Abstract
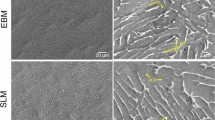
FeSiB alloys have been fabricated by selective laser melting (SLM) using a laser scan rate of 0.1–1.5 m/s, laser power of 90 W, scan line spacing of 40 μ m, and layer thickness of 50 μ m. X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy, profilometer, microdurometer, and vibrating sample magnetometer have been used to investigate the structural, microstructural, roughness, microhardness, and magnetic property changes during the laser melting process. The produced samples exhibit a nanocomposite structure consisting of nanocrystalline α-Fe0.95Si0.05 and Fe2B phases embedded into an amorphous ε-FeSi-type matrix. The selective laser-melted samples show high density, low surface roughness, higher microhardness values (1654–2273 Hv), and soft magnetic properties (Ms = 188.6–199 emu/g and Hc = 43.8–73 Oe).














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chua, C.K., Leong, K.F.: 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing: Principles and Applications, 4th ed. World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd, Singapore (2014)
Yasa, E., Kruth, J., Deckers, J.: Manufacturing by combining selective laser melting and selective laser erosion/laser re-melting. J. Man. Techn. 60, 263–266 (2011)
Gu, D.D., Meiners, W., Wissenbach, K., Poprawe, R.: Laser additive manufacturing of metallic components: materials, processes and mechanisms. Int. Mater. Rev. 57, 133–164 (2012)
Buchbinder, D., Schleifenbaum, H., Heidrich, S., Meiners, W., Bültmann, J.: High power selective laser melting (HPSLM) of aluminium parts. Phys. Procedia A 12, 271–278 (2011)
Song, B., Dong, S., Coddet, P., Zhou, G., Ouyang, S., Liao, H., Coddet, C.: Microstructure and tensile behavior of hybrid nano-micro SiC reinforced iron matrix composites produced by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compds. 579, 415–419 (2013)
Jia, Q., Gu, D.: Selective laser melting additive manufacturing of Inconel 718 superalloy parts: densification, microstructure and properties. J. Alloys Compds. 585, 713–721 (2014)
Yadroitsev, I.: Selective Laser Melting: Direct Manufacturing of 3D-Objects by Selective Laser Melting of Metal Powders. LAP Lambert Academic Publishing AG & Co KG (2009)
Zhang, B.C., Liao, H.L., Coddet, C.: Microstructure evolution and density behavior of CP Ti parts elaborated by self-developed vacuum selective laser melting system. Appl. Surf. Sci. 279, 310–316 (2013)
Ma, M., Wang, Z., Wang, D., Zeng, X.: Control of shape and performance for direct laser fabrication of precision large-scale metal parts with 316L stainless steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 45, 209–210 (2013)
Efimov, Y.V., Mukhin, G.G., Lazarev, E.M., Korotkov, N.A., Ryabtsev, L.A., Dmitriev, V.N., Frolova, T.M.: The structure of rapidly hardened Fe-Si-B alloys. Russ. Metall. 4, 167–173 (1986)
Haginaro, M., Inoue, A., Masu, T.: Mechanical properties of FeSiB amorphous wires produced by in-rotating-water spinning method. Metal. Trans. A 13, 373–382 (1982)
Suwa, Y., Agatsuma, S., Hashi, S., Ishiyama, K.: Study of strain sensor using FeSiB magnetoresistive thin films. IEEE Trans. Magn. 46(2), 666–669 (2010)
Li, S., Horikawa, S., Park, M., Chai, Y., Vodyanoy, V.J., Chi, B.A.: Amorphous metallic glass biosensors. Intermetallics 30, 80–85 (2012)
Inoue, A., Komuro, M., Masumoto, T.: Fe-si-b amorphous alloys with high silicon concentration. J. Mater. Sci. 19, 4125 (1984)
