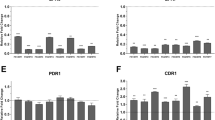
Abstract
We previously showed that the expression of ENO1 (enolase) in the fungal pathogen Candida albicans is critical for cell growth. In this study, we investigate the contribution of the ENO1 gene to virulence. We conducted our functional study of ENO1 in C. albicans by constructing an eno1/eno1 null mutant strain in which both ENO1 alleles in the genome were knockouted with the SAT1 flipper cassette that contains the nourseothricin-resistance marker. Although the null mutant failed to grow on synthetic media containing glucose, it was capable of growth on media containing yeast extract, peptone, and non-fermentable carbon sources. The null mutant was more susceptible to certain antifungal drugs. It also exhibited defective hyphal formation, and was avirulent in BALB/c mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angiolella, L., Micocci, M.M., D’Alessio, S., Girolamo, A., Maras, B., and Cassone, A. 2002. Identification of major glucan-associated cell wall proteins of Candida albicans and their role in fluconazole resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 46, 1688–1694.
Arguelles, J.C., Rodriguez, T., and Alvarez-Peral, F.J. 1999. Trehalose hydrolysis is not required for human serum-induced dimorphic transition in Candida albicans: evidence from a tps1/tps1 mutant deficient in trehalose synthesis. Res. Microbiol. 150, 521–529.
Baron, U., Gossen, M., and Bujard, H. 1997. Tetracycline-controlled transcription in eukaryotes: novel transactivators with graded transactivation potential. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 2723–2729.
Baron, U., Schnappinger, D., Helbl, V., Gossen, M., Hillen, W., and Bujard, H. 1999. Generation of conditional mutants in higher eukaryotes by switching between the expression of two genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 1013–1018.
Chen, C.G., Yang, Y.L., Cheng, H.H., Su, C.L., Huang, S.F., Chen, C.T., Liu, Y.T., Su, I.J., and Lo, H.J. 2006. Non-lethal Candida albicans cph1/cph1 efg1/efg1 transcription factor mutant establishing restricted zone of infection in a mouse model of systemic infection. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 19, 561–565.
Chen, C.G., Yang, Y.L., Tseng, K.Y., Shih, H.I., Liou, C.H., Lin, C.C., and Lo, H.J. 2009. Rep1p negatively regulating MDR1 efflux pump involved in drug resistance in Candida albicans. Fungal Genet. Biol. 46, 714–720.
Chibana, H., Uno, J., Cho, T., and Mikami, Y. 2005. Mutation in IRO1 tightly linked with URA3 gene reduces virulence of Candida albicans. Microbiol. Immunol. 49, 937–939.
Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). 1997. Reference method for broth dilution antifungal susceptibility testing of yeasts; approved standard. M27A, Wayne, PA, USA.
De Backer, M.D., Nelissen, B., Logghe, M., Viaene, J., Loonen, I., Vandoninck, S., de Hoogt, R., Dewaele, S., Simons, F.A., Verhasselt, P., and et al. 2001. An antisense-based functional genomics approach for identification of genes critical for growth of Candida albicans. Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 235–241.
Eroles, P., Sentandreu, M., Elorza, M.V., and Sentandreu, R. 1997. The highly immunogenic enolase and Hsp70p are adventitious Candida albicans cell wall proteins. Microbiology 143, 313–320.
Feo, S., Arcuri, D., Piddini, E., Passantino, R., and Giallongo, A. 2000. ENO1 gene product binds to the c-myc promoter and acts as a transcriptional repressor: relationship with Myc promoter-binding protein 1 (MBP-1). FEBS Lett. 473, 47–52.
Jong, A.Y., Chen, S.H., Stins, M.F., Kim, K.S., Tuan, T.L., and Huang, S.H. 2003. Binding of Candida albicans enolase to plasmin (ogen) results in enhanced invasion of human brain microvascular endothelial cells. J. Med. Microbiol. 52, 615–622.
Keren, P., George, J., Shaish, A., Levkovitz, H., Janakovic, Z., Afek, A., Goldberg, I., Kopolovic, J., Keren, G., and Harats, D. 2000. Effect of hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia on atherosclerosis in LDL receptor-deficient mice: establishment of a combined model and association with heat shock protein 65 immunity. Diabetes 49, 1064–1069.
Kim, R.Y. and Wistow, G.J. 1993. Expression of the duck alpha-enolase/tau-crystallin gene in transgenic mice. FASEB J. 7, 464–469.
Klingspor, L., Stintzing, G., and Tollemar, J. 1997. Deep Candida infection in children with leukaemia: clinical presentations, diagnosis and outcome. Acta Paediatr. 86, 30–36.
Lo, H.J., Kohler, J.R., DiDomenico, B., Loebenberg, D., Cacciapuoti, A., and Fink, G.R. 1997. Nonfilamentous C. albicans mutants are avirulent. Cell 90, 939–949.
Lo, H.J., Wang, J.S., Lin, C.Y., Chen, C.G., Hsiao, T.Y., Hsu, C.T., Su, C.L., Fann, M.J., Ching, Y.T., and Yang, Y.L. 2005. Efg1 involved in drug resistance by regulating the expression of ERG3 in Candida albicans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 49, 1213–1215.
Mason, A.B., Buckley, H.R., and Gorman, J.A. 1993. Molecular cloning and characterization of the Candida albicans enolase gene. J. Bacteriol. 175, 2632–2639.
McAlister, L. and Holland, M.J. 1982. Targeted deletion of a yeast enolase structural gene. Identification and isolation of yeast enolase isozymes. J. Biol. Chem. 257, 7181–7188.
