Abstract
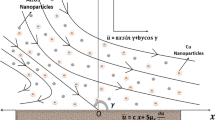
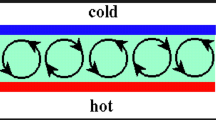
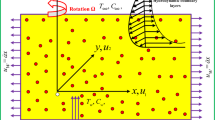
This study investigates the oblique flow of a nanofluid near a stagnation point past a lubricated plate. A power-law fluid is utilized for lubrication. A suitable set of transformation is utilized to obtain system of dimensionless governing equations. A well-known numerical technique known as Keller-box method is employed to get the similar solution. Influence of emerging parameters on the flow characteristics has been discussed in the presence of lubrication through graphs and numerical data ranging from no slip (\(\beta \to \infty )\) to full slip (\(\beta \to 0)\). Impact of thermophoresis and Brownian motion is further investigated. A comparison in the special cases between the present and published data validates this work.














Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(Q\) :
-
Flow rate
- \(T_{\text{w}}\) :
-
Wall temperature
- \(T_{\infty }\) :
-
Free stream temperature
- \(T\) :
-
Fluid temperature
- \(\delta\) :
-
Thickness of lubrication layer
- \(C\) :
-
Concentration of nanoparticles
- \(x,y\) :
-
Rectangular coordinates
- \(u,v\) :
-
Velocity components in \(x\) and \(y\) directions for nanofluid
- \(k\) :
-
Consistency coefficient
- \(\rho_{\text{f}}\) :
-
Density of base fluid
- \(D_{\text{B}}\) :
-
Brownian diffusion coefficient
- \(\alpha\) :
-
Boundary layer displacement
- \(\lambda\) :
-
Free parameter
- \(N_{\text{b}}\) :
-
Brownian motion parameter
- \(\eta\) :
-
Dimensionless independent variable
- \(L_{\text{visc}}\) :
-
Viscous length scale
- \(C_{\text{w}}\) :
-
Concentration at wall
- \(u_{e} , v_{e}\) :
-
Free stream velocities
- \(C_{\infty }\) :
-
Concentration at free stream
- \(\beta\) :
-
Slip (lubrication) parameter
- \(\mu_{L}\) :
-
Apparent viscosity
- \(D_{\text{T}}\) :
-
Thermophoresis diffusion coefficient
- \(N_{\text{t}}\) :
-
Thermophoresis parameter
- \(U,V\) :
-
Velocity components in \(x\) and \(y\) directions for a power-law fluid
- \(n\) :
-
Flow behavior index
- \(\rho_{\text{p}}\) :
-
Density of nanoparticles
- \(\nu\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity
- \(\alpha^{*}\) :
-
Thermal diffusivity
- \(\gamma\) :
-
Shear at free stream
- \(\phi\) :
-
Dimensionless concentration
- \(Pr\) :
-
Prandtl number
- \(\theta\) :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- \(f,g\) :
-
Dimensionless velocities
- \(L_{\text{lub}}\) :
-
Lubrication length scale
References
Ahmad K, Nazar R (2010) Unsteady MHD mixed convection stagnation-point flow of a viscoelastic fluid on a vertical surface. J Quart Meas Anal 6:105–117
Blyth MG, Pozrikidis C (2005) Stagnation-point flow against a liquid film on a plane wall. Acta Mech 180:203–219
Borrelli A, Giantesio G, Patria MC (2012) MHD oblique stagnation-point flow of a Newtonian fluid. ZAMP 63:271–294
Bradshaw P, Cebeci T, Whitelaw JH (1981) Engineering calculation methods for turbulent flows. Academic, London
Buongiorno J (2006) Convective transport in nanofluids. ASME J Heat Transf 128:240–250
Buongiorno J et al (2009) A benchmark study on the thermal conductivity of nanofluids. J Appl Phys 106:094312
Cebeci T, Bradshaw P (1984) Physical and computational aspects of convective heat transfer. Springer, New York
Choi SUS (1995) Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. ASME Int Mech Eng 66:99–105
Dalkilic AS, Kayaci N, Celen A, Tabatabaei M, Yildiz O, Daungthongsuk W, Wongwises S (2012) Forced convective heat transfer of nanofluids: a review of the recent literature. Curr Nanosci 8:949–969
Das SK, Choi SUS, Yu W (2007) Nanofluids, science and technology. Wiley, Hoboken
Daungthongsuk W, Wongwises S (2007) A critical review of convective heat transfer nanofluids. Renew Sustain Eng Rev 11:797–817
Dorrepaal JM (1986) An exact solution of the Navier–Stokes equation which describes non-orthogonal stagnation-point flow in two dimensions. J Fluid Mech 163:141–147
Dorrepaal JM (2000) Is two-dimensional oblique stagnation point flow unique? Can Appl Math Q 8:61–66
Drazin P, Riley N (2006) The Navier–Stokes equations: a classification of flows and exact solutions. Lond Math Soc Lect Note Ser 334:1–196
