Abstract
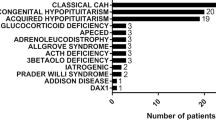
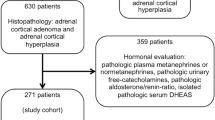
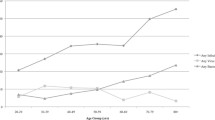
The aim of the study was to assess the epidemiology and risk factors of adrenal crises (AC) in children with adrenal insufficiency (AI). Children diagnosed with AI between 1990 and 2017 at four Israeli pediatric endocrinology units were studied. Demographic and clinical data were retrieved retrospectively from their files. The study population consisted of 120 children (73 boys, 47 girls) and comprised 904 patient years. Median age at diagnosis was 0.3 years (0–17.5). Thirty-one AC events in 26 children occurred during the study period, accounting for a frequency of 3.4 crises/100 patient years. Fifty-two percent of AC events occurred at presentation. The significant risk factors for developing AC were the following: younger age at diagnosis (P = 0.003), primary AI vs. secondary AI (P = 0.016), specific diagnosis of autoimmune AI, adrenal hypoplasia congenita and salt wasting congenital adrenal hyperplasia (P < 0.001), mineralocorticoid treatment (P < 0.001), and recurrent hospital admissions (P > 0.001). After applying a stepwise logistic regression model, only the group of diagnoses, including salt wasting CAH, AHC, and Addison’s disease, remained significant predictor of AC (OR 17.5, 95% CI 4.7–64.9, P < 0.001). There was no AC-associated mortality during the study period.
Conclusions: Since significant percent of AC events occurred at presentation, measures to increase the awareness to signs and symptoms of AI among primary care physicians should be taken. Efforts to prevent AC should be focused on younger patients, especially those with primary AI.
What Is Known: • Diagnosis and long-term management of pediatric patients with adrenal insufficiency (AI) remain a challenge. • Adrenal crises (AC) pose life-threatening emergencies in affected youngsters. Studies on the rate and risk factors of AC in children with AI are scarce, and they were done mainly on children with congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH). What Is New: • The rate of AC was relatively low and there was no AC-associated mortality during the study period. • Children with primary AI were at higher risk for AC than children with secondary AI. Specifically, children with salt wasting CAH, adrenal hypoplasia congenita, and Addison’s disease at the highest risk. |
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC:
-
Adrenal crises
- ACTH:
-
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone
- AHC:
-
Adrenal hypoplasia congenita
- AI:
-
Adrenal insufficiency
- ALD:
-
Adrenoleukodystrophy
- CAH:
-
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
References
Bancos I, Hahner S, Tomlinson J, Arlt W (2015) Diagnosis and management of adrenal insufficiency. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 3:216–226
Hsieh S, White PC (2011) Presentation of primary adrenal insufficiency in childhood. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:E925–E928
Bornstein SR, Allolio B, Arlt W, Barthel A, Don-Wauchope A, Hammer GD, Husebye ES, Merke DP, Murad MH, Stratakis CA, Torpy DJ (2016) Diagnosis and treatment of primary adrenal insufficiency: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 101:364–389
Arlt W, Allolio B (2003) Adrenal insufficiency. Lancet 361:1881–1893
Grossman AB (2010) The diagnosis and management of central hypoadrenalism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:4855–4863
Burman P, Mattsson AF, Johannsson G, Höybye C, Holmer H, Dahlqvist P, Berinder K, Engström BE, Ekman B, Erfurth EM, Svensson J, Wahlberg J, Karlsson FA (2013) Deaths among adult patients with hypopituitarism: hypocortisolism during acute stress, and de novo malignant brain tumors contribute to an increased mortality. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:1466–1475