Alleg, S., Ibrir, M., Fenineche, N.E., Azzaza, S., Suñol, J.J.: Magnetic and structural characterization of the mechanically alloyed Fe75Si15B10 powders. J. Alloys Compds. 494, 109–115 (2010)
Murty, B.S., Ranganathan, S.: Novel materials synthesis by mechanical alloying/milling. Int. Mater. Rev. 43(3), 101–141 (1998)
Quispe Marcatoma, J., Peña Rodrígueze, V.A., Baggio-Saitovitch M.: Fesib amorphous alloy prepared by mechano-synthesis. Hyp. Int. 134, 207–212 (2001)
Takahara, Y., Matsuda, H.: Effect of cold rolling on the physical properties and the structure of Fe79B16Si15 amorphous alloy. Trans. JIM 28, 535 (1987)
Coïsson, M., Celegato F., Olivetti E., Tiberto P., Vinai F., Baricco M.: Stripe domains and spin reorientation transition in Fe78B13Si9 thin films produced by rf sputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 104(3), 033902 (2008)
Alleg, S., Ibrir, M., Fenineche, N.E., Suñol, J.J.: Microstructure and magnetic properties of HVOF thermally sprayed Fe75Si15B10 coatings. Surf. Coat. Techn. 205(2), 281–286 (2010)
Dong, S., Song, B., Zhang, X., Deng, C., Fenineche, N.E., Hansz, B., Liao, H., Coddet, C.: Fabrication of FeSiB magnetic coatings with improved saturation magnetization by plasma spray and dry-ice blasting. J. Alloys Compds. 584, 254–260 (2014)
Sypień, A., Kusinski, J., Stobiecki, T., Czapkiewicz, M.: TEM Study of the FeSiB amorphous alloy nanocrystallized by means of nd:YAG pulsed laser heating. Mat. Chem. Phys. 81, 390–392 (2003)
Katakam, S., Hwang, J.Y., Vora, H., Harimkar, S.P., Banerjee, R., Dahotre, N.B.: Laser-induced thermal and spatial nanocrystallization of amorphous Fe–Si–B alloy. J. Scr. Mater. 66, 538–54 (2012)
Lutterotti, L.: MAUD CPD Newsletter (IUCr), 24 (2000)
Rietveld, H.M.: A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. Acta Crystallogr. 2, 65–71 (1969)
Vocadlo, L., Knight, K.S., Price, G.D., Wood, I.G.: Thermal expansion and crystal structure of FeSi between 4 and 1173 K determined by time-of-flight neutron powder diffraction. Phys. Chem. Minerals 29, 132–139 (2002)
Le Bail, A.: Modelling the silica glass structure by the Rietveld method. J. Non-Crystalline Solids 183, 39–42 (1995)
Tokunaga, T., Ohtani, H., Hasebe, M.: Thermodynamic evaluation of the phase equilibria and glass-forming ability of the Fe–Si–B system. Calphad 28, 354–362 (2004)
de Boer, F., Boom, R., Mattens, W.C.M., Miedema, A.R., Niessen, A.K.: Cohesion in Metals, p 276. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1988)
Omori, S., Moriyama, J.: Thermodynamic properties of Fe2B and FeB by EMF measurements of cells with solid oxide electrolytes. Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met. 217, 90–796 (1980)
Raghavan, V.: B-fe-si (boron-iron-silicon). journal of phase equilibria and diffusion, materials park 28, 380–381 (2007)
Iga, A., Tawara, Y., Yanase, A.: Magnetocrystalline anisotropy of Fe2B. J. Phys. Soc. Jap. 21(2), 404–404 (1966)
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministère de l’Enseignement Supérieur et de la Recherche Scientifique Algérie.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alleg, S., Drablia, R. & Fenineche, N. Effect of the Laser Scan Rate on the Microstructure, Magnetic Properties, and Microhardness of Selective Laser-Melted FeSiB. J Supercond Nov Magn 31, 3565–3577 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4621-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4621-z