Abstract
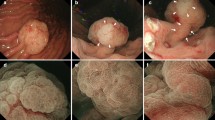
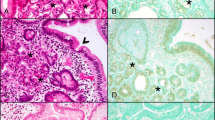
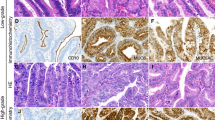
McCune-Albright Syndrome (MAS) is a rare sporadic syndrome caused by post-zygotic mutations in the GNAS oncogene, leading to constitutional mosaicism for these alterations. Somatic activating GNAS mutations also commonly occur in several gastrointestinal and pancreatic neoplasms, but the spectrum of abnormalities in these organs in patients with MAS has yet to be systematically described. We report comprehensive characterization of the upper gastrointestinal tract in seven patients with MAS and identify several different types of polyps, including gastric heterotopia/metaplasia (7/7), gastric hyperplastic polyps (5/7), fundic gland polyps (2/7), and a hamartomatous polyp (1/7). In addition, one patient had an unusual adenomatous lesion at the gastroesophageal junction with high-grade dysplasia. In the pancreas, all patients had endoscopic ultrasound findings suggestive of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN), but only two patients met the criteria for surgical intervention. Both of these patients had IPMNs at resection, one with low-grade dysplasia and one with high-grade dysplasia. GNAS mutations were identified in the majority of lesions analyzed, including both IPMNs and the adenomatous lesion from the gastroesophageal junction. These studies suggest that there is a broad spectrum of abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas in patients with MAS and that patients with MAS should be evaluated for gastrointestinal pathology, some of which may warrant clinical intervention due to advanced dysplasia.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyce AM, Collins MT (1993) Fibrous dysplasia/McCune-Albright syndrome. In: Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH et al (eds) GeneReviews(R). University of Washington, Seattle, Seattle (WA) All rights reserved
Weinstein LS, Shenker A, Gejman PV, Merino MJ, Friedman E, Spiegel AM (1991) Activating mutations of the stimulatory G protein in the McCune-Albright syndrome. N Engl J Med 325(24):1688–1695. doi:10.1056/nejm199112123252403
Wu J, Matthaei H, Maitra A, Dal Molin M, Wood LD, Eshleman JR, Goggins M, Canto MI, Schulick RD, Edil BH, Wolfgang CL, Klein AP, Diaz LA, Jr., Allen PJ, Schmidt CM, Kinzler KW, Papadopoulos N, Hruban RH, Vogelstein B (2011) Recurrent GNAS mutations define an unexpected pathway for pancreatic cyst development. Science Translational Medicine 3 (92):92ra66. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3002543
Matsubara A, Sekine S, Kushima R, Ogawa R, Taniguchi H, Tsuda H, Kanai Y (2013) Frequent GNAS and KRAS mutations in pyloric gland adenoma of the stomach and duodenum. J Pathol 229(4):579–587. doi:10.1002/path.4153
Gaujoux S, Salenave S, Ronot M, Rangheard AS, Cros J, Belghiti J, Sauvanet A, Ruszniewski P, Chanson P (2014) Hepatobiliary and pancreatic neoplasms in patients with McCune-Albright syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 99(1):E97–101. doi:10.1210/jc.2013-1823
Zacharin M, Bajpai A, Chow CW, Catto-Smith A, Stratakis C, Wong MW, Scott R (2011) Gastrointestinal polyps in McCune Albright syndrome. J Med Genet 48(7):458–461. doi:10.1136/jmg.2010.086330
Lumbroso S, Paris F, Sultan C, European Collaborative S (2004) Activating Gsalpha mutations: analysis of 113 patients with signs of McCune-Albright syndrome—a European collaborative study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(5):2107–2113. doi:10.1210/jc.2003-031225