Weintrob N, Drouin J, Vallette-Kasic S, Taub E, Marom D, Lebenthal Y et al (2006) Low estriol levels in the maternal triple-marker screen as a predictor of isolated adrenocorticotropic hormone deficiency caused by a new mutation in the TPIT gene. Pediatrics 117:E322–E327
Charmandari E, Nicolaides NC, Chrousos GP (2014) Adrenal insufficiency. Lancet 383:2152–2167
Nagarur A, Axelrod L, Dighe AS (2017) Case 9-2017. N Engl J Med 376:1159–1167
Bleicken B, Hahner S, Ventz M, Quinkler M (2010) Delayed diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency is common: a cross-sectional study in 216 patients. Am J Med Sci 339:525–531
Perry R, Kecha O, Paquette J, Huot C, Van Vliet G, Deal C (2005) Primary adrenal insufficiency in children: twenty years experience at the Sainte-Justine Hospital, Montreal. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:3243–3250
Eyal O, Limor R, Oren A, Schachter-Davidov A, Stern N, Weintrob N (2016) Establishing normal ranges of basal and ACTH-stimulated serum free cortisol in children. Horm Res Paediatr 86:94–99
Weintrob N, Davidov AS, Becker AS, Israeli G, Oren A, Eyal O (2018) Serum free cortisol during glucagon stimulation test in healthy short-statured children and adolescents. Endocr Pract 24:288–293
Weintrob N, Sprecher E, Josefsberg Z, Weininger C, Aurbach-Klipper Y, Lazard D, Karp M, Pertzelan A (1998) Standard and low-dose short adrenocorticotropin test compared with insulin-induced hypoglycemia for assessment of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in children with idiopathic multiple pituitary hormone deficiencies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:88–92
Maghnie M, Uga E, Temporini F, Di Iorgi N, Secco A, Tinelli C et al (2005) Evaluation of adrenal function in patients with growth hormone deficiency and hypothalamic-pituitary disorders: comparison between insulin-induced hypoglycemia, low-dose ACTH, standard ACTH and CRH stimulation tests. Eur J Endocrinol 152:735–741
Lindholm J (2015) Problems in interpretation of the short Acth test: an update and historical notes. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 123:441–445
Esposito D, Pasquali D, Johannsson G (2018) Primary adrenal insufficiency: managing mineralocorticoid replacement therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 103:376–387
Webb EA, Krone N (2015) Current and novel approaches to children and young people with congenital adrenal hyperplasia and adrenal insufficiency. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 29:449–468
White K, Arlt W (2010) Adrenal crisis in treated Addison’s disease: a predictable but under-managed event. Eur J Endocrinol 162:115–120
Hahner S, Spinnler C, Fassnacht M, Burger-Stritt S, Lang K, Milovanovic D, Beuschlein F, Willenberg HS, Quinkler M, Allolio B (2015) High incidence of adrenal crisis in educated patients with chronic adrenal insufficiency: a prospective study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100:407–416
Papierska L, Rabijewski M (2013) Delay in diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency is a frequent cause of adrenal crisis. Int J Endocrinol 2013:482370
Hahner S, Loeffler M, Bleicken B, Drechsler C, Milovanovic D, Fassnacht M, Ventz M, Quinkler M, Allolio B (2010) Epidemiology of adrenal crisis in chronic adrenal insufficiency: the need for new prevention strategies. Eur J Endocrinol 162:597–602
Rushworth RL, Torpy DJ, Stratakis CA, Falhammar H (2018) Adrenal crises in children: perspectives and research directions. Hormone Reseaerch in Pediatrics 89:341–351
Allolio B (2015) Extenesive expertise in endocrinology: adrenal crisis. Eur J Endocrinol 172:R115–R124
Ishii T, Adachi M, Takasawa K, Okada S, Kamasaki H, Kubota T, Kobayashi H, Sawada H, Nagasaki K, Numakura C, Harada S, Minamitani K, Sugihara S, Tajima T (2018) Incidence and characteristics of adrenal crisis in children younger than 7 years with 21-hydroxylase deficiency: a nationwide survey in Japan. Hormone Research in Paediatrics 89:166–171
