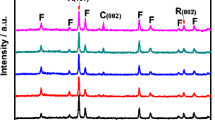
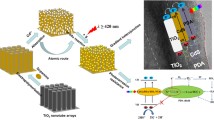
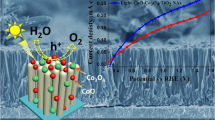
Abstract
Photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting into hydrogen and oxygen using hybridized semiconductor photoelectrodes has become a promising strategy for converting solar energy into clean and sustainable H2 fuel. Here, we report a promising hybrid photoanode constructed by electrodepositing an amorphous Co–Pi film onto semiconducting CdSe/TiO2 nanowire arrays for photoelectrochemical hydrogen production. This photoanode exhibits a high water-splitting photocurrent density, which is attributed to the broad visible light absorption and efficient charge carrier separation by the virtue of the type-II heterojunction formed between TiO2 and CdSe. Photoconversion efficiency of Co–Pi/CdSe/TiO2 and CdSe/TiO2 photoanodes increase by 3.3 and 2.1 times, compared with the pristine TiO2 photoanode. Moreover, Co–Pi/CdSe/TiO2 photoelectrode shows greatly improved PEC stability, the drop in photocurrent of Co–Pi/CdSe/TiO2 nanowire arrays photoelectrode is about 10% after 1 h illumination, because of the addition of the Co–Pi film protecting the light absorber CdSe/TiO2 from photocorrosion. The enhanced PEC performance mechanism of triple hybrid photoanode is also discussed in this paper.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen X, Shen S, Guo L, Mao SS (2010) Semiconductor-based photocatalytic hydrogen generation. Chem Rev 110:6503–6570
Maeda K, Domen K (2016) Development of novel photocatalyst and cocatalyst materials for water splitting under visible light. Bull Chem Soc Jpn 89:627–648
Su T, Shao Q, Qin Z, Guo Z, Wu Z (2018) Role of interfaces in two-dimensional photocatalyst for water splitting. ACS Catal 8:2253–2276
Wen J, Xie J, Chen X, Li X (2017) A review on g-C3N4-based photocatalysts. Appl Surf Sci 391:72–123
Sun J, Zhong DK, Gamelin DR (2010) Composite photoanodes for photoelectrochemical solar water splitting. Energy Environ Sci 3:1252
Fujishima A, Honda K (1972) Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 238:37–38
Qu X, Xie D, Gao L, Cao L, Du F (2014) Synthesis and characterization of TiO2/WO3 composite nanotubes for photocatalytic applications. J Mater Sci 50:21–27
Vanalakar SA, Mali SS, Pawar RC, Tarwal NL, Moholkar AV, Kim JH, Patil PS (2012) Photoelectrochemical properties of CdS sensitized ZnO nanorod arrays: effect of nanorod length. J Appl Phys 112:044302
Wang G, Ling Y, Wheeler DA, George KE, Horsley K, Heske C, Zhang JZ, Li Y (2011) Facile synthesis of highly photoactive α-Fe2O3-based films for water oxidation. Nano Lett 11:3503–3509
Ye SH, He XJ, Ding LX, Pan ZW, Tong YX, Wu M, Li GR (2014) Cu2O template synthesis of high-performance PtCu alloy yolk–shell cube catalysts for direct methanol fuel cells. Chem Commun 50:12337–12340
de Respinis M, Joya KS, De Groot HJM, D’Souza F, Smith WA, van de Krol R, Dam B (2015) Solar water splitting combining a BiVO4 light absorber with a Ru-based molecular cocatalyst. J Phys Chem C 119:7275–7281
Luo J, Ma L, He T, Ng CF, Wang S, Sun H, Fan HJ (2012) TiO2/(CdS, CdSe, CdSeS) nanorod heterostructures and photoelectrochemical properties. J Phys Chem C 116:11956–11963
Cheng C, Zhang H, Ren W, Dong W, Sun Y (2013) Three dimensional urchin-like ordered hollow TiO2/ZnO nanorods structure as efficient photoelectrochemical anode. Nano Energy 2:779–786
Chen HM, Chen CK, Liu RS, Zhang L, Zhang J, Wilkinson DP (2012) Nano-architecture and material designs for water splitting photoelectrodes. Chem Soc Rev 41:5654–5671
