Abstract
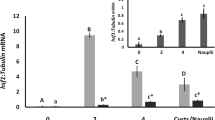
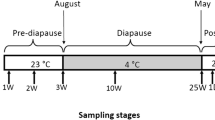
The expression of metabolic enzyme genes and heat-shock protein genes (Hsp) during early embryogenesis in diapause and non-diapause eggs of the silkworm Bombyx mori was quantified by semi-quantitative RT-PCR. The trehalase gene (Tre) was expressed in non-diapause eggs up-to nine days, while in diapause eggs was not up regulated. The glycogen phosphorylase gene (GPase) was expressed in non-diapause eggs, whereas in diapause eggs a high level was observed in early stage, but down regulated in later stage. The phosphofructokinase gene (PFK) and sorbitol dehyrogenase-2 gene (SDH-2) expression was fluctuated in non-diapause eggs, whereas in diapause eggs these were expressed only at early stage and not observed in later stage. The glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene (G6P-DH) in non-diapause eggs was highly expressed during the differentiation phase and decreased in the organogenesis phase. In contrast to this, expression in diapause eggs was of low level during differentiation phase and of high level observed in the organogenesis phase. In the tissues, PFK and SDH-2 were selectively expressed in cuticle and midgut, whereas Tre expression was high in midgut and ovary of larvae incubated at 15°C. The Hsp (20.4, 20.8, 40, 70, and 90) were expressed in both diapause and non-diapause eggs. Their expression was, however, selective in tissues with Hsp20.4 in midgut and ovary, Hsp40 in head, Hsp70 in cuticle and Hsp90 in ovary and head in high amounts at 15°C. These results suggest that the metabolic enzyme genes studied except Hsp play a major role during embryogenesis of diapause and non-diapause silkworm.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DH:
-
diapause hormone
- GPase:
-
glycogen phosphorylase
- G6P-DH:
-
glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- Hsp:
-
heat-shock protein
- PFK:
-
phosphofructokinase
- SDH:
-
sorbitol dehydrogenase
- Tre:
-
trehalase
References
Andrewartha H.G. 1952. Diapause in relation to the ecology of insects. Biol. Rev. 27: 50–107.
Benson D.A., Karsch-Mizrachi I., Lipman D.J., Ostell J. & Wheeler D.L. 2007. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 35 (Data-base Issue): D21–D25.
Chen C.P. & Denlinger D.L. 1990. Activation of phosphorylase in response to cold and heat stress in the flesh fly Sarcophaga crassipalpis. J. Insect Physiol. 36: 549–553.
Coulon B.M. & Mathelin J. 1991. Variations in the rates of synthesis of heat shock proteins, Hsp70, between laying and neurula in the diapausing embryo of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Sericologia 31: 295–300.
Coulon M. & Dorel C. 1991. The arrest of embryogenesis at gastrula stage in the diapausing silkworm Bombyx mori is related to the synthesis of protein p61. Dev. Genes Evol. 199: 469–475.
Denlinger D.L., Rinehart J.P. & Yocum G.D. 2001. Stress proteins: a role in insect diapause?, pp. 155–171. In: Denlinger D.L., Giebultowicz J.M. & Saunders D.S. (eds), Insect Timing: Circadian Rhythmicity to Seasonality, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Feder M.E. & Hofmann G.E. 1999. Heat shock proteins, molecular chaperones, and the stress response: evolutionary and ecological physiology. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 61: 243–282.
Fujiwara Y., Shindome C., Takeda M. & Shiomi K. 2006. The role of ERK and p38 MAPK signaling cascades on embryonic diapause initiation and termination of the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 36: 47–53.
Furusawa T. & Yang W.J. 1987. Fluctuation of the free sugar with embryonic development of non-diapause eggs of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J. Sericult. Sci. Japan 56: 143–149.
