Abstract.
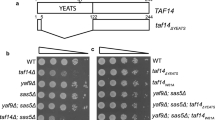
The G1 cell cycle arrest imposed by Kluyveromyces lactis zymocin on Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires a functional RNA polymerase II (pol II) TOT/Elongator complex. In a study of zymocin's mode of action, genetic scenarios known to impair transcription or affect the pol II machinery itself were found to elicit hypersensitivity to zymocin. Thus, mutations in components of SAGA, SWI/SNF, Mediator and Ccr4-Not, complexes involved in transcriptionally relevant functions such as nucleosome modification, chromatin remodelling and formation of the preinitiation complex, make yeast cells hypersensitive to the lethal effects of zymocin. The defects at the level of transcriptional elongation displayed by rtf1Δ, ctk1, fcp1 and rpb2 mutants also result in zymocin hypersensitivity. Intriguingly, inactivation of histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity, which is expected to reduce the demand for the histone acetyltransferase (HAT) function of TOT/Elongator, also reduces sensitivity to zymocin. Thus, zymocin interferes with pol II-dependent transcription, and this effect requires the HAT function of TOT, presumably while the Elongator complex is associated with pol II.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kitamoto, .H., Jablonowski, .D., Nagase, .J. et al. Defects in yeast RNA polymerase II transcription elicit hypersensitivity to G1 arrest induced by Kluyveromyces lactis zymocin. Mol Gen Genomics 268, 49–55 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-002-0720-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-002-0720-3