Song X, Li W, He D, Wu H, Ke Z, Jiang C, Wang G, Xiao X (2018) The “Midas Touch” Transformation of TiO2 nanowire arrays during visible light photoelectrochemical performance by carbon/nitrogen coimplantation. Adv Energy Mater 8:1800165
Li Z, Yao C, Wang F, Cai Z, Wang X (2014) Cellulose nanofiber-templated three-dimension TiO2 hierarchical nanowire network for photoelectrochemical photoanode. Nanotechnology 25:504005
Xu Z, Yin M, Sun J, Ding G, Lu L, Chang P, Chen X, Li D (2016) 3D periodic multiscale TiO2 architecture: a platform decorated with graphene quantum dots for enhanced photoelectrochemical water splitting. Nanotechnology 27:115401
Chen C, Wei Y, Yuan G, Liu Q, Lu R, Huang X, Cao Y, Zhu P (2017) Synergistic effect of Si doping and heat treatments enhances the photoelectrochemical water oxidation performance of TiO2 nanorod arrays. Adv Funct Mater 27:1701575
Asahi R, Morikawa T, Ohwaki T, Aoki K, Taga Y (2001) Visible-light photocatalysis in nitrogen-doped titanium oxides. Science 293:269–271
Xu M, Da P, Wu H, Zhao D, Zheng G (2012) Controlled Sn-doping in TiO2 nanowire photoanodes with enhanced photoelectrochemical conversion. Nano Lett 12:1503–1508
Wu N (2018) Plasmonic metal-semiconductor photocatalysts and photoelectrochemical cells: a review. Nanoscale 10:2679–2696
Liu G, Du K, Xu J, Chen G, Gu M, Yang C, Wang K, Jakobsen H (2017) Plasmon-dominated photoelectrodes for solar water splitting. J Mater Chem A 5:4233–4253
Wei Y, Ke L, Kong J, Liu H, Jiao Z, Lu X, Du H, Sun XW (2012) Enhanced photoelectrochemical water-splitting effect with a bent ZnO nanorod photo anode decorated with Ag nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 23:235401
Li X, Yu J, Low J, Fang Y, Xiao J, Chen X (2015) Engineering heterogeneous semiconductors for solar water splitting. J Mater Chem A 3:2485–2534
Li H, Cheng C, Li X, Liu J, Guan C, Tay YY, Fan HJ (2012) Composition-graded ZnxCd1−xSe@ZnO core–shell nanowire array electrodes for photoelectrochemical hydrogen generation. J Phys Chem C 116:3802–3807
Wang C, Sun L, Yun H, Li J, Lai Y, Lin C (2009) Sonoelectrochemical synthesis of highly photoelectrochemically active TiO2 nanotubes by incorporating CdS nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 20:295601
Bang JH, Kamat PV (2010) Solar cells by design: photoelectrochemistry of TiO2 nanorod arrays decorated with CdSe. Adv Funct Mater 20:1970–1976
Chen C, Ye M, Lv M, Gong C, Guo W, Lin C (2014) Ultralong rutile TiO2 nanorod arrays with large surface area for CdS/CdSe quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. Electrochim Acta 121:175–182
Lee J-C, Kim TG, Choi H-J, Sung Y-M (2007) Enhanced photochemical response of TiO2/CdSe heterostructured nanowires. Cryst Growth Des 7:2588
Mukherjee B, Smith YR, Subramanian V (2012) CdSe nanocrystal assemblies on anodized TiO2 nanotubes: optical, surface, and photoelectrochemical properties. J Phys Chem C 116(29):15175–15184
Liu Y, Zhao L, Li M, Guo L (2014) TiO2/CdSe core-shell nanofiber film for photoelectrochemical hydrogen generation. Nanoscale 6:7397–7404
Hensel J, Wang G, Li Y, Zhang JZ (2010) Synergistic effect of cdse quantum dot sensitization and nitrogen doping of TiO2 nanostructures for photoelectrochemical solar hydrogen generation. Nano Lett 10:478–483
Abbasi A, Ghanbari D, Salavati-Niasari M, Hamadanian M (2016) Photo-degradation of methylene blue: photocatalyst and magnetic investigation of Fe2O3–TiO2 nanoparticles and nanocomposites. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27:4800–4809
Lutterman DA, Surendranath Y, Nocera DG (2009) A self-healing oxygen-evolving catalyst. J Am Chem Soc 131:3838–3839
