Abstract
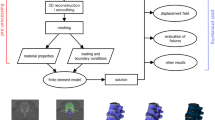
Finite elements analysis (FEA) is now used routinely to interpret skeletal form in terms of function in both medical and biological applications. To produce accurate predictions from FEA models, it is essential that the loading due to muscle action is applied in a physiologically reasonable manner. However, it is common for muscle forces to be represented as simple force vectors applied at a few nodes on the model’s surface. It is certainly rare for any wrapping of the muscles to be considered, and yet wrapping not only alters the directions of muscle forces but also applies an additional compressive load from the muscle belly directly to the underlying bone surface. This paper presents a method of applying muscle wrapping to high-resolution voxel-based finite element (FE) models. Such voxel-based models have a number of advantages over standard (geometry-based) FE models, but the increased resolution with which the load can be distributed over a model’s surface is particularly advantageous, reflecting more closely how muscle fibre attachments are distributed. In this paper, the development, application and validation of a muscle wrapping method is illustrated using a simple cylinder. The algorithm: (1) calculates the shortest path over the surface of a bone given the points of origin and ultimate attachment of the muscle fibres; (2) fits a Non-Uniform Rational B-Spline (NURBS) curve from the shortest path and calculates its tangent, normal vectors and curvatures so that normal and tangential components of the muscle force can be calculated and applied along the fibre; and (3) automatically distributes the loads between adjacent fibres to cover the bone surface with a fully distributed muscle force, as is observed in vivo. Finally, we present a practical application of this approach to the wrapping of the temporalis muscle around the cranium of a macaque skull.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austman RL, Milner JS, Holdsworth DW, Dunning CE (2008) The effect of the density-modulus relationship selected to apply material properties in a finite element model of long bone. J Biomech 41(15): 3171–3176
Blemker S, Delp S (2005) Three-dimensional representation of complex muscle architectures and geometries. Ann Biomed Eng 33(5): 661–673
Blemker S, Pinksy P, Delp S (2005) A 3D model of muscle reveals the cause of non-uniform strains in the biceps brachii. J Biomech 38: 657–665
Camacho DLA, Hopper RH, Lin GM, Myers BS (1997) An improved method for finite element mesh generation of geometrically complex structures with application to the skull base. J Biomech 30: 1067–1070
Charras GT, Guldberg RE (2000) Improving the local solution accuracy of large-scale digital image-based finite element analyses. J Biomech 33: 255–259
Chen J, Han Y (1990) Shortest paths on a polyhedron. In: SCG ’90: Proceedings of the sixth annual symposium on Computational geometry. ACM, New York, NY, USA, pp 360–369
Curtis N, Kupczik K, O’Higgins P, Moazen M, Fagan MJ (2008) Predicting skull loading: applying multibody dynamics analysis to a macaque skull. Anat Rec 291: 491–501
Curtis N, Jones M, Evans SE, Shi JF, O’Higgins P, Fagan MJ (2009) Predicting muscle activation patterns from motion and anatomy: modelling the skull of Sphenodon (Diapsida: rhynchocephalia). J Roy Soc Interface. doi:10.1098/rsif.2009.0139
Dijkstra E (1959) A note on two problems in connection with graphs. Numer Math 1: 269–271
Dumont ER, Piccirillo J, Grosse IR (2005) Finite-element analysis of biting behavior and bone stress in the facial skeletons of bats. Anat Rec A 283(2): 319–330
Fagan MJ, Dobson CA, Ganney PS, Sisias G, Phillips R, Langton CM (1999) Finite element analysis of cancellous bone resorption. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng 2(4): 257–270
Fagan MJ, Curtis N, Dobson CA, Kupczik K, Moazen M, Page L, Phillips R, O’Higgins P (2007) Voxel-based finite element analysis—working directly with microCT scan data. J Morph 268(12): 1071
Freeman H (1974) Computer processing of line drawing images. ACM Comput Surv 6(1): 57–94
Gröning F, Liu J, Fagan MJ, O’Higgins P (2009) Validating a voxel-based finite element model of a human mandible using digital speckle pattern interferometry. J Biomech 42(9): 1224–1229
Grosse IR, Dumont ER, Coletta C, Tolleson A (2007) Techniques for modelling muscle-induced forces in finite element models of skeletal structures. Anat Rec 290: 1069–1088
Guldberg RE, Hollister SJ, Travers GT (1998) The accuracy of digital image-based finite element models. J Biomech Eng 120: 289–295
Harrison NM, McDonnell PF, O’Mahoney DC, Kennedy OD, O’Brien FJ, McHugh PE (2008) Heterogeneous linear elastic trabecular bone modelling using micro-CT attenuation data and experimentally measured heterogeneous tissue properties. J Biomech 41(11): 2589–2596
Helgason B, Perilli E, Schileo E, Taddei F, Brynjólfsson S, Viceconti M (2008) Mathematical relationships between bone density and mechanical properties: a literature review. Clin Biomech 23(2): 135–146
Helgason B, Taddei F, Pálsson H, Schileo E, Cristofolini L, Viceconti M, Brynjólfsson S (2008) A modified method for assigning material properties to FE models of bones. Med Eng Phys 30(4): 444–453
Keyak JH, Lee IY, Skinner HB (1994) Correlations between orthogonal mechanical properties and density of trabecular bone: use of different densitometric measures. J Biomed Mater Res 28: 1329–1336
