided by the Fondo Nacional de Desarrollo, Científico y Tecnológico, FONDECYT 1170931, and the Comisión Nacional de Investigación Científica y Tecnológica, CONICYT Doctoral Fellowship 21150615. We thank the Scientific and Technological Bioresource Nucleus BIOREN- UFRO for equipment support. This study is dedicated for the memory of the Professor of Environmental Microbiology, Yoav Bashan (1952–2018) of the Bashan Institute of Science, Auburn, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Antony Van der Ent.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ortiz, J., Soto, J., Almonacid, L. et al. Alleviation of metal stress by Pseudomonas orientalis and Chaetomium cupreum strains and their effects on Eucalyptus globulus growth promotion. Plant Soil 436, 449–461 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-03946-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-03946-w