Li Y, Wang R, Li H, Wei X, Feng J, Liu K, Dang Y, Zhou A (2015) Efficient and stable photoelectrochemical seawater splitting with TiO2@g-C3N4 nanorod arrays decorated by Co–Pi. J Phys Chem C 119(35):20283–20292
Moniz SJA, Zhu J, Tang J (2014) 1D Co–Pi modified BiVO4/ZnO junction cascade for efficient photoelectrochemical water cleavage. Adv Energy Mater 4:1301590
Seabold JA, Choi K-S (2011) Effect of a cobalt-based oxygen evolution catalyst on the stability and the selectivity of photo-oxidation reactions of a WO3 photoanode. Chem Mater 23:1105–1112
Barroso M, Cowan AJ, Pendlebury SR, Gratzel M, Klug DR, Durrant JR (2011) The role of cobalt phosphate in enhancing the photocatalytic activity of α-Fe2O3 toward water oxidation. J Am Chem Soc 133:14868–14871
Li Y, Takata T, Cha D, Takanabe K, Minegishi T, Kubota J, Domen K (2013) Vertically aligned Ta3N5 nanorod arrays for solar-driven photoelectrochemical water splitting. Adv Mater 25:125–131
Pilli SK, Furtak TE, Brown LD, Deutsch TG, Turner JA, Herring AM (2011) Cobalt-phosphate (Co–Pi) catalyst modified Mo-doped BiVO4 photoelectrodes for solar water oxidation. Energy Environ Sci 4:5028
Liu B, Wang D, Wang L, Sun Y, Lin Y, Zhang X, Xie T (2013) Glutathione-assisted hydrothermal synthesis of CdS-decorated TiO2 nanorod arrays for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. Electrochim Acta 113:661–667
Liu B, Aydil ES (2009) Growth of oriented single-crystalline rutile TiO2 nanorods on transparent conducting substrates for dye-sensitized solar cells. J Am Chem Soc 131:3985–3990
Erat S, Metin H, Arı M (2008) Influence of the annealing in nitrogen atmosphere on the XRD, EDX, SEM and electrical properties of chemical bath deposited CdSe thin films. Mater Chem Phys 111:114–120
Luo Q, Wu Z, He J, Cao Y, Bhutto WA, Wang W, Zheng X, Li S, Lin S, Kong L, Kang J (2015) Facile synthesis of composition-tuned ZnO/ZnxCd1−xSe nanowires for photovoltaic applications. Nanoscale Res Lett 10:181
Sudhagar P, Chandramohan S, Kumar RS, Sathyamoorthy R, Hong C-H, Kang YS (2011) Fabrication and charge-transfer characteristics of CdS QDs sensitized vertically grown flower-like ZnO solar cells with CdSe cosensitizers. Phys Stat Sol (a) 208:474–479
Zhang G, Miao H, Wang Y, Zhang D, Fan J, Han T, Mu J, Hu X (2017) The fabrication and photoelectrocatalytic study of composite ZnSe/Au/TiO2 nanotube films. J Phys D Appl Phys 50:185102
Ai G, Mo R, Li H, Zhong J (2015) Cobalt phosphate modified TiO2 nanowire arrays as co-catalysts for solar water splitting. Nanoscale 7:6722–6728
Wang G, Wang H, Ling Y, Tang Y, Yang X, Fitzmorris RC, Wang C, Zhang JZ, Li Y (2011) Hydrogen-treated TiO2 nanowire arrays for photoelectrochemical water splitting. Nano Lett 11:3026–3033
Yu Q, Meng X, Wang T, Li P, Ye J (2015) Hematite films decorated with nanostructured ferric oxyhydroxide as photoanodes for efficient and stable photoelectrochemical water splitting. Adv Funct Mater 25:2686–2692
Kim JH, Jang JW, Kang HJ, Magesh G, Kim JY, Kim JH, Lee J, Lee JS (2014) Palladium oxide as a novel oxygen evolution catalyst on BiVO4 photoanode for photoelectrochemical water splitting. J Catal 317:126–134
Ai G, Li H, Liu S, Mo R, Zhong J (2015) Solar water splitting by TiO2/CdS/Co–Pi nanowire array photoanode enhanced with Co–Pi as hole transfer relay and CdS as light absorber. Adv Funct Mater 25(35):5706–5713
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11574081).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, Z., Yin, Y., Yang, W. et al. Amorphous Co–Pi anchored on CdSe/TiO2 nanowire arrays for efficient photoelectrochemical hydrogen production. J Mater Sci 54, 3284–3293 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-3079-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-3079-5