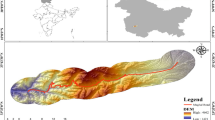
Abstract
Highway transportation was seriously affected by the rare 2008 snow disaster which occurred in China. Shaanxi Province (China) was one of the most affected areas. Research on risk assessment can play an important role in the mitigation of highway snow disasters. Based on a theoretical model, an index system of highway snow cover risk assessment was put forward. This system covers hazard of environment and the vulnerability of disaster-affected entities. The historical disaster hazard and the potential disaster hazard are the two aspects considered for hazard of environment. Physical exposure of the disaster-affected entities to environment and the societal disaster recovery capabilities are considered as the main factors in the vulnerability of disaster-affected entities. Grades of indices and their weights were prompted based on the assessment model. Assessment of the hazard of environment, the vulnerability of disaster-affected entities and the risk of highway snow disaster in Shaanxi Province were carried out by GIS. The risk was divided into five grades using statistical methods in accordance with regional characteristics of highway snow disasters. A distribution of trunk highway snow disaster risks in Shaanxi was put forward. The results are consistent with actual events.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen LP, Yang B, Liu ChZh (2001) Review of regional geological disaster risk assessment. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 28:75–78
Chen XL, Qi SW, Ye H (2007) Fuzzy comprehensive study on seismic landslide hazard based on GIS. Acta Sci Nat Univ Pekin 7(2):1–6
Chen Y, Lin QZH, Wang QJ (2010a) Summary of regional geological hazard assessment model. J Inst Disaster Prev 12:42–45
Chen YQ, Yang JY, Su W et al (2010b) Risk assessment of snow disaster on county scale. Trans CSAE 26:307–311
Fu Y, Xiao JS, Xiao RX et al (2010) Risk assessment model of snow disaster in Qinghai Province based on GIS. Trans CSAE 26:197–205
Gao YL, Fei XJ, Ma ZhQ (2009) A geo-hazard assessment study based on AHP-FUZZY. Coal. Geol China 21:29–31
He YQ, Zhou BR, Zhang HJ et al (2010) Assessment model on risk degree of snow disaster and its risk division in Qinghai Plateau. Pratacultural Sci 27:37–42
Huang RQ, Xiang XQ, Ju NP (2004) Assessment of China’s regional geo-hazards: present situation and problems. Geol Bull China 23:1078–1082
Jiang HB (2007) Research on the framework of GIS-based real-time dynamic geo-hazard assessment system. Chin J Geol Hazard Control 18:19–23 (in Chinese)
Li W (2010) Study on the evolution of urban regional traffic flow under the condition of snow and ice. Dissertation, Harbin Institute of Technology
Li JCh, Han M, Zheng RP (2011) Regional hazards risk evaluation of slope disaster for highways. J. Highw. Transp. Res. Dev. 28:120–123
Li HM, Li L, Gao G et al (2013) Snow disaster in Qinghai Plateau: risk division and countermeasure. J Glaciol Geocryol 35:656–661
Liu M(2011) The design and developing of the ice and snow disaster early warning and road network scheduling of mountain highway system. Dissertation, Chongqing Jiao Tong University
Liu XY, Liang TG, Guo ZhG et al (2008) Early warning and risk assessment of snow disaster in pastoral area of northern Xinjiang. Chin J Appl Ecol 19:133–138
Ma BC (2011) Research on identification technology of highway flood damage. Dissertation, Chang’an University
National Climate Center (2008) Analysis of disaster and climate of snow and frozen in China Southern at the beginning of 2008. Meteorology Press, Beijing
Qi HL(2011) Study on evaluation system of highway natural disasters. Dissertation, Chang’an University
Qi HL, Tian WP, Shu YJ (2010a) Index system of hydrological regionalization for highway in China. J Chang’an Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 30:39–43
Qi HL, Tian WP, Shu YJ (2010b) Research on hydrological regionalization for highway in China based on slope runoff intensity. J Highw Transp Res Dev 27:12–16
Qi HL, Tian WP, Shu YJ (2011) Research on hydrological regionalization for highway in China based on river runoff intensity. J Highw Transp Res Dev 28:55–60
Qi HL, Tian WP, Li JCh (2015) Regional risk evaluation of flood disasters for the trunk highway in Shaanxi, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:13861–13870. doi:10.3390/ijerph121113861
Stocker TF, Qin D, Plattner G-K et al (2013) Climate change 2013: the physical science basis working group I contribution to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change (summary for policymakers). Printed by the IPCC, Switzerland
Wang FH (2011) research on assessment and prediction of regional highway slop disaster based on GIS. Dissertation, Chang’an University
Wu JD, Li N, Yang HJ et al (2008) Risk evaluation of heavy snow disasters using BP artificial neural network: the case of Xilingol in Inner Mongolia. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 22:719–725
Xiang XQ, Huang RQ (2000) Application of GIS-based artificial neural networks on assessment of geo-hazards risk. Chin J Geol Hazard Control 11:23–27
Yang TL (2005) Research on database creation and risk assessment for highway geological disasters in southern Shaanxi based on GIS. Dissertation, Chang’an University
Zhang ChSh, Han JL, Sun WF et al (2008) Assessment of geo-hazard danger zoning in Longxian County, Shaanixi, China. Geol Bull China 27:1795–1801
Zhang F, He ZhW, Yang B et al (2009a) Debris flow hazard assessment system based on GIS and neural network. Comput Eng 35:205–207
Zhang GS, Fu Y, Yan LD et al (2009b) Study on warning indicator system of snow disaster and risk management in headwaters region. Pratacultural Sci 26:144–150
Zhang L, Li GJ, Zhou ZhG et al (2009c) Grey clustering method-based zoning assessment of regional geological disaster. J Nat Disasters 18:164–168
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities Project (Natural Sciences) (310821161014) and Western Region Communications Construction Project, Ministry of Transport, People’s Republic of China (2006 318 000 07).
Author contributions
Hong-liang Qi, Wei-ping Tian and Fei Zhao worked together. Specifically, Hong-liang Qi provided the concepts, conducted all the analysis, interpreted the results and revised the manuscript according to the reviews. Wei-ping Tian provided guidance and insight for the literature. Fei Zhao provided the detailed information and data related to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, Hl., Tian, Wp. & Zhao, F. Risk assessment of snow disaster for trunk highway transportation in Shaanxi, China. Nat Hazards 85, 523–536 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2584-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-016-2584-6