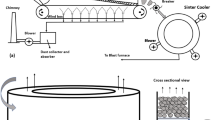
Abstract
An unsteady one-dimensional model of an iron ore sintering bed with multiple solid phases was proposed. The proposed model confers a phase on each solid material. The present model was established with a series of conservation equations in the form of a partial differential equation for each solid phase and gas phase. Coke combustion, limestone decomposition, gaseous reaction, heat transfers in/between each phase, and geometric changes of the solid particles are reflected by each term of the governing equations. Simulation results are compared with the limited experimental data set of sintering pot tests. Parametric studies for various initial water contents and coke diameters have also been performed. The simulation results predict the experimental results well and show physically reasonable trends for various parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A:
-
volumetric surface area, m2/m3, pre-exponential factor, s−1
- C:
-
molar concentration, kmol/m3
- dp :
-
particle size, m
- E:
-
activation energy, J/kmol
- fshrink :
-
shrink factor
- fip :
-
ratio of internal pore generation
- H:
-
heat of reaction or combustion, J/kmol
- h:
-
enthalpy, J; convection coefficient, W/m2K
- I+, I− :
-
radiation intensity upward or downward, W/m2s
- k:
-
rate constant, s−1, conductivity, W/mK; mass transfer coefficient, m/s
- M:
-
volumetric mass generation rate, kg/m3s
- m:
-
mass fraction
- np :
-
particle number density, 1/m3
- p:
-
pressure, N/m2
- q:
-
volumetric heat generation rate, J/m3s
- R:
-
universal gas constant
- r:
-
reaction rate, kmol/m3s
- T:
-
temperature, K
- t:
-
time, s
- V:
-
vulume, m3
- v:
-
superficial velocity, m/s
- W:
-
molecular weight, kg/kmol
- y:
-
vertical coordinate, m
- y:
-
fraction of heat absorbed by solid
- ε:
-
porosity
- τ:
-
transmissivity
- ζ:
-
particle area factor
- κ:
-
absorption coefficient, m−1
- ν:
-
stoichiometric coefficient
- ρ:
-
density, kg/m3
- ϕ:
-
general scalar quantity
- a:
-
exponent of temperature
- b:
-
exponent of pressure
- b:
-
black body
- eff:
-
diffusion through the ash layer
- g:
-
gas phase
- I:
-
index of solid phase
- i:
-
component of the solid phase
- ip:
-
internal pore
- j:
-
chemical species of the solid phase
- k:
-
reaction or combustion process
- m:
-
mass transfer
- o:
-
initial value
- r:
-
kinetic
- s:
-
solid phase
References
P. R. Austin, H. Nogami, and J. Yagi,ISIJ Int. 37, 458 (1997).
P. L. M. Wong, M. J. Kim, and H. S. Kim,Met. Mater._-Int. 6, 151 (2000)
I. Muchi and J. Higuchi,Tetsu-to-Hagané 56, 371 (1970)
R. W. Young,Ironmak. Steelmak. 6, 321 (1977).
M. J. Cumming and J. A. Thurlby,Ironmak. Steelmak. 17, 245 (1990).
F. Patisson, J. P. Bellot, D. Ablitzer, E. Marli, C. Dulcy, and J. M. Steiler,Ironmak. Steelmak. 18, 89 (1991).
N. K. Nath, A. J. Da Silva, and N. Chakraborti,Steel Res. 68, 285 (1997).
E. Kasai, M. V. Ramos, J. Kano, F. Saito, and Y. Waseda,3rd World Congress on Particle Technology, Brighton, England (1998).
M. V. Ramos, E. Kasai, J. Kano, and T. Nakamura,ISIJ Int. 40, 448 (2000).
W. Yang, C. Ryu, S. Choi, E. Choi, D. Lee, and W. Huh,ISIJ Int. 44, 492 (2004).
M. L. Hobbs, P. T. Radulovic, and L. D. Smoot,AIChE J. 38, 681 (1992).
D. H. Shin and S. Choi,Combust. and Flame,121, 167 (2000).
N. Wakao and S. Kaguei,Heat and Mass Transfer in Packed Beds, Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, New York (1982).
J. A. Kunipers, W. Prins, and W. P. M. van Swaaij,AIChE J. 38, 1079 (1992).
R. B. Bird, W. E. Stewart, and E. N. LightfootTransport Phenomena 2nd ed., p. 525 Wiley Int., New York (2001).
D. Merrick,Fuel 62, 540 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, W., Ryu, C., Choi, S. et al. Mathematical model of thermal processes in an iron ore sintering bed. Met. Mater. Int. 10, 493–500 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027355
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027355