Abstract
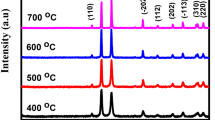
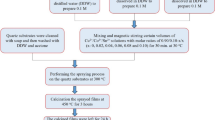
In the present study, a simple chemical method for the preparation of CuO nanostructures by varying Mn-doping concentration has been reported. It also provides an extensive investigation of structural, surface, and optical and dielectric properties of Mn-doped CuO nanostructures. Single-phase monoclinic crystal structure of CuO formation for all samples with average crystallite size of 20–24 nm has been observed from X-ray diffraction (XRD) results. A morphological transformation from nanosheets to spherical nanoparticles have been found with Mn doping as depicted by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images. The successful doping of Mn ions into CuO crystal has also been supported by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) results. The widening of the optical bandgap of CuO nanostructures has been observed with increasing Mn doping which may be attributed to band-filling effects and exchange interactions. Interestingly, the values of dielectric constant of CuO nanostructures have been observed to increase systematically with Mn doping making it potential material for high-frequency device applications.








Similar content being viewed by others

References
S. Anandan, S. Yang, Emergent methods to synthesize and characterize semiconductor CuO nanoparticles with various morphologies-an overview. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2, 23–56 (2007)
M.K. Song, S. Park, F.M. Alamgir, J. Cho, M. Liu, Nanostructured electrodes for lithium-ion and lithium-air batteries: the latest developments, challenges, and perspectives. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 72, 203–252 (2011)
K. Han, M. Tao, Electrochemically deposited p–n homojunction cuprous oxide solar cells. Sol Energy Mater. Sol Cells 93, 153–157 (2009)
S. Steinhauer, E. Brunet, T. Maier, G. Mutinati, A. Kock, O. Freudenberg, C. Gspan, W. Grogger, A. Neuhold, R. Resel, Gas sensing properties of novel CuO nanowire devices. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 187, 50–57 (2013)
Y. Tokura, H. Takagi, S. Uchida, A superconducting copper oxide compound with electrons as the charge carriers. Nature 337, 345–347 (1989)
G. Ren, D. Hu, E.W. Cheng, M.A. Vargas-Reus, P. Reip, R.P. Allaker, Characterisation of copper oxide nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 33, 587–590 (2009)
C.H. Han, Z.Y. Li, J.Y. Shen, Photocatalytic degradation of dodecyl-benzenesulfonate over TiO2–Cu2O under visible irradiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 168, 15–219 (2009)
H. Ahmad, S.K. Kamarudin, L.J. Minggu, M. Kassim, Hydrogen from photo–catalytic water splitting process: a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 43, 599–610 (2015)
B. Yan, Y. Wang, T. Jiang, X. Wu, Synthesis and enhanced photocatalytic property of La-doped CuO nanostructures by electrodeposition method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 5389–5394 (2016)
W.T. Yao, S.H. Yu, Y. Zhou, J. Jiang, Q.S. Wu, L. Zhang, J. Jiang, Formation of uniform CuO nanorods by spontaneous aggregation: selective synthesis of CuO, Cu2O, and Cu nanoparticles by a solid–liquid phase arc discharge process. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 14011 (2005)
Y.K. Su, C.M. Shen, H.T. Yang, H.L. Li, H.J. Gao, Controlled synthesis of highly ordered CuO nanowire arrays by template-based sol-gel route. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 17, 783 (2007)
J.T. Chen, F. Zhang, J. Wang, G.A. Zhang, B.B. Miao, X.Y. Fan, D. Yan, P.X. Yan, CuO nanowires synthesized by thermal oxidation route. J. Alloys Compd. 454, 268 (2008)
Y. Liu, Y. Chu, M. Li, L. Li, L. Dong, In situ synthesis and assembly of copper oxide nanocrystals on copper foil via amild hydrothermal process. J. Mater. Chem. 16, 192 (2006)
M. Vaseem, A. Umar, Y.B. Hahn, D.H. Kim, K.S. Lee, J.S. Jang, J.S. Lee, Flower-shaped CuO nanostructures: Structural, photocatalytic and XANES studies. Catal. Commun. 10, 11–16 (2008)
