Abstract
Background
Convexal subarachnoid hemorrhage (c-SAH) is an infrequent condition with variable causes. c-SAH concomitant to acute ischemic stroke (AIS) is even less frequent, and the relationship between the two conditions remains unclear.
Methods
Between January 2016 and January 2018, we treated four patients who were referred to our stroke unit with ischemic stroke and concomitant nontraumatic c-SAH. The patients underwent an extensive diagnostic workup, including digital subtraction angiography (DSA).
Results
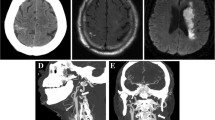
All four patients developed acute focal neurological symptoms with restricted MRI diffusion in congruent areas. In three of the patients, infarcts were in a border zone between the main cerebral arteries and c-SAH was nearby. The fourth patient showed a small cortical infarct, and c-SAH was in a border zone territory of the contralateral hemisphere. An embolic source was discovered or strongly suspected in all cases. One patient was treated with intravenous thrombolysis, but this treatment was not related to c-SAH. None of the four patients showed microbleeds or further cortical siderosis, thus excluding cerebral amyloid angiopathy. In addition, DSA did not show signs of vasculitis, reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome, or intracranial arterial dissection.
Conclusions
We proposed the embolism or hemodynamic changes of the border zone arterioles as a unifying pathogenetic hypothesis of coexisting c-SAH and AIS.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar S, Goddeau RP Jr, Selim MH, Thomas A, Schlaug G, Alhazzani A et al (2010) Atraumatic convexal subarachnoid hemorrhage: clinical presentation, imaging patterns, and etiologies. Neurology 74:893–899
Mangla R, Drumsta D, Alamst J, Mangla M, Potchen M (2015) Cerebral convexitysubarachnoid hemorrhage: various causes and role of diagnostic imaging. Emerg Radiol 22:181–195
Khurram A, Kleinig T, Leyden J (2014) Clinical associations and causes of convexity subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 45:1151–1153
Geraldes R, Sousa PR, Fonseca AC, Falcão F, Canhão P, Pinho e Melo T (2014) Nontraumatic convexity subarachnoid hemorrhage: different etiologies and outcomes. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 23:e23–e30
Usmani N, Ahmad FU, Koch S (2015) Convexity subarachnoid hemorrhage in ischemicstroke. J Neurol Sci 348:259–261
Beitzke M, Gattringer T, Enzinger C, Wagner G, Niederkorn K, Fazekas F (2011) Clinical presentation, etiology, and long-term prognosis in patients with nontraumatic convexal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 42:3055–3060
Nakajima M, Inatomi Y, Yonehara T, Hirano T, Ando Y (2014) Nontraumatic convexalsubarachnoid hemorrhage concomitant with acute ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 23:1564–1570
Beitzke M, Enzinger C, Pichler A, Wünsch G, Fazekas F (2018) Acute diffusion-weighted imaging lesions in cerebral amyloid angiopathy-related convexal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 38:225–229
Fukuma K, Ihara M, Tanaka T, Morita Y, Toyoda K, Nagatsuka K (2015) Intracranial cerebral artery dissection of anterior circulation as a cause of convexity subarachnoid hemorrhage. Cerebrovasc Dis 40:45–51
Lee MH, Kim SU, Lee DH, Kim YI, Cho CB, Yang SH et al (2016) Evaluation and treatment of the acute cerebral infarction with convexal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg 18:271–275
Spanou I, Vassilopoulou S, Koroboki E, Tountopoulou A, Velonakis G, Mitsikostas DD (2017) Convexity subarachnoid hemorrhage due to cardioembolic stroke in a woman with thyrotoxicosis: a case report. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 26:e195–e196
Geraldes R, Santos C, Canhão P (2011) Atraumatic localized convexity subarachnoid hemorrhage associated with acute carotid artery occlusion. Eur J Neurol 18:e28–e29
Kleinig TJ, Kimber TE, Thompson PD (2009) Convexity subarachnoid haemorrhage associated with bilateral internal carotid artery stenoses. J Neurol 256:669–671
Linn J, Halpin A, Demaerel P, Ruhland J, Giese AD, Dichgans M et al (2010) Prevalence of superficial siderosis in patients with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Neurology 74:1346–1350
Joinlambert C, Saliou G, Flamand-Roze C, Masnou P, Sarov M, Souillard R et al (2012) Cortical border-zone infarcts: clinical features, causes and outcome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83:771–775
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to all patients included in this study.
The image of vascular territories was courtesy of Prof. Frank Gaillard. We would like to thank Maria Tappatà, MD, for her help and availability.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AI, DMM, and MP contributed the conception and design of the study; FD, LC and SZ performed the neuroimages acquisitions and their interpretation; AI wrote the first draft of the manuscript with the equal contribution of DMM and MP and the support of MS.
ILS revised the manuscript for content, including medical writing for content, study concept or design, analysis or interpretation of data, study supervision and coordination.
All of the authors provided final approval of the version to be published and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Statement of ethics
This study was approved by the local ethics committee. All patients gave written informed consent.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Introna, A., Mezzapesa, D.M., Petruzzellis, M. et al. Convexal subarachnoid hemorrhage and acute ischemic stroke: a border zone matter?. Neurol Sci 40, 1419–1424 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-019-03868-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-019-03868-6