Abstract
Purpose
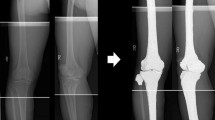
The purpose of this study was to compare the femoral mechanical-anatomical (FMA) and mechanical femoro-tibial (MFT) angles in an osteoarthritic population using the 2D (two dimension) and the 3D (three dimension) EOS low-dose biplanar radiographic system (EOS).
Methods
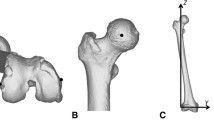
FMA and MFT angles were calculated in 127 adults with osteoarthritis. In 2D, FMA angle was measured between the femoral mechanical axis and the femoral anatomical axis, and MFT angle between the femoral mechanical axis and the tibial mechanical axis. In 3D, the measurement of FMA angle consisted of identifying specific anatomical landmarks on X-rays. MFT angle was then measured between the femoral mechanical axis and the tibial mechanical axis. The distribution of 2D and 3D values was assessed in terms of means and variances.
Results
Mean age was 69 ± 12 years. A total of 10% of the patients having a 3D FMA angle between 4° and 7° have a 2D-measured FMA over or underestimated. Particularly, FMA values tend to be underestimated in women in 2D. Finally, we found that men showed a tendency to a more varus morphology, with MFT values being significantly underestimated in 2D.
Conclusions
The EOS 3D reconstruction system is a reliable method to measure FMA and MFT angles in an osteoarthritic population.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharkey PF, Hozack WJ, Rothman RH et al (2002) Insall award paper. Why are total knee arthroplasties failing today? Clin Orthop 7–13
Parratte S, Pagnano MW, Trousdale RT, Berry DJ (2010) Effect of postoperative mechanical axis alignment on the fifteen-year survival of modern, cemented total knee replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Am 92:2143–2149. doi:10.2106/JBJS.I.01398
Bellemans J (2011) Neutral mechanical alignment: a requirement for successful TKA: opposes. Orthopedics 34:e507–e509. doi:10.3928/01477447-20110714-41
Kinzel V, Scaddan M, Bradley B, Shakespeare D (2004) Varus/valgus alignment of the femur in total knee arthroplasty. Can accuracy be improved by pre-operative CT scanning? Knee 11:197–201. doi:10.1016/S0968-0160(03)00106-6
Bardakos N, Cil A, Thompson B, Stocks G (2007) Mechanical axis cannot be restored in total knee arthroplasty with a fixed valgus resection angle: a radiographic study. J Arthroplasty 22:85–89. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2007.04.018
Kharwadkar N, Kent RE, Sharara KH, Naique S (2006) 5 degrees to 6 degrees of distal femoral cut for uncomplicated primary total knee arthroplasty: is it safe? Knee 13:57–60. doi:10.1016/j.knee.2005.07.001
Deakin AH, Basanagoudar PL, Nunag P et al (2012) Natural distribution of the femoral mechanical-anatomical angle in an osteoarthritic population and its relevance to total knee arthroplasty. Knee 19:120–123. doi:10.1016/j.knee.2011.02.001
Desmé D, Galand-Desmé S, Besse J-L et al (2006) Axial lower limb alignment and knee geometry in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Rev Chir Orthop Réparatrice Appar Mot 92:673–679
Tang WM, Zhu YH, Chiu KY (2000) Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am 82-A:1603–1608
Wang Y, Zeng Y, Dai K et al (2010) Normal lower-extremity alignment parameters in healthy Southern Chinese adults as a guide in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 25:563–570. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2009.03.021
Hsu RW, Himeno S, Coventry MB, Chao EY (1990) Normal axial alignment of the lower extremity and load-bearing distribution at the knee. Clin Orthop 215–227
Schlégl ÁT, Szuper K, Somoskeöy S, Than P (2015) Three dimensional radiological imaging of normal lower-limb alignment in children. Int Orthop 39:2073–2080. doi:10.1007/s00264-015-2851-2
Farrar MJ, Newman RJ, Mawhinney RR, King R (1999) Computed tomography scan scout film for measurement of femoral axis in knee replacement. J Arthroplasty 14:1030–1031
