Abstract
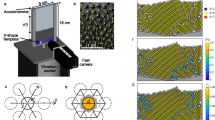
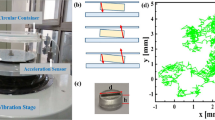
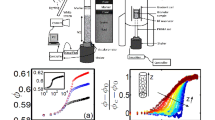
Recent experimental and computational studies of vibrated thin layers of identical spheres have shown transitions to ordered phases similar to those seen in equilibrium systems. Motivated by these results, we carry out simulations of hard inelastic spheres forced by homogenous white noise. We find a transition to an ordered state of the same symmetry as that seen in the experiments, but the clear phase separation observed in the vibrated system is absent. Simulations of purely elastic spheres also show no evidence for phase separation. We show that the energy injection in the vibrated system is dramatically different in the different phases, and suggest that this creates an effective surface tension not present in the equilibrium or randomly forced systems. We do find, however, that inelasticity suppresses the onset of the ordered phase with random forcing, as is observed in the vibrating system, and that the amount of the suppression is proportional to the degree of inelasticity. The suppression depends on the details of the energy injection mechanism, but is completely eliminated when inelastic collisions are replaced by uniform system-wide energy dissipation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I.S. Aranson, L.S. Tsimring, Rev. Mod. Phys. 78, 641 (2006)
J.S. Olafsen, J.S. Urbach, Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 4369 (1998)
J.S. Olafsen, J.S. Urbach, Phys. Rev. E 60, R2468 (1999)
W. Losert, D.G.W. Cooper, J. Delour, A. Kudrolli, J.P. Gollub, Chaos 9, 682 (1999)
G.W. Baxter, J.S. Olafsen, Nature 425, 680 (2003)
P.M. Reis, R.A. Ingale, M.D. Shattuck, Phys. Rev. E 75, 051311 (2007)
G.W. Baxter, J.S. Olafsen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 028001 (2007)
A. Burdeau, P. Viot, Phys. Rev. E 78, 061306 (2009)
A. Prevost, D.A. Egolf, J.S. Urbach, Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 084301 (2002)
T.P.C. van Noije, M.H. Ernst, Gran. Matt. 1, 57 (1998)
T.P.C. van Noije, M.H. Ernst, E. Trizac, I. Pagonabarraga, Phys. Rev. E 59, 4326 (1999)
I. Pagonabarraga, E. Trizac, T.P.C van Noije, M.H. Ernst, Phys. Rev. E 65, 011303 (2002)
J.S. Olafsen, J.S. Urbach, Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 098002 (2005)
P.M. Reis, R.A. Ingale, M.D. Shattuck, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 258001 (2006)
A. Prevost, P. Melby, D.A. Egolf, J.S. Urbach, Phys. Rev. E 70, 050301(R) (2004)
P. Melby, F. Vega Reyes, A. Prevost, R. Robertson, P. Kumar, D.A. Egolf, J.S. Urbach, J. Phys. Cond. Mat. 17, S2689 (2005)
F. Vega Reyes, J.S. Urbach, Phys. Rev. E 78, 051301 (2008)
M.G. Clerc, P. Cordero, J. Dunstan, K. Huff, N. Mujica, D. Risso, G. Vargas, Nat. Phys. 4, 249 (2008)
S.F. Foerster, M.Y. Louge, H. Chang, H. Allia, Phys. Fluids 6, 1108 (1994)
D.C. Rapaport, The Art of Molecular Dynamics simulation., 2nd ed. (Cambridge University Press, 2004)
X. Nie, E. Ben-Naim, S.Y. Chen, Europhys. Lett. 51, 679 (2000)
L.E. Silbert, D. Ertas, G.S. Grest, T.C. Halsey, D. Levine, S.J. Plimpton, Phys. Rev. E 64, 051302 (2001)
J. Sun, F. Battaglia, S. Subramaniam, Phys. Rev. E 74, 061307 (2006)
P. Melby, A. Prevost, D. A. Egolf, J. S. Urbach, Phys. Rev. E 76, 051307 (2007)
T. Pöschel, T. Schwager, Computational Granular Dynamics, Ch. 3 (Springer Verlag, 2005)
C. Bizon, M.D. Shattuck, J.B. Swift, H.L. Swinney, Phys. Rev. E 60, 4340 (1999)
B. Pansu, P. Pieranski, P. Pieranski, J. Phys. (France) 45, 331 (1983)
P. Pieranski, L. Strzelecki, B. Pansu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 50, 900 (1983)
B. Pansu, P. Pieranski, P. Pieranski, J. Phys. (France) 45, 331 (1984)
M. Schmidt, H. Löwen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, 4552 (1996)
M. Schmidt, H. Löwen, Phys. Rev. E 55, 7228 (1997)
R. Zangi, S.A. Rice, Phys. Rev. E 61, 660 (2000)
A. Fiege, T. Aspelmeier, A. Zippelius, Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 098001 (2009)
R. Cafiero, S. Luding, H.J. Herrmann, Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 6014 (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lobkovsky, A., Reyes, F. & Urbach, J. The effects of forcing and dissipation on phase transitions in thin granular layers. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 179, 113–122 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2010-01197-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2010-01197-y