Abstract
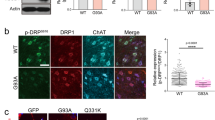
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a severe neurodegenerative disease caused by the loss of upper and lower motor neurons resulting in muscle weakness and paralysis. Recently, VGF, a neuropeptide that is a precursor of bioactive polypeptides, was found to be decreased in ALS patients, and its inducer exerted protective effects in models of ALS. These findings suggested that VGF was involved in the pathology of ALS. Here, we investigated the neuroprotective effects of various VGF-derived peptides in an in vitro ALS model. We applied seven VGF-derived peptides (TLQP-21, AQEE-30, AQEE-11, LQEQ-19, QEEL-16, LENY-13, and HVLL-7) to the motor neuron-derived cell line, NSC-34, expressing SOD1G93A, which is one of the mutated proteins responsible for familial ALS. Nuclear staining revealed that AQEE-30 and LQEQ-19, which are derived from the C-terminal polypeptide of the VGF precursor protein, attenuated neuronal cell death. Furthermore, immunoblot analysis demonstrated that LQEQ-19 promoted the phosphorylation of Akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2, and inhibiting these mitogen-activated MAP kinases (MAPKs) with phosphoinositide 3-kinase or MEK/ERK inhibitors, eliminated the neuroprotective effects of LQEQ-19. In conclusion, these results suggest that VGF C-terminal peptides exert their neuroprotective effects via activation of MAPKs such as Akt and ERK1/2. Furthermore, these findings indicate that VGF-derived peptides have potential application in ALS therapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vande Velde C, Dion PA, Rouleau GA (2011) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: new genes, new models, and new mechanisms. F1000 Biol Rep 3:18
Trani E, Giorgi A, Canu N, Amadoro G, Rinaldi AM, Halban PA, Ferri GL, Possenti R, Schinina ME, Levi A (2002) Isolation and characterization of VGF peptides in rat brain. Role of PC1/3 and PC2 in the maturation of VGF precursor. J Neurochem 81:565–574
Lewis JE, Brameld JM, Jethwa PH (2015) Neuroendocrine role for VGF. Front Endocrinol 6:3
Mead B, Logan A, Berry M, Leadbeater W, Scheven BA (2014) Paracrine-mediated neuroprotection and neuritogenesis of axotomised retinal ganglion cells by human dental pulp stem cells: comparison with human bone marrow and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS ONE 9:e109305
Noli B, Sanna F, Brancia C, D’Amato F, Manconi B, Vincenzoni F, Messana I, Melis MR, Argiolas A, Ferri GL, Cocco C (2017) Profiles of VGF peptides in the rat brain and their modulations after phencyclidine treatment. Front Cell Neurosci 11:158
Sato H, Fukutani Y, Yamamoto Y, Tatara E, Takemoto M, Shimamura K, Yamamoto N (2012) Thalamus-derived molecules promote survival and dendritic growth of developing cortical neurons. J Neurosci 32:15388–15402
Behnke J, Cheedalla A, Bhatt V, Bhat M, Teng S, Palmieri A, Windon CC, Thakker-Varia S, Alder J (2017) Neuropeptide VGF promotes maturation of hippocampal dendrites that is reduced by single nucleotide polymorphisms. Int J Mol Sci 18:612
Jiang C, Lin WJ, Sadahiro M, Labonte B, Menard C, Pfau ML, Tamminga CA, Turecki G, Nestler EJ, Russo SJ, Salton SR (2018) VGF function in depression and antidepressant efficacy. Mol Psychiatry 23:1632–1642
Lewis JE, Brameld JM, Hill P, Cocco C, Noli B, Ferri GL, Barrett P, Ebling FJ, Jethwa PH (2017) Hypothalamic over-expression of VGF in the Siberian hamster increases energy expenditure and reduces body weight gain. PLoS ONE 12:e0172724
Noda Y, Shimazawa M, Tanaka H, Tamura S, Inoue T, Tsuruma K, Hara H (2015) VGF and striatal cell damage in in vitro and in vivo models of Huntington’s disease. Pharmacol Res Perspect 3:e00140
Shimazawa M, Tanaka H, Ito Y, Morimoto N, Tsuruma K, Kadokura M, Tamura S, Inoue T, Yamada M, Takahashi H, Warita H, Aoki M, Hara H (2010) An inducer of VGF protects cells against ER stress-induced cell death and prolongs survival in the mutant SOD1 animal models of familial ALS. PLoS ONE 5:e15307
Valbuena GN, Rizzardini M, Cimini S, Siskos AP, Bendotti C, Cantoni L, Keun HC (2016) Metabolomic analysis reveals increased aerobic glycolysis and amino acid deficit in a cellular model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Mol Neurobiol 53:2222–2240
Miyazaki K, Masamoto K, Morimoto N, Kurata T, Mimoto T, Obata T, Kanno I, Abe K (2012) Early and progressive impairment of spinal blood flow-glucose metabolism coupling in motor neuron degeneration of ALS model mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32:456–467
Zhang W, Ni C, Sheng J, Hua Y, Ma J, Wang L, Zhao Y, Xing Y (2013) TLQP-21 protects human umbilical vein endothelial cells against high-glucose-induced apoptosis by increasing G6PD expression. PLoS ONE 8:e79760
