Abstract
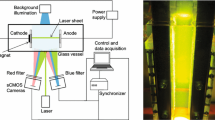
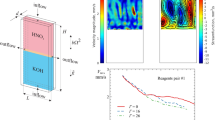
Magnetic fields are well-established in electrochemistry as an attractive tool to improve both the quality of the deposit as well as the deposition rate. The key mechanism is a mass transfer enhancement by Lorentz-force-driven convection. However, during electrolysis this convection interacts with buoyancy-driven convection, which arises from concentration differences, in a sometimes intriguing way. In the case of a Lorentz force opposing buoyancy, this is due to the growth of a bubble-like zone of less-concentrated cupric ion solution at the lower part of the vertical cathode when copper electrolysis is performed. If buoyancy is strong enough to compete with the Lorentz force, this zone rises along the cathode and causes surprisingly unsteady initial transient behaviour. We explore this initial transient under galvanostatic conditions by analyzing the development of the concentration and velocity boundary layers obtained by Mach-Zehnder interferometry and particle image velocimetry. Particular attention is also paid to higher current densities above the limiting current, obtained from potentiodynamic measurements, at which a chaotic advection takes place. The results are compared by scaling analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Alemany, J.P. Chopart, in Magnetohydrodynamics – Historical Evolution and Trends, edited by S. Molokov, R. Moreau, H.K. Moffatt (Springer, Dordrecht, 2007), p. 391
T.Z. Fahidy, in Modern Aspects of Electrochemistry, No. 32, edited by B.E. Conway, (Kluwer Academic, New York, 1999), p. 333
R.N. O’Brien, K.S.V. Santhanam, J. Appl. Electrochem. 27, 573 (1997)
A. Sugiyama, M. Hashiride, R. Morimoto, Y. Nagai, R. Aogaki, Electrochim. Acta 49, 5115 (2004)
T. Weier, J. Hüller, G. Gerbeth, F.-P. Weiss, Chem. Eng. Sci. 60, 293 (2005)
X. Yang, K. Eckert, K. Seidel, M. Uhlemann, Electrochim. Acta 54, 352 (2008)
S. Mühlenhoff, G. Mutschke, D. Koschichow, X. Yang, A. Bund, J. Fröhlich, S. Odenbach, K. Eckert, Electrochim. Acta 69, 209 (2012)
D. Koschichow, G. Mutschke, X. Yang, A. Bund, J. Fröhlich, Russ. J. Electrochem. 48, 682 (2012)
M. Uhlemann, A. Gebert, M. Herrich, A. Krause, A. Cziraki, L. Schultz, Electrochim. Acta 48, 3005 (2003)
I. Tabakovic, S. Riemer, M. Sun, V.A. Vas’ko, M.T. Kief, J. Electrochem. Soc. 152, C851 (2005)
H. Matsushima, Y. Fukunaka, Y. Ito, A. Bund, W. Plieth, J. Electroanal. Chem. 587, 93 (2006)
J.A. Koza, M. Uhlemann, A. Gebert, Ch. Mickel, S. Baunack, L. Schultz, Magnetohydrodynamics 45, 259 (2009)
J. Jorné, J. Electrochem. Soc. 131, 2283 (1984)
C.R. Wilke, M. Eisenberg, C.W. Tobias, J. Electrochem. Soc. 100, 513 (1953)
F.R. McLarnon, R.H. Muller, C.W. Tobias, Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundamen. 18, 97 (1979)
S. Mühlenhoff, Ph.D. thesis, TU Dresden, 2012
X. Yang, K. Eckert, A. Heinze, M. Uhlemann, J. Electroanal. Chem. 613, 97 (2008)
P.A. Nikrityuk, M. Ungarish, K. Eckert, R. Grundmann, Phys. Fluids 17, 067101 (2005)
J. Patterson, J. Imberger, J. Fluid Mech. 65, 100 (1980)
V.M.M. Lobo (ed.), Handbook of Electrolyte Solutions Parts A and B (Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, 1989)
T.Z. Fahidy, J. Appl. Electrochem. 13, 553 (1983)
X. Yang, K. Eckert, S. Mühlenhoff, S. Odenbach, Electrochim. Acta 54, 7056 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Mühlenhoff, S., Nikrityuk, P.A. et al. The initial transient of natural convection during copper electrolysis in the presence of an opposing Lorentz force: Current dependence. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 220, 303–312 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2013-01815-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2013-01815-2