Abstract
Background
It is necessary to set the standard serum creatinine (Cr) values for the medical care of pediatric chronic kidney disease patients. The estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR, ml/min/1.73 m2) = κ × body length (cm)/serum Cr value (mg/dl) determined by the Jaffe method devised by Schwartz has been used clinically. However, enzymatic methods have recently been used to measure Cr instead of the Jaffe method, making it necessary to reevaluate the coefficient κ of the above equation. Following transformation of the above formula, the normal serum Cr level should be proportional to body length: normal serum Cr value (mg/dl) = k × body length (m).
Methods
Serum Cr values were measured by an enzymatic method in children who did not present with kidney disease or infectious disease, and the relationship between the body length and serum Cr level was determined by linear regression analysis.
Results
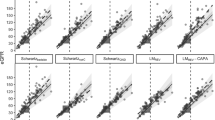
We found a regression equation capable of estimating the reference value of serum Cr from body length. In children aged 1–12 years, body length (m) × 0.30 yielded a value similar to the reference serum Cr level.
Conclusion
There have been no previous reports of the determination of reference serum Cr levels by enzymatic methods in Japanese children. Our formula will be applicable for screening of renal function in Japanese children.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schwartz GJ, Brion LP, Spitzer A. The use of plasma creatinine concentration for estimating glomerular filtration rate in infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1987;34:571–90.
Schwartz GJ, Feld LG, Langford DJ. A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in full-term infants during the first year of life. J Pediatr. 1984;104:849–54.
Schwartz GJ, Haycock GB, Edelmann CM Jr, Spitzer A. A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in children derived from body length and plasma creatinine. Pediatrics. 1976;58:259–63.
Schwartz GJ, Gauthier B. A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in adolescent boys. J Pediatr. 1985;106:522–6.
DuBois D, DuBois EF. A formula to estimate the approximate surface area if height and weight be known. Arch Intern Med. 1916;17:863–71.
Zappitelli M, Parvex P, Joseph L, Paradis G, Grey V, Lau S, et al. Derivation and validation of cystatin C-based prediction equations for GFR in children. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;48:221–30.
Counahan R, Chantler C, Ghazali S, Kirkwood B, Rose F, Barratt TM. Estimation of glomerular filtration rate from plasma creatinine concentration in children. Arch Dis Child. 1976;51:875–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Uemura, O., Ushijima, K., Nagai, T. et al. Reference serum creatinine levels determined by an enzymatic method in Japanese children: relationship to body length. Clin Exp Nephrol 13, 585–588 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-009-0211-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-009-0211-5