Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the tibiofemoral rotational profiles during navigated posterior-stabilized (PS) total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and investigate the effect on post-operative maximum flexion angles.
Methods
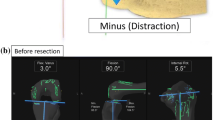
Twenty-five subjects, treated with navigated PS TKA, were enrolled, and the effect of posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) resection and component implantation on tibiofemoral rotational kinematics was statistically evaluated. Then, the effect of rotational alignment changes on the post-operative maximum angles was retrospectively examined in 96 subjects using the multiple regression analysis.
Results
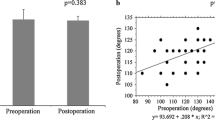
Tibial internal rotation was significantly increased in full extension (p < 0.01 and <0.001, respectively) and at 60° and 90° flexion (p < 0.05) after PCL resection, which further increased after implantation, compared with that before resection. The amount of tibial internal rotation from 90° flexion to maximum flexion was significantly decreased after PCL resection and implantation, compared with that before resection (p < 0.05). The internal changes in the rotational alignment were independent factors for the minimal improvement in the post-operative maximum flexion angles (R 2 = 0.078, p = 0.0067).
Conclusion
PCL resection changed the tibial rotational alignment and decreased the amount of tibial internal rotation. The implantation of PS components further increased the internal rotational alignment and could not compensate for the tibiofemoral rotation. Finally, the internal changes in rotational alignment affected the improvement of the maximum flexion angles, suggesting that rotational alignment is an important factor for improving post-operative maximum flexion angles.
Level of evidence
II.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi M, Mori S, Nishimura S, Nishimura A, Asano T, Hamanishi C (2005) Variability of extraarticular tibial rotation references for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 436:172–176
Akagi M, Oh M, Nonaka T, Tsujimoto H, Asano T, Hamanishi C (2004) An anteroposterior axis of the tibia for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 420:213–219
Arnout N, Vanlommel L, Vanlommel J, Luyckx JP, Labey L, Innocenti B, Victor J, Bellemans J (2015) Post-cam mechanics and tibiofemoral kinematics: a dynamic in vitro analysis of eight posterior-stabilized total knee designs. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23(11):3343–3353
Athwal KK, Daou HE, Kittl C, Davies AJ, Deehan DJ, Amis AA (2016) The superficial medial collateral ligament is the primary medial restraint to knee laxity after cruciate-retaining or posterior-stabilised total knee arthroplasty: effects of implant type and partial release. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24(8):2646–2655
Barrack RL, Schrader T, Bertot AJ, Wolfe MW, Myers L (2001) Component rotation and anterior knee pain after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 392:46–55
Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash HE (1998) Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 356:144–153
Dennis DA, Komistek RD, Mahfouz MR, Haas BD, Stiehl JB (2003) Multicenter determination of in vivo kinematics after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 416:37–57
Eckhoff DG, Johnston RJ, Stamm ER, Kilcoyne RF, Wiedel JD (1994) Version of the osteoarthritic knee. J Arthroplasty 9(1):73–79
Fujimoto E, Sasashige Y, Masuda Y, Hisatome T, Eguchi A, Masuda T, Sawa M, Nagata Y (2013) Significant effect of the posterior tibial slope and medial/lateral ligament balance on knee flexion in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21(12):2704–2712
Ghosh KM, Hunt N, Blain A, Athwal KK, Longstaff L, Amis AA, Rushton S, Deehan DJ (2015) Isolated popliteus tendon injury does not lead to abnormal laxity in posterior-stabilised total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23(6):1763–1769
Hernandez-Vaquero D, Noriega-Fernandez A, Fernandez-Carreira JM, Fernandez-Simon JM, Llorens de los Rios J (2014) Computer-assisted surgery improves rotational positioning of the femoral component but not the tibial component in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22(12):3127–3134
Hino K, Kutsuna T, Oonishi Y, Watamori K, Kiyomatsu H, Iseki Y, Watanabe S, Ishimaru Y, Miura H (2016) Assessment of the midflexion rotational laxity in posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-016-4175-1
Hino K, Oonishi Y, Kutsuna T, Watamori K, Iseki Y, Kiyomatsu H, Watanabe S, Miura H (2016) Preoperative varus-valgus kinematic pattern throughout flexion persists more strongly after cruciate-retaining than after posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Knee 23(4):637–641
Incavo SJ, Wild JJ, Coughlin KM, Beynnon BD (2007) Early revision for component malrotation in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 458:131–136
Ishida K, Matsumoto T, Tsumura N, Chinzei N, Kitagawa A, Kubo S, Chin T, Iguchi T, Akisue T, Nishida K, Kurosaka M, Kuroda R (2012) In vivo comparisons of patellofemoral kinematics before and after ADVANCE Medial-Pivot total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 36(10):2073–2077
Ishida K, Shibanuma N, Matsumoto T, Sasaki H, Takayama K, Hiroshima Y, Kuroda R, Kurosaka M (2016) Navigation-based tibial rotation at 90 degrees of flexion is associated with better range of motion in navigated total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24(8):2447–2452
Ishida K, Shibanuma N, Matsumoto T, Sasaki H, Takayama K, Matsuzaki T, Tei K, Kuroda R, Kurosaka M (2016) Navigation-based femorotibial rotation pattern correlated with flexion angle after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24(1):89–95
Ishida K, Shibanuma N, Matsumoto T, Sasaki H, Takayama K, Toda A, Kuroda R, Kurosaka M (2015) Factors affecting intraoperative kinematic patterns and flexion angles in navigated total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23(6):1741–1747
