Abstract
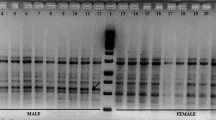
Hippophae rhamnoides L. ssp. turkestanica (Elaeagnaceae) is a predominantly dioecious and wind-pollinated medicinal plant species. The mature fruits of the species possess antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, anticancerous, and antistimulatory properties that are believed to improve the immune system. The identification of male and female plants in H. rhamnoides ssp. turkestanica is quite difficult until flowering which usually takes 3–4 years or more. A sex-linked marker can be helpful in establishing the orchards through identification of genders at an early stage of development. Therefore, we studied the genetic diversity of populations in Ladakh with the aim to identify a gender-specific marker using ISSR markers. Fifty-eight ISSR primers were used to characterize the genome of H. rhamnoides ssp. turkestanica, of which eight primers generated 12 sex-specific fragments specific to one or more populations. The ISSR primer (P-45) produced a fragment which faithfully segregates all the males from the female plants across all the three valleys surveyed. This male-specific locus was converted into a SCAR. Forward and reverse primers designed from this fragment amplified a 750-bp sequence in males only, thus specifying it as an informative male-specific sex-linked marker. This SCAR marker was further validated for its capability to differentiate gender on an additional collection of plants, representing three geographically isolated valleys (Nubra, Suru, and Indus) from Ladakh region of India. The results confirmed sex-linked specificity of the marker suggesting that this conserved sequence at the Y chromosome is well preserved through the populations in Ladakh region. At present, there are no reliable markers which can differentiate male from female plants across all the three valleys of Ladakh region at an early stage of plant development. It is therefore envisaged that the developed SCAR marker shall provide a reliable molecular tool for early identification of the sex in this commercial crop. The genetic diversity of populations as surveyed by ISSR primers revealed 85.71 % polymorphism at the population level. The dendrogram obtained divided the genotypes into three different clusters, and the distribution of male and female genotypes in all the clusters was random. The Nei’s genetic similarity index was in the range of 0.63–0.96.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari S, Saha S, Bandyopadhyay TK, Ghosh P (2014) Identification and validation of a new male sex-specific ISSR marker in pointed gourd (Trichosanthes dioica Roxb.). Sci World J. doi:10.1155/2014/216896
Alpert P, Lumaret RD, Giusto F (1993) Population structure inferred from allozyme analysis in the clone herb Fragaria chiloensis (Rosaceae). Am J Bot 80:1002–1006
APG III (2009) An update of the angiosperm phylogeny group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG III. Bot J Linn Soc 161:105–121
Bachtrog D (2013) Y chromosome evolution: emerging insights into processes of Y chromosome degeneration. Nat Rev Genet 14:113–124
Bal LM, Meda V, Naik SN, Satya S (2011) Sea buckthornberries: apotential source of valuable nutrients for neutraceuticals and cosmoceuticals. Food Res Int 44:1718–1727
Barrett SCH (2002) The evolution of plant sexual diversity. Nature Rev Genet 3:274–284
Barrett SCH, Kohn JR (1991) Genetics and evolutionary consequences of small population size in plants: implications for conservation. In: Falk DA, Holsinger KE (eds) Genetics and conservation of rare plants. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 3–30
Bull JJ (1983) Evolution of sex determining mechanisms. Benjamin/Cummings, Menlo Park
Charlesworth D (2016) The status of supergenes in the 21st century: recombination suppression in Batesian mimicry and sex chromosomes and other complex adaptations. Evol Appl 9:74–90
Cheng J, Long Y, Khan MA, Wei C, Shelly F, Junjiang F (2015) Development and significance of RAPD-SCAR markers for the identification of Litchi chinensis Sonn. by improved RAPD amplification and molecular cloning. Electron J Biotechnol 18:35–39
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Gakov MA (1980) Prospects for the development of Hippophae rhamnoides in the USSR. Lesn khoz 2:51–52
Ganie SH, Ali Z, Das S, Srivastava PS, Sharma MP (2015a) Molecular characterization and chemical profiling of different populations of Convolvulus pluricaulis (Convolvulaceae); an important herb of Ayurvedic medicine. 3 Biotec 5:295–302
Ganie SH, Upadhyay P, Das S, Sharma MP (2015b) Authentication of medicinal plants by DNA markers. Plant Gene 4:83–99
Goddard MR (2016) Sex accelerates adaptation. Nature 531:176–177
Gray JC, Goddard MR (2012) Gene-flow between niches facilitates local adaptation in sexual populations. Ecol Lett 15:955–962
Jadhav MS, Sharma TR (2014) Identification of gender specific DNA markers in sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.). Ind Res J Genet Biotech 6:464–469
Korekar G, Sharma RK, Kumar R, Meenu, Bisht NC, Srivastava RB, Ahuja PS, Stobdan T (2012) Identification and validation of sex-linked SCAR markers in dioecious Hippophae rhamnoides L. (Elaeagnaceae). Biotechnol Lett 34:973–978