Goto S.G. & Kimura M.T. 2004. Heat-shock-responsive genes are not involved in the adult diapause of Drosophila triauraria, Gene 326: 117–122.
Hayakawa Y. & Chino H. 1982. Phosphofructokinase as a possible key enzyme regulating glycerol or trehalose accumulation in diapausing insects. Insect Biochem. 12: 639–642.
Hayward S.A.L., Rinehart J.P. & Denlinger D.L. 2004. Desiccation and rehydration elicit distinct heat shock protein transcript responses in flesh fly pupae. J. Exp. Biol. 207: 963–971.
Horie Y., Kanda T. & Mochida Y. 2000. Sorbitol as an arrester of embryonic development in diapausing eggs of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J. Insect Physiol. 46: 1009–1016.
Hwang J.S., Go H.J., Goo T.W.S., Yun E.Y., Ahn M.Y., Kim S.R., Park K.H., Kim I., Jeon J.P. & Kang S.W. 2007. Molecular characterization of small heat shock protein (Hsp 20.8A) from the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Int. J. Indust. Entomol. 15: 75–78.
Hwang J.S., Go H.J., Goo T.W., Yun E.Y., Choi K.H., Su I.S., Lee S.M., Lee B.H., Kim I., Chun T. & Kang S.W. 2005. The analysis of differentially expressed novel transcripts in diapausing and diapause-activated eggs of Bombyx mori. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 59: 197–201.
Joplin K.H., Yocum G.D. & Denlinger D.L. 1990. Cold shock elicits expression of the heat shock protein in the flesh fly Sarcophaga crassipalpis. J. Insect Physiol. 36: 825–834.
Kitazawa T., Kanda T. & Takami T. 1963. Changes of mitotic activity in silkworm eggs in relation to diapause. Bull. Sericult. 18: 283–285.
Kostal V., Tollarova M. & Sula J. 2004. Adjustments of the enzymatic complement for polyol biosynthesis and accumulation in diapausing cold-acclimated adults of Pyrrhocoris apterus. J. Insect Physiol. 50: 303–313.
Krishnaswami S. 1978. New Technology of Silkworm Rearing. Bulletin No. 2. Central Sericultural Research and Training Institute, Mysore, Central Silk Board, Government of India.
Lindquist S. & Craig E.A. 1988. The heat shock proteins. Annu. Rev. Genet. 22: 631–677.
Moribe Y., Niimi T., Yamashita O. & Yaginuma T. 2001. Samui, a novel cold inducible gene, encoding a protein with a BAG domain similar to silencer of death domains (SODD/BAG-4) isolated from Bombyx diapause eggs. Eur. J. Biochem. 268: 3432–3442.
Niimi T., Yamashita O. & Yaginuma T. 1993. A cold-inducible Bombyx gene encoding a protein similar to mammalian sorbitol dehydrogenase: yolk nuclei-dependent gene expression in diapause eggs. Eur. J. Biochem. 213: 1125–1131.
Rinehart J.P. & Denlinger D.L. 2000. Heat shock protein 90 is down regulated during pupal diapause in the flesh fly, Sarcophaga crassipalpis, but remains responsible to thermal stress. Insect Mol. Biol. 9: 641–645.
Rinehart J.P., Li A., Yocum G.D., Robich R.M., Hayward A.L. & Denlinger D.L. 2007. Up regulation of heat shock protein is essential for cold survival during insect diapause. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104: 11130–11137.
Rinehart J.P., Yocum G.D. & Denlinger D.L. 2000. Developmental up regulation of inducible Hsp 70 transcripts, but not the cognate form, during pupal diapause in the flesh fly, Sarcophaga carssipalsi. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 30: 515–521.
Sawada H., Yamahama Y., Yamamoto T., Mase K., Ogawa H. & Ino T. 2006. A novel RNA helicase like protein during early embryonic development in silkworm Bombyx mori; Molecular characterization and intracellular localization. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 36: 911–920.