Idowu BD, Al-Adnani M, O'Donnell P, Yu L, Odell E, Diss T, Gale RE, Flanagan AM (2007) A sensitive mutation-specific screening technique for GNAS1 mutations in cases of fibrous dysplasia: the first report of a codon 227 mutation in bone. Histopathology 50(6):691–704. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2007.02676.x
Dal Molin M, Matthaei H, Wu J, Blackford A, Debeljak M, Rezaee N, Wolfgang CL, Butturini G, Salvia R, Bassi C, Goggins MG, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Eshleman JR, Hruban RH, Maitra A (2013) Clinicopathological correlates of activating GNAS mutations in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) of the pancreas. Ann Surg Oncol 20(12):3802–3808. doi:10.1245/s10434-013-3096-1
Chen G, Olson MT, O'Neill A, Norris A, Beierl K, Harada S, Debeljak M, Rivera-Roman K, Finley S, Stafford A, Gocke CD, Lin MT, Eshleman JR (2012) A virtual pyrogram generator to resolve complex pyrosequencing results. The Journal of molecular diagnostics : JMD 14(2):149–159. doi:10.1016/j.jmoldx.2011.12.001
Yu J, Sadakari Y, Shindo K, Suenaga M, Brant A, Almario JA, Borges M, Barkley T, Fesharakizadeh S, Ford M, Hruban RH, Shin EJ, Lennon AM, Canto MI, Goggins M (2016) Digital next-generation sequencing identifies low-abundance mutations in pancreatic juice samples collected from the duodenum of patients with pancreatic cancer and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Gut. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2015-311166
Adsay NV, Merati K, Basturk O, Iacobuzio-Donahue C, Levi E, Cheng JD, Sarkar FH, Hruban RH, Klimstra DS (2004) Pathologically and biologically distinct types of epithelium in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: delineation of an “intestinal” pathway of carcinogenesis in the pancreas. Am J Surg Pathol 28(7):839–848
Parvanescu A, Cros J, Ronot M, Hentic O, Grybek V, Couvelard A, Levy P, Chanson P, Ruszniewski P, Sauvanet A, Gaujoux S (2014) Lessons from McCune-Albright syndrome-associated intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: GNAS-activating mutations in pancreatic carcinogenesis. JAMA surgery 149(8):858–862. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2014.535
Amato E, Molin MD, Mafficini A, Yu J, Malleo G, Rusev B, Fassan M, Antonello D, Sadakari Y, Castelli P, Zamboni G, Maitra A, Salvia R, Hruban RH, Bassi C, Capelli P, Lawlor RT, Goggins M, Scarpa A (2014) Targeted next-generation sequencing of cancer genes dissects the molecular profiles of intraductal papillary neoplasms of the pancreas. J Pathol 233(3):217–227. doi:10.1002/path.4344
Matsubara A, Ogawa R, Suzuki H, Oda I, Taniguchi H, Kanai Y, Kushima R, Sekine S (2015) Activating GNAS and KRAS mutations in gastric foveolar metaplasia, gastric heterotopia, and adenocarcinoma of the duodenum. Br J Cancer 112(8):1398–1404. doi:10.1038/bjc.2015.104
Kushima R, Sekine S, Matsubara A, Taniguchi H, Ikegami M, Tsuda H (2013) Gastric adenocarcinoma of the fundic gland type shares common genetic and phenotypic features with pyloric gland adenoma. Pathol Int 63(6):318–325. doi:10.1111/pin.12070
Wood LD, Salaria SN, Cruise MW, Giardiello FM, Montgomery EA (2014) Upper GI tract lesions in familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP): enrichment of pyloric gland adenomas and other gastric and duodenal neoplasms. Am J Surg Pathol 38(3):389–393. doi:10.1097/pas.0000000000000146
Hashimoto T, Ogawa R, Matsubara A, Taniguchi H, Sugano K, Ushiama M, Yoshida T, Kanai Y, Sekine S (2015) Familial adenomatous polyposis-associated and sporadic pyloric gland adenomas of the upper gastrointestinal tract share common genetic features. Histopathology 67(5):689–698. doi:10.1111/his.12705