Pinto G, Tardy V, Trivin C, Thalassinos C, Lortat-Jacob S, Nihoul-Fékété C, Morel Y, Brauner R (2003) Follow-up of 68 children with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency: relevance of genotype for management. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:2624–2633
Odenwald B, Nennstiel-Ratzel U, Dörr HG, Schmidt H, Wildner M, Bonfig W (2016) Children with classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia experience salt loss and hypoglycemia: evaluation of adrenal crises during the first 6 years of life. Eur J Endocrinol 174:177–186
Chrisp GL, Maguire AM, Quartararo M, Falhammar H, King BR, Munns CF, Torpy DJ, Hameed S, Rushworth RL (2018) Variations in the management of acute illness in children with congenital adrenal hyperplasia: an audit of three paediatric hospitals. Clin Endocrinol 89(5):577–585
Dixon WJ (ed) (1993) BMDP Statistical software. University of California Press, Los Angeles
Rushworth RL, Torpy DJ (2015) Adrenal insufficiency in Australia: is it possible that the use of lower dose, short-acting glucocorticoids has increased the risk of adrenal crises? Horm Metab Res 47:427–432
El-Maouche D, Hargreaves CJ, Sinaii N, Mallappa A, Veeraraghavan P, Merke DP (2018) Longitudinal assessment of illnesses, stress dosing, and illness sequelae in patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 103:2336–2345
Reisch N, Willige M, Kohn D, Schwarz HP, Allolio B, Reincke M, Quinkler M, Hahner S, Beuschlein F (2012) (2012) frequency and causes of adrenal crises over lifetime in patients with 21-hydroxylase deficiency. Eur J Endocrinol 167:35–42
White PC (2009) Neonatal screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Nat Rev Endocrinol 5:490–498
Rushworth RL, Chrisp GL, Dean B, Falhammar H, Torpy DJ (2017) Hospitalization in children with adrenal insufficiency and hypopituitarism: is there a differential burden between boys and girls and between age groups. Horm Res Paediatr 88:339–346
Rushworth RL, Falhammar H, Munns CF, Maguire AM, Torpy DJ (2016) Hospital admission patterns in children with CAH: admission rates and adrenal crises decline with age. Int J Endocrinol 2016:5748264
Smans LC, Van der Valk ES, Hermus AR, Zelissen PM (2016) Incidence of adrenal crisis in patients with adrenal insufficiency. Clin Endocrinol 84:17–22
Rushworth RL, Torpy DJ (2015) Modern hydrocortisone replacement regimens in adrenal insufficiency patients and the risk of adrenal crisis. Horm Metab Res 47:637–642
Kampmeyer D, Haas CS, Moenig H, Harbeck B (2017) Self-management in adrenal insufficiency - towards a better understanding. Endocr J 64:379–385
Puar TH, Stikkelbroeck NM, Smans LC, Zelissen PM, Hermus AR (2016) Adrenal crisis: still a deadly event in the 21st century. Am J Med 129:339.e1–339.e9
Sun T, Plutynski A, Ward S, Rubin JB (2015) An integrative view on sex differences in brain tumors. Cell Mol Life Sci 72:3323–3342
Acknowledgments
We thank Pearl Lilos for the statistical analysis and Esther Eshkol for professional English editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
OE and NW: Study design, literature search, data analysis and interpretation, writing the manuscript
YL: Data collection and analysis, literature search
AO: Study design, data analysis, and interpretation
AZ, MR, ASD, and ASB: Data collection, analysis, and interpretation
All authors were involved in the preparation of the manuscript, critically reviewed the manuscript, and approved the final manuscript as submitted.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
This study was approved by the medical ethics committee of each participating center; the requirement for informed consent was waived.
Additional information
Communicated by Peter de Winter
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eyal, O., Levin, Y., Oren, A. et al. Adrenal crises in children with adrenal insufficiency: epidemiology and risk factors. Eur J Pediatr 178, 731–738 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-019-03348-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-019-03348-1