Abstract
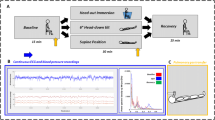
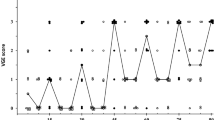
Supine subjects exposed to hypergravity show a marked arterial desaturation. Previous work from our laboratory has also shown a paradoxical reduction of lung perfusion in dependent lung regions in supine subjects exposed to hypergravity. We reasoned that the increased lung weight during hypergravity caused either direct compression of the blood vessels in the dependent lung tissue or that poor regional ventilation caused reduced perfusion through hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction (HPV). The objective of this study was to evaluate the importance of HPV through measurements of arterial oxygenation during exposure to hypergravity with normal and attenuated HPV. A further increased arterial desaturation during hypergravity with attenuated HPV would support the hypothesis that HPV contributes to the paradoxical redistribution of regional perfusion. In a two-phased randomized study we first exposed 12 healthy subjects to 5 G while supine during two single-blinded conditions; control and after 50 mg sildenafil p.o.. In a second phase, 12 supine subjects were exposed to 5 G during three single-blinded conditions; control, after 100 mg sildenafil p.o. and after inhalation of 10 μg iloprost. There was a substantial arterial desaturation by 5–30% units in all subjects with no or only minor differences between conditions. The results speak against HPV as a principal mechanism for the hypergravity-induced reduction of lung perfusion in dependent lung regions in supine humans.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baranov VM, Tikhonov MA, Kotov AN (1992) The external respiration and gas exchange in space missions. Acta Astronaut 27:45–50
Barker SJ, Tremper KK (1987) Pulse oximetry: applications and limitations. Int Anesthesiol Clin 25(3):155–175
Bowes WA 3rd, Corke BC, Hulka J (1989) Pulse oximetry: a review of the theory, accuracy, and clinical applications. Obstet Gynecol 74(3, part 2):541–546
Carvajal JA, Germain AM, Huidobro-Toro JP, Weiner CP (2000) Molecular mechanism of cGMP-mediated smooth muscle relaxation. J Cell Physiol 184:409–420
Dernaika TA, Beavin M, Kinasewitz GT (2010) Iloprost improves gas exchange and exercise tolerance in patients with pulmonary hypertension and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respiration 79:377–382
Domino KB, Wetstein L, Glasser SA, Lindgren L, Marshall C, Harken A, Marshall BE (1983) Influence of mixed venous oxygen tension (PVO2) on blood flow to atelectatic lung. Anesthesiology 59:428–434
Faoro V, Lamotte M, Deboeck G, Pavelescu A, Huez S, Guenard H, Martinot JB, Naeije R (2007) Effects of sildenafil on exercise capacity in hypoxic normal subjects. High Alt Med Biol 8:155–163
Fesler P, Pagnamenta A, Rondelet B, Kerbaul F, Naeije R (2006) Effects of sildenafil on hypoxic pulmonary vascular function in dogs. J Appl Physiol 101:1085–1090
Ghofrani HA, Reichenberger F, Kohstall MG, Mrosek EH, Seeger T, Olschewski H, Seeger W, Grimminger F (2004) Sildenafil increased exercise capacity during hypoxia at low altitudes and at Mount Everest base camp: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial. Ann Intern Med 141:169–177
Glaister D (2001) Effects of acceleration on the lung. In: Prisk G, Paiva M, West J (eds) Gravity and the lung; lessons from microgravity. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 39–74
Hsu AR, Barnholt KE, Grundmann NK, Lin JH, McCallum SW, Friedlander AL (2006) Sildenafil improves cardiac output and exercise performance during acute hypoxia, but not normoxia. J Appl Physiol 100:2031–2040
Hughes JM, Glazier JB, Maloney JE, West JB (1968) Effect of lung volume on the distribution of pulmonary blood flow in man. Respir Physiol 4:58–72
Krug S, Sablotzki A, Hammerschmidt S, Wirtz H, Seyfarth HJ (2009) Inhaled iloprost for the control of pulmonary hypertension. Vasc Health Risk Manag 5:465–474
Lee SH, Channick RN (2005) Endothelin antagonism in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 26:402–408
Owall A, Davilen J, Sollevi A (1991) Influence of adenosine and prostacyclin on hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in the anaesthetized pig. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 35:350–354
Petersson J, Rohdin M, Sanchez-Crespo A, Nyren S, Jacobsson H, Larsson SA, Lindahl SG, Linnarsson D, Glenny RW, Mure M (2006) Paradoxical redistribution of pulmonary blood flow in prone and supine humans exposed to hypergravity. J Appl Physiol 100:240–248
Pirlo AF, Benumof JL, Trousdale FR (1981) Potentiation of lobar hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction by intermittent hypoxia in dogs. Anesthesiology 55:226–230
Ricart A, Maristany J, Fort N, Leal C, Pages T, Viscor G (2005) Effects of sildenafil on the human response to acute hypoxia and exercise. High Alt Med Biol 6:43–49
Rimeika D, Sanchez-Crespo A, Nyren S, Lindahl SG, Wiklund CU (2009) Iloprost inhalation redistributes pulmonary perfusion and decreases arterial oxygenation in healthy volunteers. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 53:1158–1166
Rohdin M, Petersson J, Mure M, Glenny RW, Lindahl SG, Linnarsson D (2003) Protective effect of prone posture against hypergravity-induced arterial hypoxaemia in humans. J Physiol 548:585–591
Rohdin M, Petersson J, Mure M, Glenny RW, Lindahl SG, Linnarsson D (2004a) Distributions of lung ventilation and perfusion in prone and supine humans exposed to hypergravity. J Appl Physiol 97:675–682
Rohdin M, Sundblad P, Linnarsson D (2004b) Effects of hypergravity on the distributions of lung ventilation and perfusion in sitting humans assessed with a simple two-step maneuver. J Appl Physiol 96:1470–1477
von Euler US, Liljestrand G (1946) Observations on the pulmonary arterial blood pressure in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand 12:301–320
Zhao L, Mason NA, Morrell NW, Kojonazarov B, Sadykov A, Maripov A, Mirrakhimov MM, Aldashev A, Wilkins MR (2001) Sildenafil inhibits hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 104:424–428
Zwissler B, Kemming G, Habler O, Kleen M, Merkel M, Haller M, Briegel J, Welte M, Peter K (1996) Inhaled prostacyclin (PGI2) versus inhaled nitric oxide in adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 154:1671–1677
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the dedication of our subjects and the technical support from Björn Johannesson. This study was supported by the Swedish Society of Medical Research, Swedish National Space Board, European Space Agency, and Fraenckel’s Fund for Medical Research, Swedish Heart and Lung Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Susan A. Ward.
L. L. Karlsson and M. Rohdin contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karlsson, L.L., Rohdin, M., Nekludov, M. et al. No protective role for hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction in severe hypergravity-induced arterial hypoxemia. Eur J Appl Physiol 111, 2099–2104 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1810-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1810-2