Kawahara S, Matsuda S, Okazaki K, Tashiro Y, Mitsuyasu H, Nakahara H, Iwamoto Y (2012) Relationship between the tibial anteroposterior axis and the surgical epicondylar axis in varus and valgus knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20(10):2077–2081
Konigsberg B, Hess R, Hartman C, Smith L, Garvin KL (2014) Inter- and intraobserver reliability of two-dimensional CT scan for total knee arthroplasty component malrotation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472(1):212–217
Lai YS, Chen WC, Huang CH, Cheng CK, Chan KK, Chang TK (2015) The effect of graft strength on knee laxity and graft in situ forces after posterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. PLoS ONE 10(5):e0127293
Langlois J, Charles-Nelson A, Katsahian S, Beldame J, Lefebvre B, Bercovy M (2015) Predictors of flexion using the rotating concave-convex total knee arthroplasty: preoperative range of motion is not the only determinant. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23(6):1734–1740
Li G, Gill TJ, DeFrate LE, Zayontz S, Glatt V, Zarins B (2002) Biomechanical consequences of PCL deficiency in the knee under simulated muscle loads–an in vitro experimental study. J Orthop Res 20(4):887–892
Li G, Papannagari R, Li M, Bingham J, Nha KW, Allred D, Gill T (2008) Effect of posterior cruciate ligament deficiency on in vivo translation and rotation of the knee during weightbearing flexion. Am J Sports Med 36(3):474–479
Liu MF, Chou PH, Liaw LJ, Su FC (2010) Lower-limb adaptation during squatting after isolated posterior cruciate ligament injuries. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 25(9):909–913
Lutzner J, Kirschner S, Gunther KP, Harman MK (2012) Patients with no functional improvement after total knee arthroplasty show different kinematics. Int Orthop 36(9):1841–1847
Matsuda S, Kawahara S, Okazaki K, Tashiro Y, Iwamoto Y (2013) Postoperative alignment and ROM affect patient satisfaction after TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res 471(1):127–133
Matsuda S, Miura H, Nagamine R, Urabe K, Hirata G, Iwamoto Y (2001) Effect of femoral and tibial component position on patellar tracking following total knee arthroplasty: 10-year follow-up of Miller-Galante I knees. Am J Knee Surg 14(3):152–156
Meijer MF, Reininga IH, Boerboom AL, Bulstra SK, Stevens M (2014) Does imageless computer-assisted TKA lead to improved rotational alignment or fewer outliers? A systematic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472(10):3124–3133
Miyazaki Y, Nakamura T, Kogame K, Saito M, Yamamoto K, Suguro T (2011) Analysis of the kinematics of total knee prostheses with a medial pivot design. J Arthroplasty 26(7):1038–1044
Nicoll D, Rowley DI (2010) Internal rotational error of the tibial component is a major cause of pain after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92(9):1238–1244
Nishio Y, Onodera T, Kasahara Y, Takahashi D, Iwasaki N, Majima T (2014) Intraoperative medial pivot affects deep knee flexion angle and patient-reported outcomes after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 29(4):702–706
Orita N, Deie M, Shimada N, Iwaki D, Asaeda M, Hirata K, Ochi M (2015) Posterior tibial displacement in the PCL-deficient knee is reduced compared to the normal knee during gait. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23(11):3251–3258
Roh YW, Jang J, Choi WC, Lee JK, Chun SH, Lee S, Seong SC, Lee MC (2013) Preservation of the posterior cruciate ligament is not helpful in highly conforming mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21(12):2850–2859
Schmidt R, Komistek RD, Blaha JD, Penenberg BL, Maloney WJ (2003) Fluoroscopic analyses of cruciate-retaining and medial pivot knee implants. Clin Orthop Relat Res 410:139–147
Seon JK, Park JK, Shin YJ, Seo HY, Lee KB, Song EK (2011) Comparisons of kinematics and range of motion in high-flexion total knee arthroplasty: cruciate retaining vs. substituting designs. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19(12):2016–2022
Sharkey PF, Hozack WJ, Rothman RH, Shastri S, Jacoby SM (2002) Insall Award paper. Why are total knee arthroplasties failing today? Clin Orthop Relat Res 404:7–13
Tei K, Ishida K, Matsumoto T, Kubo S, Sasaki H, Shibanuma N, Akisue T, Nishida K, Kurosaka M, Kuroda R (2012) Novel image-matching software for postoperative evaluation after TKA. Orthopedics 35(12):e1711–e1715
Wada K, Mikami H, Hamada D, Yonezu H, Oba K, Sairyo K (2016) Measurement of rotational and coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty using a navigation system is reproducible. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 136(2):271–276
Wasielewski RC, Galante JO, Leighty RM, Natarajan RN, Rosenberg AG (1994) Wear patterns on retrieved polyethylene tibial inserts and their relationship to technical considerations during total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:31–43
Watanabe S, Sato T, Omori G, Koga Y, Endo N (2014) Change in tibiofemoral rotational alignment during total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci 19(4):571–578
Wunschel M, Leasure JM, Dalheimer P, Kraft N, Wulker N, Muller O (2013) Differences in knee joint kinematics and forces after posterior cruciate retaining and stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Knee 20(6):416–421
Yang JH, Dahuja A, Kim JK, Yun SH, Yoon JR (2016) Alignment in knee flexion position during navigation-assisted total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24(8):2422–2429
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
This study was not funded by any company.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishida, K., Shibanuma, N., Matsumoto, T. et al. Tibiofemoral rotational alignment affects flexion angles in navigated posterior-stabilized total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 26, 1532–1539 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-017-4557-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-017-4557-z