Bartolomucci A, Bresciani E, Bulgarelli I, Rigamonti AE, Pascucci T, Levi A, Possenti R, Torsello A, Locatelli V, Muller EE, Moles A (2009) Chronic intracerebroventricular injection of TLQP-21 prevents high fat diet induced weight gain in fast weight-gaining mice. Genes Nutr 4:49–57
Brancia C, Cocco C, D’Amato F, Noli B, Sanna F, Possenti R, Argiolas A, Ferri GL (2010) Selective expression of TLQP-21 and other VGF peptides in gastric neuroendocrine cells and modulation by feeding. J Endocrinol 207:329–341
Riedl MS, Braun PD, Kitto KF, Roiko SA, Anderson LB, Honda CN, Fairbanks CA, Vulchanova L (2009) Proteomic analysis uncovers novel actions of the neurosecretory protein VGF in nociceptive processing. J Neurosci 29:13377–13388
Okamura H, Tanaka M, Kanemasa K, Ban Y, Inouye ST, Ibata Y (1995) In situ hybridization histochemistry of vgf mRNA in the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus: co-localization with vasopressin/neurophysin and VIP/PHI. Neurosci Lett 189:181–184a
Snyder SE, Peng B, Pintar JE, Salton SR (2003) Expression of VGF mRNA in developing neuroendocrine and endocrine tissues. J Endocrinol 179:227–235
van den Pol AN, Decavel C, Levi A, Paterson B (1989) Hypothalamic expression of a novel gene product, VGF: immunocytochemical analysis. J Neurosci 9:4122–4137
Brancia C, Noli B, Boido M, Boi A, Puddu R, Borghero G, Marrosu F, Bongioanni P, Orru S, Manconi B, D’Amato F, Messana I, Vincenzoni F, Vercelli A, Ferri GL, Cocco C (2016) VGF protein and its C-terminal derived peptides in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: human and animal model studies. PLoS ONE 11:e0164689
Zhao Z, Lange DJ, Ho L, Bonini S, Shao B, Salton SR, Thomas S, Pasinetti GM (2008) VGF is a novel biomarker associated with muscle weakness in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), with a potential role in disease pathogenesis. Int J Med Sci 5:92–99
Akane M, Shimazawa M, Inokuchi Y, Tsuruma K, Hara H (2011) SUN N8075, a novel radical scavenger, protects against retinal cell death in mice. Neurosci Lett 488:87–91
Kotani Y, Morimoto N, Oida Y, Tamura Y, Tamura S, Inoue T, Shimazawa M, Yoshimura S, Iwama T, Hara H (2007) Prevention of in vitro and in vivo acute ischemic neuronal damage by (2S)-1-(4-amino-2,3,5-trimethylphenoxy)-3-{4-[4-(4-fluorobenzyl) phenyl]-1-piperazinyl}-2-propanol dimethanesulfonate (SUN N8075), a novel neuroprotective agent with antioxidant properties. Neuroscience 149:779–788
Oyagi A, Oida Y, Hara H, Izuta H, Shimazawa M, Matsunaga N, Adachi T, Hara H (2008) Protective effects of SUN N8075, a novel agent with antioxidant properties, in in vitro and in vivo models of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res 1214:169–176
Alder J, Thakker-Varia S, Bangasser DA, Kuroiwa M, Plummer MR, Shors TJ, Black IB (2003) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-induced gene expression reveals novel actions of VGF in hippocampal synaptic plasticity. J Neurosci 23:10800–10808
Succu S, Mascia MS, Melis T, Sanna F, Melis MR, Possenti R, Argiolas A (2005) Pro-VGF-derived peptides induce penile erection in male rats: involvement of paraventricular nitric oxide. Neuropharmacology 49:1017–1025
Thakker-Varia S, Jean YY, Parikh P, Sizer CF, Jernstedt Ayer J, Parikh A, Hyde TM, Buyske S, Alder J (2010) The neuropeptide VGF is reduced in human bipolar postmortem brain and contributes to some of the behavioral and molecular effects of lithium. J Neurosci 30:9368–9380
Molteni L, Rizzi L, Bresciani E, Possenti R, Petrocchi Passeri P, Ghe C, Muccioli G, Fehrentz JA, Verdie P, Martinez J, Omeljaniuk RJ, Biagini G, Binda A, Rivolta I, Locatelli V, Torsello A (2017) Pharmacological and biochemical characterization of TLQP-21 activation of a binding site on CHO cells. Front Pharmacol 8:167
Chen YC, Pristera A, Ayub M, Swanwick RS, Karu K, Hamada Y, Rice AS, Okuse K (2013) Identification of a receptor for neuropeptide VGF and its role in neuropathic pain. J Biol Chem 288:34638–34646
Hannedouche S, Beck V, Leighton-Davies J, Beibel M, Roma G, Oakeley EJ, Lannoy V, Bernard J, Hamon J, Barbieri S, Preuss I, Lasbennes MC, Sailer AW, Suply T, Seuwen K, Parker CN, Bassilana F (2013) Identification of the C3a receptor (C3AR1) as the target of the VGF-derived peptide TLQP-21 in rodent cells. J Biol Chem 288:27434–27443
Takata M, Tanaka H, Kimura M, Nagahara Y, Tanaka K, Kawasaki K, Seto M, Tsuruma K, Shimazawa M, Hara H (2013) Fasudil, a rho kinase inhibitor, limits motor neuron loss in experimental models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Br J Pharmacol 170:341–351
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noda, Y., Motoyama, S., Nakamura, S. et al. Neuropeptide VGF-Derived Peptide LQEQ-19 has Neuroprotective Effects in an In Vitro Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Neurochem Res 44, 897–904 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02725-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02725-4