J. Zhu, H. Bi, Y. Wang, X. Wang, X. Yang, L. Lu, Synthesis of flower-like CuO nanostructures via a simple hydrolysis route. Mater. Lett. 61, 5236–5238 (2007)
C.H. Kuo, M.H. Huang, Facile synthesis of Cu2O nanocrystals with systematic shape evolution from cubic to octahedral structures. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 183 (2008)
S. Sonia, I.J. Annsi, P.S. Kumar, D. Mangalaraj, C. Viswanathan, N. Ponpandian, Hydrothermal synthesis of novel Zn doped CuO nanoflowers as an efficient photo-degradation material for textile dyes. Mater. Lett. 144, 127–130 (2015)
A. Yildiz, S. Horzum, N. Serin, T. Serin, Hopping conduction in In-doped CuO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 318, 105–107 (2014)
W.L. Gao, S.H. Yang, S.G. Yang, L.Y. Lv, Y.W. Du, Synthesis and magnetic properties of Mn doped CuO. Phys. Lett. A 375, 180–182 (2010)
P. Chand, A. Gaur, A. Kumar, U.K. Gaur, Structural and optical study of Li doped CuO thin films on Si (100) substrate deposited by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 307, 280–286 (2014)
N.M. Basith, J.J. Vijaya, L.J. Kennedy, M. Bououdina, Structural, optical and room-temperature ferromagnetic properties of Fe doped CuO nanostructures. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 53, 193–199 (2013)
N.M. Basith, J.J. Vijaya, L.J. Kennedy, M. Bououdina, Structural, morphological, optical, and magnetic properties of Ni-doped CuO nanostructures prepared by a rapid microwave combustion method. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 17, 110–118 (2014)
S. Ravi, F. Winfred, Shashikanth, Ferromagnetism in Mn doped copper oxide nanoflake like structures with high Neel temperature. Mater. Lett. 141, 132–134 (2015)
T. Jiang, J. Kong, Y. Wang, D. Meng, D. Wang, M. Yu, Optical and Photocatalytic properties of Mn-doped CuO nanosheets prepared by hydrothermal method. Cryst. Res. Technol. 51, 58–64 (2016)
W. Gao, S. Yang, S. Yang, L. Lv, Y. Du, Synthesis and magnetic properties of Mn doped CuO nanowires. Phys. Lett. A 375, 180–182 (2010)
A. Chamola, H. Singh, U.C. Naithani, Study of Pb(Zr0.65Ti0.35)O3 PZT (65/35) doping on structural, dielectric and conductivity properties of BaTiO3 (BT) ceramics. Adv. Mat. Lett 2(2), 148–152 (2011)
Y.X. Zhang, M. Huang, F. Li, Z.Q. Wen, Controlled synthesis of hierarchical CuO nanostructures for electrochemical capacitor electrodes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 8, 8645–8661 (2013)
N. Bouazizi, R. Bargougui, A. Oueslati, R. Benslama, Effect of synthesis time on structural, optical and electrical properties of CuO nanoparticles synthesized by reflux condensation method. Adv. Mater. Lett. 6, 158–164 (2015)
K. Borgohain, J.B. Singh, M.V.R. Rao, T. Shripathi, S. Mahamuni, Quantum size effects in CuO nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 61, 11093–11096 (2000)
G.J. Exarhos, Characterization of Optical Materials(Materials Characterization). Butterworth-Heinemann Ltd. (1993). ISBN 10: 0750692987. ISBN 13: 9780750692984
D. Sivalingam, J.B. Gopalakrishnan, J.B.B. Rayappan, Structural, morphological, electrical and vapour sensing properties of Mn doped nanostructured ZnO thin films. Sens. Actuators B 166, 624–631 (2012)
B.E. Sernelius, K.F. Berggren, Z.C. Jin, I. Hamberg, C.G. Granqvist, Band-gap tailoring of ZnO by means of heavy Al doping. Phys. Rev. B 37, 10244 (1988)
Y. Gülen, F. Bayansal, B. Şahin, H.A. Cetinkara, H.S. Güder, Fabrication and characterization of Mn-doped CuO thin films by the SILAR method. Ceram. Int. 39, 6475–6480 (2013)
T. Prodromakis, C. Papavassiliou, Engineering the Maxwell–Wagner polarization effect. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 6989 (2009)
R.D. Shannon, Dielectric polarizabilities of ions in oxides and fluorides. J. Appl. Phys. 73, 348 (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sajid, M., Imran, M., Salahuddin et al. Tailoring structural, surface, optical, and dielectric properties of CuO nanosheets for applications in high-frequency devices. Appl. Phys. A 124, 768 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2179-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2179-z