Vieth M, Kushima R, Borchard F, Stolte M (2003) Pyloric gland adenoma: a clinico-pathological analysis of 90 cases. Virchows Archiv : an international journal of pathology 442(4):317–321. doi:10.1007/s00428-002-0750-6
Vieth M, Montgomery EA (2014) Some observations on pyloric gland adenoma: an uncommon and long ignored entity! J Clin Pathol 67(10):883–890. doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2014-202553
Chen ZM, Scudiere JR, Abraham SC, Montgomery E (2009) Pyloric gland adenoma: an entity distinct from gastric foveolar type adenoma. Am J Surg Pathol 33(2):186–193. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31817d7ff4
Park JY, Cornish TC, Lam-Himlin D, Shi C, Montgomery E (2010) Gastric lesions in patients with autoimmune metaplastic atrophic gastritis (AMAG) in a tertiary care setting. Am J Surg Pathol 34(11):1591–1598. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181f623af
Abraham SC, Singh VK, Yardley JH, Wu TT (2001) Hyperplastic polyps of the stomach: associations with histologic patterns of gastritis and gastric atrophy. Am J Surg Pathol 25(4):500–507
Pittman ME, Voltaggio L, Bhaijee F, Robertson SA, Montgomery EA (2015) Autoimmune metaplastic atrophic gastritis: recognizing precursor lesions for appropriate patient evaluation. Am J Surg Pathol 39(12):1611–1620. doi:10.1097/pas.0000000000000481
Ueyama H, Yao T, Nakashima Y, Hirakawa K, Oshiro Y, Hirahashi M, Iwashita A, Watanabe S (2010) Gastric adenocarcinoma of fundic gland type (chief cell predominant type): proposal for a new entity of gastric adenocarcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 34(5):609–619. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181d94d53
Wu J, Jiao Y, Dal Molin M, Maitra A, de Wilde RF, Wood LD, Eshleman JR, Goggins MG, Wolfgang CL, Canto MI, Schulick RD, Edil BH, Choti MA, Adsay V, Klimstra DS, Offerhaus GJ, Klein AP, Kopelovich L, Carter H, Karchin R, Allen PJ, Schmidt CM, Naito Y, Diaz LA Jr, Kinzler KW, Papadopoulos N, Hruban RH, Vogelstein B (2011) Whole-exome sequencing of neoplastic cysts of the pancreas reveals recurrent mutations in components of ubiquitin-dependent pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(52):21188–21193. doi:10.1073/pnas.1118046108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors acknowledge the following sources of support: Intramural Research Program of the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research; NIH/NCI P50 CA62924; NIH/NIDDK K08 DK107781; Sol Goldman Pancreatic Cancer Research Center; Buffone Family Gastrointestinal Cancer Research Fund; Kaya Tuncer Career Development Award in Gastrointestinal Cancer Prevention; AGA-Bernard Lee Schwartz Foundation Research Scholar Award in Pancreatic Cancer; Sidney Kimmel Foundation for Cancer Research Kimmel Scholar Award; AACR-Incyte Corporation Career Development Award for Pancreatic Cancer Research; Rolfe Pancreatic Cancer Foundation; Joseph C Monastra Foundation for Pancreatic Cancer Research; The Gerald O Mann Charitable Foundation (Harriet and Allan Wulfstat, Trustees); Sigma Beta Sorority; Tampa Bay Fisheries Inc.; Dutch Digestive Foundation (MLDS CDG 14-02).
Conflict of interest
Dr. Wood is a paid consultant for Personal Genome Diagnostics.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wood, L.D., Noë, M., Hackeng, W. et al. Patients with McCune-Albright syndrome have a broad spectrum of abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas. Virchows Arch 470, 391–400 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-017-2086-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-017-2086-2