Abstract
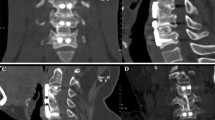
The optimal surgical strategy for multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) has not been defined, and few comparative researches between hybrid decompression and multilevel corpectomy have been conducted. Here, we reported 28 patients of three-level CSM, of whom 12 underwent hybrid decompression and 16 two-level corpectomy, with each type of procedure chosen according to radiologic characteristics of those patients. Clinical and radiologic parameters of both groups showed various degrees of improvement. However, no statistically significant differences in Japanese Orthopedic Association (JOA) score improvement rate, graft fusion rate, post-operative neck disability index (NDI) or segmental lordosis between the two groups were found. We conclude that both hybrid decompression and two-level corpectomy could obtain satisfying clinical efficacy in the management of three-level CSM for appropriate patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashkenazi, E., Smorgick, Y., Rand, N., Millgram, M.A., Mirovsky, Y., Floman, Y., 2005. Anterior decompression combined with corpectomies and discectomies in the management of multilevel cervical myelopathy: a hybrid decompression and fixation technique. J. Neurosurg. Spine, 3(3):205–209. [doi:10.3171/spi.2005.3.3.0205]
Brodke, D.S., Gollogly, S., Alexander Mohr, R.A., Nguyen, B.K., Dailey, A.T., Bachus, A.K., 2001. Dynamic cervical plates: biomechanical evaluation of load sharing and stiffness. Spine, 26(12):1324–1329. [doi:10.1097/00007632-200106150-00010]
Chuang, H.C., Cho, D.Y., Chang, C.S., Lee, W.Y., Jung-Chung, C., Lee, H.C., Chen, C.C., 2006. Efficacy and safety of the use of titanium mesh cages and anterior cervical plates for interbody fusion after anterior cervical corpectomy. Surg. Neurol., 65(5):464–471. [doi:10.1016/j.surneu.2005.12.021]
Epstein, N.E., Silvergleide, R.S., 2003. Documenting fusion following anterior cervical surgery: a comparison of roentgenogram versus two-dimensional computed tomographic findings. J. Spinal Disord. Tech., 16(3):243–247.
Epstein, N.E., Silvergleide, R.S., Black, K., 2002. Computed tomography validating bony ingrowth into fibula strut allograft: a criterion for fusion. Spine, 2(2):129–133. [doi:10.1016/S1529-9430(01)00154-1]
Hee, H.T., Majd, M.E., Holt, R.T., Whitecloud, T.S. 3rd., Pienkowski, D., 2003. Complications of multilevel cervical corpectomies and reconstruction with titanium cages and anterior plating. J. Spinal Disord. Tech., 16(1):1–8.
Hu, J.H., Tian, Y., Zhang, J.G., Qian, J., Li, J.Y., Qiu, G.X., 2009. Three-level anterior cervical discectomy: radiographic and clinical results analysis. Chin. J. Orthop., 29(3):216–219 (in Chinese).
Katsuura, A., Hukuda, S., Saruhashi, Y., Mori, K., 2001. Kyphotic malalignment after anterior cervical fusion is one of the factors promoting the degenerative process in adjacent intervertebral levels. Eur. Spine J., 10(4):320–324. [doi:10.1007/s005860000243]
Li, J., Zhao, H.Y., Ruan, X.Y., Xu, Y.Q., Meng, W.Z., Li, K.P., Zhang, J.Q., 2005. A novel technique of three-dimensional reconstruction segmentation and analysis for sliced images of biological tissues. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B, 6(12):1210–1212. [doi:10.1631/jzus.2005.B1210]
Macdonald, R.L., Fehlings, M.G., Tator, C.H., Lozano, A., Fleming, J.R., Gentili, F., Bernstein, M., Wallace, M.C., Tasker, R.R., 1997. Multilevel anterior cervical corpectomy and fibular allograft fusion for cervical myelopathy. J. Neurosurg., 86(6):990–997. [doi:10.3171/jns.1997.86.6.0990]
Narotam, P.K., Pauley, S.M., McGinn, G.J., 2003. Titanium mesh cages for cervical spine stabilization after corpectomy: a clinical and radiological study. J. Neurosurg., 99(2):172–180.
Oh, M.C., Zhang, H.Y., Park, J.Y., Kim, K.S., 2009. Two-level anterior cervical discectomy versus one-level corpectomy in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine, 34(7): 692–696. [doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e318199690a]
Papadopoulos, E.C., Huang, R.C., Girardi, F.P., Synnott, K., Cammisa, F.P.Jr., 2006. Three-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion with plate fixation: radiographic and clinical results. Spine, 31(8):897–902. [doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000209348.17377.be]
Pitzen, T.R., Chrobok, J., Stulik, J., Ruffing, S., Drumm, J., Sova, L., Kucera, R., Vyskocil, T., Steudel, W.I., 2009. Implant complications, fusion, loss of lordosis, and outcome after anterior cervical plating with dynamic or rigid plates: two-year results of a multi-centric, randomized, controlled study. Spine, 34(7):641–646. [doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e318198ce10]
Reidy, D., Finkelstein, J., Nagpurkar, A., Mousavi, P., Whyne, C., 2004. Cervical spine loading characteristics in a cadaveric C5 corpectomy model using a static and dynamic plate. J. Spinal Disord. Tech., 17(2):117–122.
Sakaura, H., Hosono, N., Mukai, Y., Ishii, T., Yoshikawa, H., 2003. C5 palsy after decompression surgery for cervical myelopathy: review of the literature. Spine, 28(21): 2447–2451. [doi:10.1097/01.BRS.0000090833.96168.3F]
Singh, K., Vaccaro, A.R., Kim, J., Lorenz, E.P., Lim, T.H., An, H.S., 2004. Enhancement of stability following anterior cervical corpectomy: a biomechanical study. Spine, 29(8): 845–849. [doi:10.1097/00007632-200404150-00005]
Thalgott, J.S., Chen, X.S., Giuffre, J.M., 2003. Single stage anterior cervical reconstruction with titanium mesh cages, local bone graft, and anterior plating. Spine J., 3(4):294–300. [doi:10.1016/S1529-9430(02)00588-0]
Vaccaro, A.R., Falatyn, S.P., Scuderi, G.J., Eismont, F.J., McGuire, R.A., Singh, K., Garfin, S.R., 1998. Early failure of long segment anterior cervical plate fixation. J. Spinal Disord., 11(5):410–415. [doi:10.1097/00002517-199810000-00008]
Yuan, W., Xu, S.M., Wang, X.W., Zhang, T., Liu, B.F., 2006. Segmental anterior cervical decompression with fusion for treating multilevel cervical myelopathy: analysis of the clinical effects. Chin. J. Spine Spinal Cord, 16(2): 95–98 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Yu, Ky. & Hu, Jh. Hybrid decompression technique and two-level corpectomy are effective treatments for three-level cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 10, 696–701 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0960001
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0960001