Lebeda A (2003) Danube seabuckthorn populations, valuable for selections. In: Singh V, Khosla PK (eds) Proceedings of international workshop on seabuckthorn. New Delhi, 8–21 Lee T T. 1973. extraction and quantification of plant peroxidase isoenzymes, vol 29, Physiol Plants., pp 198–203
Mangla Y, Tandon R (2014) Pollination ecology of Himalayan sea buckthorn, Hippophae rhamnoides L. (Elaeagnaceae). Curr Sci 106(12):1731
Mangla Y, Chaudhary M, Gupta H, Thakur R, Goel S, Raina SN, Tandon R (2015) Facultative apomixis and development of fruit in a deciduous shrub with medicinal and nutritional uses. AoB Plants 7:plv098. doi:10.1093/aobpla/plv098
Ming GAO, Chen YC, Yang SS et al (2015) Progress on sex differentiation in unisexual flower plants. Acta Prataculturae Sin 2015:206–217
Moon BC, Yunui J, Young ML, Kang YM, Kim HK (2015) Authentication of Akebia quinata DECNE. from its common adulterant medicinal plant species based on the RAPD-derived SCAR markers and multiplex-PCR. Genes Genom 37:23–32
Nei M, Li WH (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 76:5269–5273
Paithankar KR, Prasad KSN (1991) Precipitation of DNA by polyethylene glycol and ethanol. Nucleic Acids Res 19:1346
Parasnis AS, Ramakrishna W, Chowdari KV, Gupta VS, Ranjekar PK (1999) Microsatellite (GATA)n reveals sex-specific differences in papaya. Theor Appl Genet 99:1047–1052
Perrier X, Jacquemound-Collet JP (2006) Darwin software. Available at http://darwin.cirad.fr/darwin
Persson HA, Nybom H (1998) Genetic sex determination and RAPD marker segregation in the dioecious species sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.). Hereditas 129:45–51
Raina S N, Jain S, Sehgal D, Kumar A, Dar T H, Bhat V, Pandey V, Vaishnavi S, Bhargav A, Singh V, Rani V, Tandon R, Tewari M, Mahmoudi A (2012) Diversity and relationships of multipurpose seabuckthorn (Hippophae L.) germplasm from the Indian Himalayas as assessed by AFLP and SAMPL markers. Gen Resour Crop Evol. doi:10.1007/s10722-011-9742-1
Ruan CJ, Li DQ (2000) Function and benefits of sea buckthorn improving eco-environment of loess plateau. Environ Prot 5:30–31
Sarwat M, Das S, Srivastava PS (2011) AFLP and SAMPL markers for characterization of genetic diversity in Terminalia arjuna: a backbone tree of Tasar silk industry. Plant Syst Evol 293:13–23
Sharma A, Zinta G, Rana S, Shirkot P (2010) Molecular identification of sex in Hippophae rhamnoides L. using isozyme and RAPD markers. For Stud China 12:62–66
Singh V, Singh B, Awasthi CP (1995) Distribution, taxonomy and nutritional values of seabuckthorn (Hippophae L.) growing in dry temperate Himalayas. In: Proceedings of international workshop Seabuckthorn, ICRTS, Beijing, China, pp 52–59
Srihari JM, Verma B, Kumar N, Chahota RK, Singh V, Rathour R, Singh SK, Sharma SK, Sharma TR (2013) Analysis of molecular genetic diversity and population structure in sea buckthorn (Hippophae spp L.) from north-western Himalayan region of India. J Med Plants Res 7:3183–3196
Suryakumar G, Gupta A (2011) Medicinal and therapeutic potential of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.). J Ethnopharmacol 138:268–278
Teng BS, Lu YH, Wang ZT, Tao XY, Wei DZ (2006) In vitro anti-tumor activity of isorhamnetin isolated from Hippophae rhamnoides L. against BEL-7402 cells. Pharmacol Res 54:186–194
Tian CJ, Lei YD, Shi SH, Nan P, Chen JK, Zhong Y (2004) Genetic diversity of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) populations in northeastern and northwestern China as revealed by ISSR markers. New Forest 27:229–237
VanBuren R, Zeng F, Chen C, Zhang J, Wai CM et al (2015) Origin and domestication of papaya Yh chromosome. Genome Res 25:524–533
Wang J, Na JK, Yub Q et al (2012) Sequencing papaya X and Yh chromosomes reveals molecular basis of incipient sex chromosome evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 34:13710–13715
Wilkinson GS, Breden F, Jmank JE et al (2015) The locus of sexual selection: moving sexual selection studies into the post-genomics era. J Evol Bio. doi:10.1111/jeb.12621.
Zluvova J, Nicolas M, Berger A, Negrutiu I, Monéger F (2006) Premature arrest of the male flower meristem precedes sexual dimorphism in the dioecious plant Silene latifolia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:18854–18859
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Department of Biotechnology, Govt. of India (Project: BT/PR10800/NDB/51/172/2008); KD extends thanks to UGC and the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment for providing fellowship during the course of the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Peter Nick
Kamal Das and Showkat Hussain Ganie contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Suppl. Table 1
Nei’s genetic similarity index based on 12 ISSR primers in different populations of H. rhamnoides ssp. turkestanica. (DOCX 29 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, K., Ganie, S.H., Mangla, Y. et al. ISSR markers for gender identification and genetic diagnosis of Hippophae rhamnoides ssp. turkestanica growing at high altitudes in Ladakh region (Jammu and Kashmir). Protoplasma 254, 1063–1077 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-016-1013-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-016-1013-8