Miceli, M.H., Bernardo, S.M., and Lee, S.A. 2009. In vitro analyses of the combination of high-dose doxycycline and antifungal agents against Candida albicans biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 34, 326–332.
Montagnoli, C., Sandini, S., Bacci, A., Romani, L., and La Valle, R. 2004. Immunogenicity and protective effect of recombinant enolase of Candida albicans in a murine model of systemic candidiasis. Med. Mycol. 42, 319–324.
Nakayama, H., Mio, T., Nagahashi, S., Kokado, M., Arisawa, M., and Aoki, Y. 2000. Tetracycline-regulatable system to tightly control gene expression in the pathogenic fungus Candida albicans. Infect. Immun. 68, 6712–6719.
Nesland, J.M., Holm, R., Johannessen, J.V., and Gould, V.E. 1988. Neuroendocrine differentiation in breast lesions. Pathol. Res. Pract. 183, 214–221.
Niedenthal, R., Riles, L., Guldener, U., Klein, S., Johnston, M., and Hegemann, J.H. 1999. Systematic analysis of S. cerevisiae chromosome VIII genes. Yeast 15, 1775–1796.
Pitarch, A., Abian, J., Carrascal, M., Sanchez, M., Nombela, C., and Gil, C. 2004. Proteomics-based identification of novel Candida albicans antigens for diagnosis of systemic candidiasis in patients with underlying hematological malignancies. Proteomics 4, 3084–3106.
Plow, E.F. and Das, R. 2009. Enolase-1 as a plasminogen receptor. Blood 113, 5371–5372.
Plow, E.F., Freaney, D.E., Plescia, J., and Miles, L.A. 1986. The plasminogen system and cell surfaces: evidence for plasminogen and urokinase receptors on the same cell type. J. Cell Biol. 103, 2411–2420.
Porter, J.D., Khanna, S., Kaminski, H.J., Rao, J.S., Merriam, A.P., Richmonds, C.R., Leahy, P., Li, J., and Andrade, F.H. 2001. Extraocular muscle is defined by a fundamentally distinct gene expression profile. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 12062–12067.
Reuss, O., Vik, A., Kolter, R., and Morschhauser, J. 2004. The SAT1 flipper, an optimized tool for gene disruption in Candida albicans. Gene 341, 119–127.
Rudner, G., Katar, M., and Maisel, H. 1990. Enolase in the avian and turtle lens. Curr. Eye Res. 9, 139–150.
Sharkey, L.L., Liao, W.L., Ghosh, A.K., and Fonzi, W.A. 2005. Flanking direct repeats of hisG alter URA3 marker expression at the HWP1 locus of Candida albicans. Microbiology 151, 1061–1071.
Sherman, F. 2002. Getting started with yeast. Methods Enzymol. 350, 3–41.
Sorger, D. and Daum, G. 2003. Triacylglycerol biosynthesis in yeast. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 61, 289–299.
Sundstrom, P. and Aliaga, G.R. 1992. Molecular cloning of cDNA and analysis of protein secondary structure of Candida albicans enolase, an abundant, immunodominant glycolytic enzyme. J. Bacteriol. 174, 6789–6799.
Sundstrom, P. and Aliaga, G.R. 1994. A subset of proteins found in culture supernatants of Candida albicans includes the abundant, immunodominant, glycolytic enzyme enolase. J. Infect. Dis. 169, 452–456.
Sung, H.J. and Cho, J.Y. 2008. Biomarkers for the lung cancer diagnosis and their advances in proteomics. BMB Rep. 41, 615–625.
Tremblay, P., Meiner, Z., Galou, M., Heinrich, C., Petromilli, C., Lisse, T., Cayetano, J., Torchia, M., Mobley, W., Bujard, H., and et al. 1998. Doxycycline control of prion protein transgene expression modulates prion disease in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 12580–12585.
Trumbly, R.J. 1992. Glucose repression in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Microbiol. 6, 15–21.
Tsuneki, H., Ishizuka, M., Terasawa, M., Wu, J.B., Sasaoka, T., and Kimura, I. 2004. Effect of green tea on blood glucose levels and serum proteomic patterns in diabetic (db/db) mice and on glucose metabolism in healthy humans. BMC Pharmacol. 4, 18.
Van der Straeten, D., Rodrigues-Pousada, R.A., Goodman, H.M., and Van Montagu, M. 1991. Plant enolase: gene structure, expression, and evolution. Plant Cell 3, 719–735.
Xin, H., Dziadek, S., Bundle, D.R., and Cutler, J.E. 2008. Synthetic glycopeptide vaccines combining beta-mannan and peptide epitopes induce protection against candidiasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 13526–13531.
Yang, Y.L., Chen, H.F., Kuo, T.J., and Lin, C.Y. 2006a. Mutations on CaENO1 in Candida albicans inhibit cell growth in the presence of glucose. J. Biomed. Sci. 13, 313–321.
Yang, Y.L., Lin, Y.H., Tsao, M.Y., Chen, C.G., Shih, H.I., Fan, J.C., Wang, J.S., and Lo, H.J. 2006b. Serum repressing efflux pump CDR1 in Candida albicans. BMC Mol. Biol. 7, 22.
Yang, Y.L., Wang, C.W., Chen, C.T., Wang, M.H., Hsiao, C.F., and Lo, H.J. 2009. Non-lethal Candida albicans cph1/cph1 efg1/efg1 mutant partially protects mice from systemic infections by lethal wild-type cells. Mycol. Res. 113, 388–390.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ko, HC., Hsiao, TY., Chen, CT. et al. Candida albicans ENO1 null mutants exhibit altered drug susceptibility, hyphal formation, and virulence. J Microbiol. 51, 345–351 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-013-2577-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-013-2577-z