Kiryati N, Szekely G (1993) Estimation shortest paths and minimal distances on digitized three-dimensional surfaces. Pattern Recogn 26(11): 1623–1637
Kiryati N, Kübler O (1995) Chain code probabilities and optimal length estimators for digitized three-dimensional curves. Pattern Recogn 28(3): 361–372
Kupczik K, Dobson CA, Crompton RH, Phillips R, Oxnard CE, Fagan MJ, O’Higgins P (2009) Masticatory loading and bone adaptation in the supraorbital torus of developing macaques. Am J Phys Anthr 139(2): 193–203
Kupczik K, Dobson CA, Fagan MJ, Crompton R, Oxnard CE, O’Higgins P (2007) Assessing mechanical function of the zygomatic region in macaques: validation and sensitivity testing of finite element models. J Anat 210: 41–53
Langton CM, Ganney PS, Dobson CA, Fagan MJ, Sisias G, Phillips R (2000) Stochastically simulated assessment of anabolic treatment following varying degrees of cancellous bone resorption. Bone 27(1): 111–118
Langton CM, Haire TJ, Dobson CA, Fagan MJ (1998) A dynamic stochastic simulation of cancellous bone resorption. Bone 22(4): 375–380
Lemos R, Rokne O, Baranoski G, Kawakami Y, Kurihara T (2005) Modeling and simulating the deformation of human skeletal muscle based on anatomy and physiology. Comput Animat Virtual Worlds 16: 319–330
Linde F, Hvid I, Madsen F (1992) The effect of specimen geometry on the mechanical behaviour of trabecular bone specimens. J Biomech 25: 359–368
McDonnell P, Harrison N, Liebschner MA, Mc Hugh PE (2009) Simulation of vertebral trabecular bone loss using voxel finite element analysis. J Biomech. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2009.07.038 (in press)
McHenry CR, Wroe S, Clausen PD, Moreno K, Cunningham E (2007) Super-modeled sabercat, predatory behaviour in Smilodon fatalis revealed by high-resolution 3-D computer simulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:16010–16015
Mitchell J, Mount D, Papadimitriou C (1987) The discrete geodesic problem. SIAM J Comput 16(4): 647–668
Moazen M, Curtis N, Evans SE, O’Higgins P, Fagan MJ (2009) Biomechanical assessment of evolutionary changes in the lepidosaurian skull. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 20: 8273–8277
Moazen M, Curtis N, Evans SE, O’Higgins P, Jones MEH, Fagan MJ (2009) Assessment of the role of sutures in a lizard skull—a computer modelling study. Proc Roy Soc B 276: 39–46
Moazen M, Curtis N, Evans SE, O’Higgins P, Fagan MJ (2008) Combined finite element and multibody dynamics analysis of biting in a Uromastyx hardwickii lizard skull. J Anat 213: 499–508
Moreno K, Wroe S, Clausen P, McHenry C, D’Amore DC, Rayfield EJ, Cunningham E (2008) Cranial performance in the Komodo dragon (Varanus komodoensis) as revealed by high resolution 3-D finite element analysis. J Anat 212: 736–746
Piegl L, Tiller W (1997) The NURBS book, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin
Rayfield E (2007) Finite element analysis and understanding the biomechanics and evolution of living and fossil organisms. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 35: 541–576
Rho JY, Hobatho MC, Ashman RB (1995) Relations of mechanical properties to density and CT numbers in human bone. Med Eng Phys 17: 347–355
Richmond BG, Wright BW, Grosse I, Dechow PC, Ross CF, Spencer MA, Strait DS (2005) Finite element analysis in functional morphology. Anat Rec 283(2): 259–274
Ross CF (2005) Finite element analysis in vertebrate biomechanics. Anat Rec 283: 253–258
Shi JF, Curtis N, Fitton L, O’Higgins P, Fagan MJ (2009) The effect of variations in muscle positions in a complex biomechanical model of a macaque skull. Am J Phys Anth 138: S48
Strait DS, Wang Q, Dechow PC, Ross CF, Richmond BG, Spencer MA, Patel BA (2005) Modelling elastic properties in finite element analysis: how much precision is needed to produce an accurate model?. Anat Rec 283: 275–287
Strait DS, Weber GW, Neubauer S, Chalk J, Richmond BG, Lucas PW, Spencer MA, Schrein C, Dechow PC, Ross CF, Grosse IR, Wright BW, Constantino P, Wood BA, Lawn B, Hylander WL, Wang Q, Byron C, Slice DE, Smith AL (2009) The feeding biomechanics and dietary ecology of Australopithecus africanus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(7): 2124–2129
Tsubota K, Suzuki Y, Yamada T, Hojo M, Makinouchi A, Adachi T (2009) Computer simulation of trabecular remodeling in human proximal femur using large-scale voxel FE models: approach to understanding Wolff’s law. J Biomech 42(8): 1088–1094
Ulrich D, van Rietbergen B, Weinans H, Rüegsegger P (1998) Finite element analysis of trabecular bone structure: a comparison of image-based meshing techniques. J Biomech 31: 1187–1192
Verhulp E, van Rietbergen B, Huiskes R (2006) Comparison of micro-level and continuum-level voxel models of the proximal femur. J Biomech 39(16): 2951–2957
Wroe S, Moreno K, Clausen P, McHenry C, Curnoe D (2007) High-resolution three-dimensional computer simulation of hominid cranial mechanics. Anat Rec 290(10): 1248–1255
Yeni YN, Christophersin GT, Dong XN, Kim D-G, Fyhrie DP (2005) Effect of microcomputed tomography voxel size on the finite element model accuracy for human cancellous bone. J Biomech Eng 127: 1–8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Shi, J., Fitton, L.C. et al. The application of muscle wrapping to voxel-based finite element models of skeletal structures. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 11, 35–47 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-011-0291-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-011-0291-5