Abstract
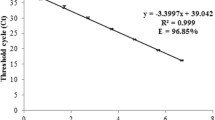
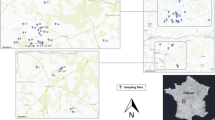
Skeletonema is a dominant diatom, especially in coastal waters. However, species identification and quantification in the natural environment has not yet been established, as species identification can be nearly impossible with light microscopy. In the present study, we developed primer sets for multiplex and real-time PCR to identify and enumerate the 10 Skeletonema species, and applied this technique to samples obtained from the tidal zone of the Chikugo River and its adjacent waters of the Ariake Sea from spring to summer. In total, eight Skeletonema species were detected during the investigation. Among the eight, the S. marinoi–dohrnii complex was detected at all three stations. Skeletonema potamos was the second most frequently detected, mainly in the Chikugo River. The overall number of detected species was low at the upper tidal zone of the Chikugo River, where salinity was < 2. These results reveal the diverse Skeletonema community in the brackish environment, and the primer sets designed in the present study are useful for analyzing species composition of Skeletonema.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balzano S, Sarno D, Kooistra WHCF (2011) Effects of salinity on the growth rate and morphology of ten Skeletonema strains. J Plankton Res 33:937–945
Bowers HA, Tengs T, Glasgow HB Jr, Burkholder JM, Rublee PA, Oldach DW (2000) Development of real-time PCR assays for rapid detection of Pfiesteria piscicida and related dinoflagellates. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:4641–4648
Canesi KL, Rynearson TA (2016) Temporal variation of Skeletonema community composition from a long-term time series in Narragansett Bay identified using high-throughput DNA sequencing. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 556:1–16
Duleba M, Ector L, Horváth Z, Kiss KT, Molnár LF, Pohner Z, Szilágyi Z, Tóth B, Vad CF, Várbíró G, Ács É (2014) Biogeography and phylogenetic position of a warm-stenotherm centric diatom, Skeletonema potamos (C.I. Weber) Hasle and its long-term dynamics in the River Danube. Protist 165:715–729
Gallagher JC (1980) Population genetics of Skeletonema costatum (Bacillariophyceae) in Narragansett Bay. J Phycol 16:464–474
Genovesi B, Shin-Grzebyk M-S, Grzebyk D, Laabir M, Gagnaire P-A, Vaquer A, Pastoureaud A, Lasserre B, Collos Y, Berrebi P, Masseret E (2011) Assessment of cryptic species diversity within blooms and cyst bank of the Alexandrium tamarense complex (Dinophyceae) in a Mediterranean lagoon facilitated by semi-multiplex PCR. J Plankton Res 33:405–414
Handy SM, Coyne KJ, Portune KJ, Demir E, Doblin MA, Hare CE, Cary SC, Hutchins DA (2005) Evaluating vertical migration behavior of harmful raphidophytes in the Delaware Inland Bays utilizing quantitative real-time PCR. Aquat Microb Ecol 40:121–132
Kaeriyama H, Katsuki E, Otsubo M, Yamada M, Ichimi K, Tada K, Harrison PJ (2011) Effects of temperature and irradiance on growth of strains belonging to seven Skeletonema species isolated from Dokai Bay, southern Japan. Eur J Phycol 46:113–124
Kamikawa R, Nagai S, Hosoi-Tanabe S, Itakura S, Yamaguchi M, Uchida Y, Baba T, Sako Y (2007) Application of real-time PCR assay for detection and quantification of Alexandrium tamaranse and Alexandrium catenella cysts from marine sediments. Harmful algae 6:413–420
Kooistra WHCF, Sarno D, Balzano S, Gu H, Andersen RA, Zingone A (2008) Global diversity and biogeography of Skeletonema species (Bacillariophyta). Protist 159:177–193
Medlin LK, Kooistra WHCF (2010) Methods to estimate the diversity in the marine photosynthetic protist community with illustrations from case studies: a review. Diversity 2:973
Nagai S (2011) Development of a multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of six Alexandrium species (Dinophyceae). J Phycol 47:703–708
Oliveira DC, de Lencastre H (2002) Multiplex PCR strategy for rapid identification of structural types and variants of the mec element in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Ch 46:2155–2161
Ouahid Y, del Campo FF (2009) Typing of toxinogenic Microcystis from environmental samples by multiplex PCR. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:405–412
Park TG, de Salas MF, Bolch CJS, Hallegraeff GM (2007) Development of a real-time PCR probe for quantification of the heterotrophic dinoflagellate Cryptoperidiniopsis brodyi (Dinophyceae) in environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2552–2560
Park BS, Baek SH, Ki J-S, Cattolico RA, Han MS (2012) Assessment of EvaGreen-based quantitative real-time PCR assay for enumeration of the microalgae Heterosigma and Chattonella (Raphidophyceae). J Appl Phycol 24:1555–1567
Sarno D, Kooistra WHCF, Medlin LK, Percopo I, Zongone A (2005) Diversity in the genus Skeletonema (Bacillariophyceae). II. An assessment of the taxonomy of S. costatum-like species with the description of four new species. J Phycol 41:151–176
Sarno D, Kooistra WHCF, Balzano S, Hargraves PE, Zingone A (2007) Diversity in the genus Skeletonema (Bacillariophyceae): III. Phylogenetic position and morphological variability of Skeletonema costatum and Skeletonema grevillei, with the description of Skeletonema ardens sp. nov. J Phycol 43:156–170
Smayda TJ (1973) The growth of Skeletonema costatum during a winter-spring bloom in Narragansett Bay, Rhode Island. Norw J Bot 20:219–247
Yamada M, Katsuki E, Otsubo M, Kawaguchi M, Ichimi K, Kaeriyama H, Tada K, Harrison PJ (2010) Species diversity of the genus Skeletonema (Bacillariophyceae) in the industrial harbor Dokai Bay, Japan. J Oceanogr 66:755–771
Yamada M, Otsubo M, Tsutsumi Y, Mizota C, Iida N, Okamura K, Kodama M, Umehara A (2013) Species diversity of the marine diatom genus Skeletonema in Japanese brackish water areas. Fish Sci 79:923–934
Yamada M, Otsubo M, Kodama M, Yamamoto K, Nishikawa T, Ichimi K, Tada K, Harrison PJ (2014) Species composition of Skeletonema (Bacillariophyceae) in planktonic and resting-stage cells in Osaka and Tokyo Bays. Plankton Benthos Res 9:168–175
Yamada M, Otsubo M, Tada K, Nakano Y, Matsubara T, Iida N, Endo Y, Montani S (2017) Species composition of the genus Skeletonema (Bacillariophyceae) in five Japanese coastal waters over the subtropics from the subarctic zone. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 83:25–33 (In Japanese with English abstract)
Zingone A, Percopo I, Sims PA, Sarno D (2005) Diversity in the genus Skeletonema (Bacillariophyceae). I. A reexamination of the type material of S. costatum with the description of S. grevillei sp. nov. J Phycol 41:140–150
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (25450259, 16K07508) from JSPS, Kasen-kikin (Nos. 261211018, 285211023) from Kasen Zaidan, and the Cooperative Monitoring Program of the Ariake Sea (COMPAS) of Saga University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Enjoji, N., Katano, T., Yoshinaka, Y. et al. Development of primer sets for multiplex and qPCR assays targeting Skeletonema species and their application to field samples. J Oceanogr 75, 319–334 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-018-00504-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-018-00504-3