Ghaffari A, Javed T, Labropulu F (2015) Oblique stagnation point flow of a non-Newtonian nanofluid over stretching surface with radiation: a numerical study. Therm Sci. doi:10.2298/TSCI150411163G
Ghaffari A, Javed T, Majeed A (2016) Influence of radiation on non-Newtonian fluid in the region of oblique stagnation point flow in a porous medium: a numerical study. Transp Porous Med 113:245–266
Javed T, Ghaffari A, Ahmad H (2015) Numerical study of unsteady MHD oblique stagnation point flow with heat transfer over an oscillating flat plate. Can J Phys 93:1138–1143
Kakac S, Pramuanjaroenkij A (2009) Review of convective heat transfer enhancement with nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf 52:3187–3196
Keller HB (1970) A new difference scheme for parabolic problems. In: Bramble J (ed) Numerical solution of partial-differential equations, vol II. Academic, New York
Keller HB, Cebeci T (1972) Accurate numerical methods for boundary layer flows II: two dimensional turbulent flows. AIAA J 10:1193–1199
Labropulu F, Ghaffar A (2014) Oblique Newtonian fluid flow with heat transfer towards a stretching sheet. Comput Probl Eng 307:93–103
Labropulu F, Li D (2008) Stagnation-point flow of a second grade fluid with slip. Int J Non-Linear Mech 43:941–947
Lok YY, Amin N, Pop I (2006) Non-orthogonal stagnation-point flow towards a stretching sheet. Int J Non-Linear Mech 41:622–627
Lok YY, Merkin JH, Pop I (2015) MHD oblique stagnation-point flow towards a stretching/shrinking surface. Meccanica 50:2949–2961
Mahmood K, Sajid M, Ali N (2016a) Non-orthogonal stagnation-point flow of a second-grade fluid past a lubricated surface. ZNA 71:273–280
Mahmood K, Sajid M, Ali N, Javed T (2016b) Slip flow of a second grade fluid past a lubricated rotating disc. Int J Phys Sci 11:96–103
Mahmood K, Sajid M, Ali N, Javed T (2016c) Heat transfer analysis in the time-dependent slip flow over a lubricated surface. Eng Sci Technol Int J 19:1949–1957
Mahmood K, Sajid M, Ali N, Javed T (2016d) Heat transfer analysis in the time-dependent axisymmetric stagnation point flow over a lubricated surface. Therm Sci. doi:10.2298/TSCI160203257M
Mohammed HA, Bhaskaran G, Shuaib NH, Saidur R (2011) Heat transfer and fluid flow characteristics in microchannels heat exchanger using nanofluids: a review. Renew Sustain Eng Rev 15:1502–1512
Sajid M, Mahmood K, Abbas Z (2012) Axisymmetric stagnation-point flow with a general slip boundary condition over a lubricated surface. Chin Phys Lett 29:024702
Santra B, Dandapat BS, Andersson HI (2007) Axisymmetric stagnation-point flow over a lubricated surface. Acta Mech 194:1–10
Stuart JT (1959) The viscous flow near a stagnation point when the external flow has uniform vorticity. J Aerosp Sci 26:124–125
Tamada KJ (1979) Two-dimensional stagnation-point flow impinging obliquely on a plane wall. J Phys Soc Jpn 46:310–311
Thompson PA, Troian SM (1997) A general boundary condition for liquid flow at solid surfaces. Nature 389:360–362
Tilley BS, Weidman PD (1998) Oblique two-fluid stagnation-point flow. Eur J Mech 17:205–217
Tooke RM, Blyth MG (2008) A note on oblique stagnation-point flow. Phys Fluids 20:033101
Trisaksri V, Wongwises S (2007) Critical review of heat transfer characteristics of nanofluids. Renew Sustain Eng Rev 11:512–523
Wang CY (2003) Stagnation flows with slip: exact solution of the Navier–Stokes equations. Z Angew Math Phys 54:184–189
Wang XQ, Mujumdar AS (2007) Heat transfer characteristics of nanofluids: a review. Int J Therm Sci 46:1–16
Wang XQ, Mujumdar AS (2008a) A review on nanofluids—part I: theoretical and numerical investigations. Braz J Chem Eng 25:613–630
Wang XQ, Mujumdar AS (2008b) A review on nanofluids—part II: experiments and applications. Braz J Chem Eng 25:631–648
Weidman PD, Putkaradze V (2003) Axisymmetric stagnation flow obliquely impinging on a circular cylinder. Eur J Mech B 22:123–131
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmood, K., Sajid, M., Ali, N. et al. Effects of lubrication in the oblique stagnation-point flow of a nanofluid. Microfluid Nanofluid 21, 100 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-017-1934-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-017-1934-3