Abstract
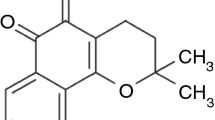
The effect of ternary solid dispersions of poor water-soluble NSAID meloxicam with moringa coagulant (obtained by salt extraction of moringa seeds) and polyvinylpyrrolidone on the in vitro dissolution properties has been investigated. Binary (meloxicam–moringa and meloxicam–polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP)) and ternary (meloxicam–moringa–PVP) systems were prepared by physical kneading and ball milling and characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, differential scanning calorimetry, and X-ray diffractometry. The in vitro dissolution behavior of meloxicam from the different products was evaluated by means of United States Pharmacopeia type II dissolution apparatus. The results of solid-state studies indicated the presence of strong interactions between meloxicam, moringa, and PVP which were of totally amorphous nature. All ternary combinations were significantly more effective than the corresponding binary systems in improving the dissolution rate of meloxicam. The best performance in this respect was given by the ternary combination employing meloxicam–moringa–PVP ratio of [1:(3:1)] prepared by ball milling, with about six times increase in percent dissolution rate, whereas meloxicam–moringa (1:3) and meloxicam–PVP (1:4) prepared by ball milling improved dissolution of meloxicam by almost 3- and 2.5-folds, respectively. The achieved excellent dissolution enhancement of meloxicam in the ternary systems was attributed to the combined effects of impartation of hydrophilic characteristic by PVP, as well as to the synergistic interaction between moringa and PVP.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Yu LX et al. A biopharmaceutics classification system: the scientific basis for bio waiver extensions. Pharm Res. 2002;19:921–5.
Chowdary KPR, Hymavathi R. Enhancement of dissolution rate of meloxicam. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2001;63(2):150–4.
Patidar K, Soni M, Sharma DK, Jain SK. Solid dispersion: approaches, technology involved, unmet need & challenges. Drug Invent Today. 2010;2(7):349–57.
Wade A, Weller PJ, editors. Handbook of pharmaceutical excipients. Washington: American Pharmaceutical Association/The Pharmaceutical Press; 1994. p. 220–399.
Arakawa T, Kita Y, Koyamac HA. Solubility enhancement of gluten and organic compounds by arginine. Int J Pharm. 2008;355:220–3.
Bhende S, Jadhav N. Moringa coagulant as a stabilizer for amorphous solids: part I. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2012;13:400–10.
Kwaambwa HM, Maikokera R. A fluorescence spectroscopic study of a coagulating protein extracted from Moringa oleifera seeds. Colloids Surf B. 2007;60:213–20.
Gassenschmidt U, Jany KD, Tauscher B, Niebergall H. Isolation and characterization of a flocculating protein from Moringa oleifera Lam. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995;1243:477–81.
Mura P, Bettinettib GP, Cirria M, Maestrellia F, Sorrentib M, Catenaccib L. Solid-state characterization and dissolution properties of naproxen–arginine–hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin ternary system. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2005;59:99–106.
Mura P, Maestrellia F, Cirri M. Ternary systems of naproxen with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and amino acids. Int J Pharm. 2003;260:293–302.
El-Maradny HA, Mortada SA, Kamel OA, Hikal AH. Characterization of ternary complexes of meloxicam-HPβCD and PVP or l-arginine prepared by the spray-drying technique. Acta Pharma. 2008;58:455–66.
Xiaodan Q, Jing Z, Wei W, Deying C. Solubility and stability of indomethacin in arginine-assisted solubilization system. Pharm Dev Technol. 2011;13:1–4.
Bramhane D, Saindane N, Vavia P. Inclusion complexation of weakly acidic NSAID with β-cyclodextrin: selection of arginine, an amino acid, as a novel ternary component. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem. 2011;69:453–60.
Hirasawa N, Ishise S, Miyata H, Danjo K. Physicochemical characterization and drug release studies of nilvadipine solid dispersions using water-insoluble polymer as a carrier. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2003;29(3):339–44.
Hirasawa N, Ishise S, Miyata H, Danjo K. Application of nilvadipine solid dispersion to tablet formulation and manufacturing using crospovidone and methylcellulose as dispersion carriers. Chem Pharm Bull. 2004;52:244–7.
Takada K, Oh-hashi M, Furuya Y, Yoshikawa H, Muranishi S. Enteric solid dispersion of ciclosporin A (CiA) having potential to deliver CiA into lymphatics. Chem Pharm Bull. 1989;37(2):471–4.
Horisawa E, Danjo K, Haruna M. Physical properties of solid dispersion of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (M-5011) with Eudragit E. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2000;26:1271–8.
Jung JY, Yoo SD, Lee SH, Kim KH, Yoon DS, Lee KH. Enhanced solubility and dissolution rate of itraconazole by a solid dispersion technique. Int J Pharm. 1999;187:209–18.
Sharma D, Soni M, Kumar S, Gupta GD. Solubility enhancement—eminent role in poorly soluble drugs. Res J Pharm Tech. 2009;2(2):222.
Chiou WL, Riegelman S. Pharmaceutical applications of solid dispersion systems. J Pharm Sci. 1971;60:1281–302.
Reintjes T. Solubility enhancement with BASF Pharma polymers. Solubilizer compendium. 2011;7–128. BASF chemical company. http://www.pharma-ingredients.basf.com.
Ndabigengesere A, Narasiah KS. Quality of water treated by coagulation using Moringa oleifera seeds. Water Res. 1998;32(3):781–91.
Ndabigengesere A, Narasiah KS, Talbot BG. Active agents and mechanism of coagulation of turbid waters using Moringa oleifera. Water Res. 1995;29(2):703–10.
Train D. Some aspects of the property of angle of repose of powders. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1958;10:127T–34T.
Carr RL. Evaluating flow properties of solids. Chem Eng. 1965;72:163–8.
Kawakita K., Ludde K. H. Some considerations on powder compression equations. Powder Technol. 1970–1971;4:61–8.
Heckel RW. Density pressure relationship in powder compaction. Trans Metall Soc AIME. 1961;221:671–5.
Fell JT, Newton JM. Determination of tablet strength by the diametral compression test. J Pharm Sci. 1970;59:688–91.
Leuenberger H. The compressibility and compactibility of powder systems. Int J Pharm. 1982;12:41–55.
Okuda T, Baes AU, Nishijima W, Okada M. Improvement of extraction method of coagulation active components from Moringa oleifera seed. Water Res. 1999;33(15):3373–8.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Noolkar Suhail B. and Bhende Santosh A. are thankful to AICTE for funding in terms of JRF.
Conflict of Interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noolkar, S.B., Jadhav, N.R., Bhende, S.A. et al. Solid-State Characterization and Dissolution Properties of Meloxicam–Moringa Coagulant–PVP Ternary Solid Dispersions. AAPS PharmSciTech 14, 569–577 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-013-9941-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-013-9941-5