Lazennec JY, Brusson A, Dominique F et al (2015) Offset and anteversion reconstruction after cemented and uncemented total hip arthroplasty: an evaluation with the low-dose EOS system comparing two- and three-dimensional imaging. Int Orthop 39:1259–1267. doi:10.1007/s00264-014-2616-3
Swanson KE, Stocks GW, Warren PD et al (2000) Does axial limb rotation affect the alignment measurements in deformed limbs? Clin Orthop 246–252
Radtke K, Becher C, Noll Y, Ostermeier S (2010) Effect of limb rotation on radiographic alignment in total knee arthroplasties. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130:451–457. doi:10.1007/s00402-009-0999-1
Jiang CC, Insall JN (1989) Effect of rotation on the axial alignment of the femur. Pitfalls in the use of femoral intramedullary guides in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 50–56
Koshino T, Takeyama M, Jiang LS et al (2002) Underestimation of varus angulation in knees with flexion deformity. Knee 9:275–279
Than P, Szuper K, Somoskeöy S et al (2012) Geometrical values of the normal and arthritic hip and knee detected with the EOS imaging system. Int Orthop 36:1291–1297. doi:10.1007/s00264-011-1403-7
Journé A, Sadaka J, Bélicourt C, Sautet A (2012) New method for measuring acetabular component positioning with EOS imaging: feasibility study on dry bone. Int Orthop 36:2205–2209. doi:10.1007/s00264-012-1650-2
Illés T, Somoskeöy S (2012) The EOS™ imaging system and its uses in daily orthopaedic practice. Int Orthop 36:1325–1331. doi:10.1007/s00264-012-1512-y
Chaibi Y, Cresson T, Aubert B et al (2012) Fast 3D reconstruction of the lower limb using a parametric model and statistical inferences and clinical measurements calculation from biplanar X-rays. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 15:457–466. doi:10.1080/10255842.2010.540758
Thelen P, Delin C, Folinais D, Radier C (2012) Evaluation of a new low-dose biplanar system to assess lower-limb alignment in 3D: a phantom study. Skelet Radiol 41:1287–1293. doi:10.1007/s00256-012-1438-x
Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS (1957) Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 16:494–502
Guenoun B, Zadegan F, Aim F et al (2012) Reliability of a new method for lower-extremity measurements based on stereoradiographic three-dimensional reconstruction. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res OTSR 98:506–513. doi:10.1016/j.otsr.2012.03.014
Lotke PA, Ecker ML (1977) Influence of positioning of prosthesis in total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 59:77–79
Moreland JR, Bassett LW, Hanker GJ (1987) Radiographic analysis of the axial alignment of the lower extremity. J Bone Joint Surg Am 69:745–749
Jeffery RS, Morris RW, Denham RA (1991) Coronal alignment after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 73:709–714
Mullaji AB, Marawar SV, Mittal V (2009) A comparison of coronal plane axial femoral relationships in Asian patients with varus osteoarthritic knees and healthy knees. J Arthroplasty 24:861–867. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2008.05.025
Tang WM, Chiu KY, Kwan MFY et al (2005) Sagittal bowing of the distal femur in Chinese patients who require total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Res Off Publ Orthop Res Soc 23:41–45. doi:10.1016/j.orthres.2004.06.013
Nagamine R, Miura H, Bravo CV et al (2000) Anatomic variations should be considered in total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci Off J Jpn Orthop Assoc 5:232–237. doi:10.1007/s007760000050232.776
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
There is no funding source.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Source of study
Patients were from Hospital Cochin, Paris, France.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sailhan, F., Jacob, L. & Hamadouche, M. Differences in limb alignment and femoral mechanical-anatomical angles using two dimension versus three dimension radiographic imaging. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 41, 2009–2016 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-017-3428-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-017-3428-z