Abstract
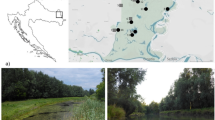
Pectinatella magnifica (Leidy, 1851) (phylum Ectoprocta) is an invasive species that is spread in many areas of the world. Its significant attribute is the production of large colonies formed by a specific gelatinous matrix which is usually occupied by microorganisms such as bacteria, algae, and cyanobacteria. This work compares the matrix characteristics of P. magnifica from five (in more details from two) locations according to the established criteria: A+B — thin layer (film) or translucent matrix (no contamination with algae and/or bacteria), C — slightly contaminated (discoloration) base, D -compact matrix, internal contamination (green, red, blue), E+F — disintegrating matrix, with a cavity, heavily contaminated (coloration), or without surface texture (inactive colony). Significant differences were identified both in the occurrence of described matrix types, and in the size and shape of P. magnifica colonies in each location.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balounovâ Z., Brezina V., Susterova K. & Rajchard J. 2015. Primary screening of potentially bio-active substances in the lyophilisate of Pectinatella magnifica biomass. Vet. Med. Czech. 60 (3): 141–146. DOI: https://doi.org/10.17221/8060-VETMED
Balounová Z., Pechoušková E., Rajchard J., Joza V. & Šinko J. 2013. World-wide distribution of the bryozoan Pectinatella magnifica (Leidy 1851). Eur. J. Environ. Sci. 3 (2): 96–100.
Canning E.U., Refardt D., Vossbrinck C.R., Okamura B. & Curry A. 2002. New diplokaryotic microsporidia (Phylum Microsporidia) from freshwater bryozoans (Bryozoa, Phylactolaemata). Eur. J. Protistol. 38 (3): 247–265. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1078/0932-4739-00867
Carroget P., Carroget L., Gruet Y., Baudet J. & Dutertre M. 2005. Presence of colonies of the bryozoan Pectinatella magnifica Leidy 1851 in the Loire and the Nantes channel at Brest (Loire-Atlantique). Bull. Soc. Sci. Nat. Óuest France 27: 19–29.
Dendy J.S. 1963. Observations on bryozoan ecology in farm ponds. Limnol. Oceanogr. 8 (4): 478–482. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1963.8.4.0478
Joo G.J., Ward A.K. & Ward G.M. 1992. Ecology of Pectinatella magnifica (Bryozoa) in an Alabama oxbowlake: colony growth and association with algae. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 11 (3): 324–333. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/1467652
Morse W. 1930. The chemical constitution of Pectinatella. Science 71 (1836): 265. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.71.1836.265
Opravilová V. 2005. K výskytu dvou druhů bezobratlých zavlečených do ČR: Dugesia tigrina (Tricladida) a Pectinatella magnifica (Bryozoa) [Occurrence of two invertebrates species imported in Czech Republic Dugesia tigrina (Tricladida) a Pectinatella magnifica (Bryozoa)]. Sborník Přírodovědeckého klubu v Brně 2001-2005: 39–50.
Šetlíková L., Balounová Z., Lukavský J. & Rajchard J. 2005. Nepůvodní druh mechovky na Třeboňsku [A non-native Bryozoan species found in the Třeboň basin]. Ziva 2005 (4): 172–174.
Šetlíková L., Skácelová O., Šinko J., Rajchard J. & Balounová Z. 2013. Ecology of Pectinatella magnifica and associated algae and cyanobacteria. Biologia 68 (6): 1136–1141. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-013-0262-7
Šetlíková V. & Pazourek J. 2013. Identification of carbohydrate isomers in flavonoid glycosides after hydrolysis by hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Chem. Pap. — Chem. Zvesti 67 (4): 357–364. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/sll696-012-0302-8
Vlková E., Killer J., Kmet V., Rada V., Musilová Š., Bunešová V., Hovorková P., Božik M., Salmonová H. & Rajchard J. 2015. Identification of microbiota associated with Pectinatella magnifica in South Bohemia. Biologia 70 (3): 365–371. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/biolog-2015-0040
Wood T.S. 1989. Ectoproct Bryozoans of Ohio. Bulletin of the Ohio Biological Survey 8 (2), 70 pp. ISBN: 0867271051, 9780867271058
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balounová, Z., Šmahel, L., Rajchard, J. et al. Characteristics of matrix of the invasive freshwater Ectoprocta species Pectinatella magnifica. Biologia 72, 1166–1170 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1515/biolog-2017-0129
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/biolog-2017-0129