Sonoda S., Fukumoto K., Izumi Y., Ashfaq M., Yoshida H. & Tsumaki H.A. 2006. Small Hsp gene is not responsible for diapause and cold tolerance acquisition in Chilo suppressalis. J. Appl. Entomol. 130: 309–313.
Storey K.B. & Storey J.M. 1988. Freeze tolerance in animals. Physiol. Rev. 68: 27–84.
Storey K.B. & Storey J.M. 1991. Biochemistry of cryoprotectants, pp. 64–93. In: Denlinger D. & Lee R.E. (eds), Insects at Low Temperature, Chapman and Hall, New York.
Su Z.H., Ikeda M., Sato Y., Imai K., Isobe M. & Yamashita O. 1994. Molecular characterization of ovary trehalase of the silkworm, Bombyx mori and its transcriptional activation by diapause hormone. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1218: 366–374.
Su Z.H., Sato Y. & Yamashita O. 1993. Purification, cDNA cloning and Northern blot analysis of trehalase of pupal midgut of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1173: 217–224.
Suzuki M.G., Terada T., Kobayashi M. & Shimada T. 1999. Diapause-associated transcription of BmEts, a gene encoding an ETS transcription factor homolog in Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 29: 339–347.
Trang L.T.D., Sehadova H., Ichihara N., Iwai S., Mita K. & Takeda M. 2006. Casein kinases I of the silkworm, Bombyx mori: their possible roles in circadian timing and developmental determination. J. Biol. Rhythms 21: 335–349.
Tsimuki H., Rojas R.R., Storey K.B., Baust J.G. 1987. The fate of (14C) glucose during cold-hardening in Eurosta solidiaginis (Fitch). Insect Biochem. 17: 347–352.
Wood F.B. & Nordin J.H. 1980. Activation of the hexose monophosphate shunt during cold induced glycerol accumulation by Protophormia terranoval. Insect Biochem. 10: 87–93.
Yaginuma T., Kobayashi M. & Yamashita O. 1990. Distinct effects of different low temperatures on the induction of NAD sorbitol dehydrogenase activity in diapause eggs of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J. Comp. Physiol. 160: 277–285.
Yaginuma T. & Yamashita O. 1978. Polyol metabolism related to diapause in Bombyx eggs: different behaviour of sorbitol from glycerol during diapause and post-diapause. J. Insect Physiol. 24: 347–354.
Yaginuma T. & Yamashita O. 1979. NAD-sorbitol dehydrogenase activity in relation to the termination of diapause in eggs of Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. 9: 547–553.
Yaginuma T. & Yamashita O. 1999. Oxygen consumption in relation to sorbitol utilization at the termination of diapause in eggs of the silkworm Bombyx mori. J. Insect Physiol. 44: 621–627.
Yamamoto T., Kanekatsu M., Nakagoshi M., Kato T., Mase K. & Sawada H. 2005. Casein kinase 2 during early embryonic development in silkworm Bombyx mori: cDNA sequence, gene expression, and enzyme activity. DNA Seq. 16: 446–455.
Yamashita O. 1996. Diapause hormone of the silkworm, Bombyx mori: structure, gene expression and function. J. Insect Physiol. 42: 669–679.
Yamashita O. & Hasegawa K. 1985. Embryonic diapause, pp. 407–434. In Kerkut G.A. & Gilbert L.I. (eds), Comprehensive Insect Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology, Pergamon Press, Oxford.
Yamashita O., Suzuki K. & Hasegawa K. 1975. Glycogen phosphorylase activity in relation to diapause initiation in Bombyx egg. Insect Biochem. 5: 707–718.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saravanakumar, R., Ponnuvel, K.M. & Qadri, S.M.H. Expression of metabolic enzyme genes and heat-shock protein genes during embryonic development in diapause and non-diapause egg of multivoltine silkworm Bombyx mori . Biologia 63, 737–744 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-008-0124-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-008-0124-x