Abstract
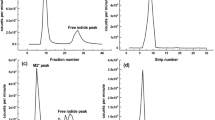
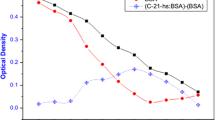
The objective of the present study was oriented to produce and purify polyclonal anti-PRL antibody as the main key store in immunoradiometric assay (IRMA) using solid phase cellulose particles for determination of PRL in human sera. The preparation of 125I-PRL was carried out by lactoperoxidase method for estimation of the titre of antibody production. The preparation of standards was undertaken. The activation of cellulose particles using 1,1-carbonyl diimidazole (CDI) and coupling of these solid phase particles with purified Rabbit anti-PRL were carried out. Optimization and validation of the assay were carried out. Results revealed that the produced PRL polyclonal antibodies have high titre. Cellulose particles IRMA system was highly sensitive and specific. The intra- and inter-assay variations were satisfactory. The recovery and dilution tests indicated accurate calibration and appropriate matrix. The present technique agreed well with IRMA commercial kit. These cellulose particles retained their characteristics during storage for 6 months at 4 °C. In conclusion, this low cost assay could be used as a useful diagnostic tool for diagnosis and follow up of galactorrhea, infertility and pituitary adenoma.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stricker, S., Grueter, F.: Compt. Rend. Soc. Biol. 99, 1978–1980 (1928)
Hwang, P., Guyda, H., Friesen, H.: J. Bid. Chem. 247, 1955–1958 (1972)
Sinha, Y.N., Gilligan, T.A., Lee, D.W., Clin, J.: Endocrinol. Metab. 58, 752–754 (1984)
Harper H.A., Rodwell V.W., Mayes P.A.: Review of Physiological Chemistry, 16th edn, pp. 506–509, Lange Medical Publication, Los Altos (1977)
Nicoll C.S.: Physiological actions of prolactin. In: Greep R.O., Astweed E.B., Knobil E., et al. (eds.) Hand Book of Physiology, Sect. 7: Endocrinology, vol. IV. Am. Physiol. Soc. 23, 253–292 (1974)
Shiu, R.P.C., Friesen, H.G.: Annu. Rev. Rhysiol. 42, 83–96 (1980)
Lyons, W.R., Li, C.H., Johnoson, R.E.: Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 14, 219–254 (1952)
Kleinberg, D.L., Jodd, J., Niemann, W., Clin, J.: Endocrinol. Metab. 47, 435–441 (1978)
Parker, D.E., Rossman, L.G., Vander Laan, E.F.: J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 36, 1119–1124 (1973)
Thorner, M.O., Round, J., Jones, A., et al.: Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 7, 463–468 (1977)
El-Kolaly, M.T., Mehany, N.L., Ragab, M.T., El-Mohty, A.A.: Arab J. Nucl. Sci. Appl. 34(2), 105–116 (2001)
Maiolini, R., Ferrua, B., Masseyeff, R., Immunol, J.: Methods 6(4), 355–362 (1975)
Persoon, T.J.: In: Berner, D.R., Langan, J.K., Wells, L.D. (eds.) Nuclear medicine technology and technique, pp. 433. The C.V. Mosby Company, St. Louis, Toronto, London (1981)
Steinbuch, M., Audran, R.: Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 134, 279–284 (1969)
Edwards R., Price J., Lalloz M., Pull I.: Devolution of RIA to the Routine Clinical Chemistry Laboratory. In: 3rd European Congress of Clinical Chemistry Abstracts, pp. 69 (1979)
Bethell, G.S., Ayers, J.S., Mancock, W.S., Hearn, M.T.W.: J. Biol. Chem. 154, 2572 (1979)
Chapman, R.S., Sutherland, R.M., Ratcliffe, G.: Application of 1,1 carbonyl-diimidazole and a rapid practical method for the production of solid phase immunoassay reagents. In: Hunter, W.M., Corrie, J.E.T. (eds.) Immunoassay for Clinical Chemistry, 2nd edn, pp. 178. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh (1983)
Ragab, M.T., Moustafa, K.A., El-Kolaly, M.T.: Arab J. Nucl. Sci. Appl. 35(2), 63 (2002)
Edwards, R.: In: Edwards, R. (ed.) Immunoassay, pp. 22. Wiley, Toronto (1996)
Miles, L.E.M., Lipschitz, D.A., Bieber, C.P., Cook, J.D.: Analyt. Biochem. 61, 209 (1974)
Ribela M.T.C.P., Peroni C.N., Bartokini P.: Antibodies immobilized on magnetic particles for radioimmunoassay and immunoradiometric assay for hormones. Final Report of Coordinated Research Program, 1991–1995, vol. 107, pp. 25, IAEA, Vienna (1996).
Pillai, M.R.A., Bhandarkar, S.D.: Radioimmunoassay principle and practice, 2nd edn. Head Isotope Division, Bhabha Atomic Energy Center, India (1998)
Conway, M.G., Biggart, E.M., Chapman, R.S.: J. Immunol. Meth. 104, 87 (1987)
Peroni C.N., Ribela M.T.C., Bartolini P.: Final Report of a Coordinated Research Program, 1991–1995, vol. 107, IAEA, Vienna (1996)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shafik, H.M. Immunoradiometric assay for in-vitro determination of prolactin hormone in human serum or plasma using solid phase anti-PRL cellulose particles. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 281, 639–646 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-009-0043-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-009-0043-5